BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True.
If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
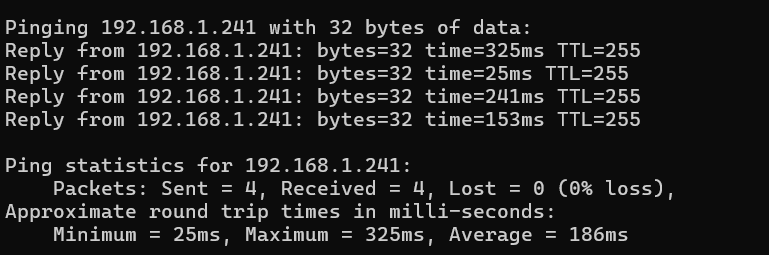
The ping command is a fundamental network utility used to test the reachability of a host on an IP network. By sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets to a target host and waiting for an echo reply, ping measures the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer.
In practical terms, executing a command like ping google.com allows users to determine if Google’s servers are reachable and assess the speed of data transmission between the user’s device and the server.
The results provide insights into network latency and packet loss, which are crucial for diagnosing connectivity issues.
Advanced options enhance the functionality of the ping command. For instance, using ping -t enables continuous pinging, which is beneficial for monitoring network connections over extended periods.
This continuous monitoring helps in identifying intermittent connectivity problems and assessing network stability.
Understanding the numerical data provided by ping, such as minimum, average, and maximum round-trip times, as well as packet loss percentage, is essential for effective network troubleshooting. These metrics offer a clear picture of network performance and can guide users in pinpointing and resolving connectivity issues.
Learn how the ping command tests network connectivity by sending ICMP echo requests and analyzing response times to diagnose issues
Leave a comment