The free command in Linux is used to display comprehensive memory usage information, reporting the total, used, free, shared, buffer/cache, and available memory, including both RAM and swap space.
It provides essential insights for system administrators and users to efficiently monitor and manage resources.
By default, running the command free outputs memory details numerically in kilobytes, presenting exact figures suitable for precise monitoring or scripting tasks.
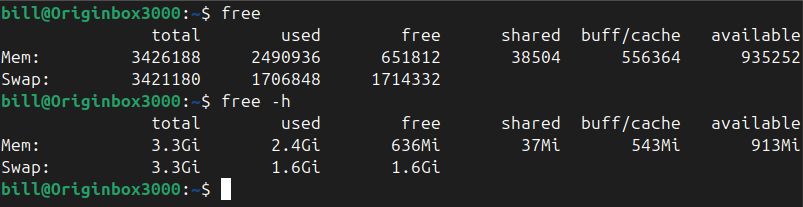
The alternative option, free -h, enhances readability by displaying the memory statistics in a human-friendly format, converting memory measurements to more familiar units such as gigabytes (Gi) or megabytes (Mi).
In the provided terminal screenshot, executing free shows memory numerically in kilobytes, providing detailed and exact usage statistics.
Conversely, when using free -h, the same memory usage details are displayed with rounded values and easy-to-read units, significantly simplifying interpretation.
This method clearly communicates how much memory the machine possesses, how much is currently utilized, and how much remains free or available.
bitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment