An expansion bus refers to the part of a computer’s internal architecture that allows additional hardware components to communicate with the CPU and other system components.
These hardware additions are known as expansion cards, which are installed into the system’s expansion slots. Expansion cards provide specialized functions not handled by the motherboard directly—such as advanced graphics processing (GPUs), sound output (sound cards), or additional storage and networking capabilities.
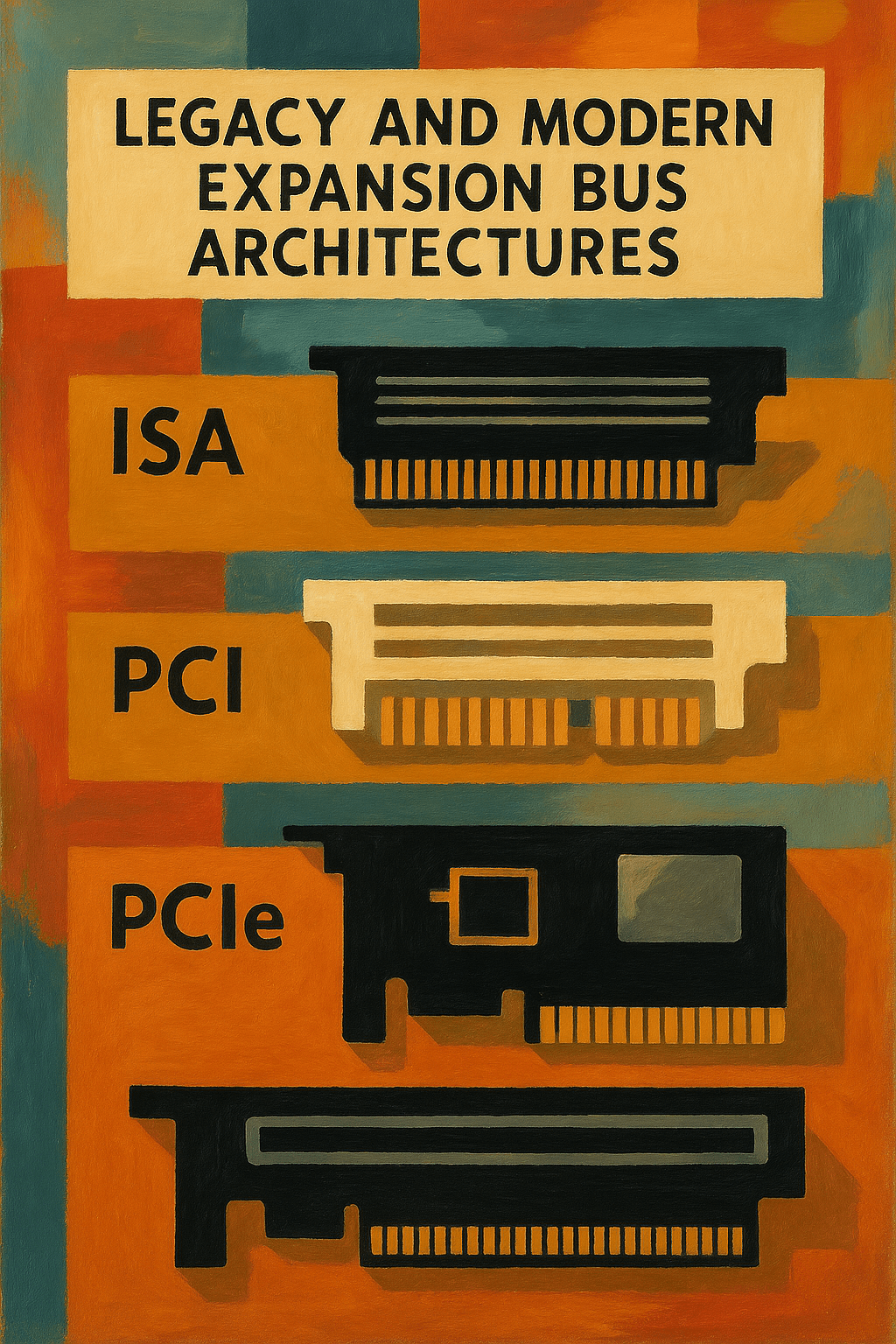
The expansion bus is responsible for transferring data to and from these cards at varying speeds depending on the bus type. The expansion bus evolved over time, starting with early standards such as ISA, EISA, and VLB, leading to today’s faster, point-to-point protocols like PCI and PCIe.
The Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) bus was widely used in early IBM-compatible PCs. It began as an 8-bit bus and later expanded to 16 bits. Though revolutionary at the time, it was limited in bandwidth and became a bottleneck as computing power increased.
The Extended ISA (EISA) introduced a 32-bit interface and allowed for backward compatibility, often used in server environments.
The VESA Local Bus (VLB) was designed primarily for video cards, offering direct access to the system’s front-side bus for faster throughput. These standards eventually gave way to PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) in the 1990s, which introduced auto-configuration and faster data handling. PCI allowed multiple devices to share the same bus without manual configuration via jumpers or DIP switches.
In modern systems, PCI Express (PCIe) has replaced older bus technologies entirely.
PCIe uses a serial point-to-point architecture, unlike the parallel structure of its predecessors.
It supports multiple lanes (x1, x4, x8, x16, etc.), with each lane offering a dedicated path between the expansion card and the CPU or chipset. This architecture allows for significantly higher data transfer rates and better scalability.
A single PCIe x16 slot is commonly used for high-performance graphics cards, while x1 or x4 slots may be used for sound cards, Wi-Fi cards, or SSDs.
AD:
Use the code BILLBURTON at check out to Get 5% off Bitaxe Mining Products
Limited to one use per customer: https://tinychiphub.com/BILLBURTON
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Need a 3 point template for briefing. Be as short as possible. Be sure to title it.
Leave a comment