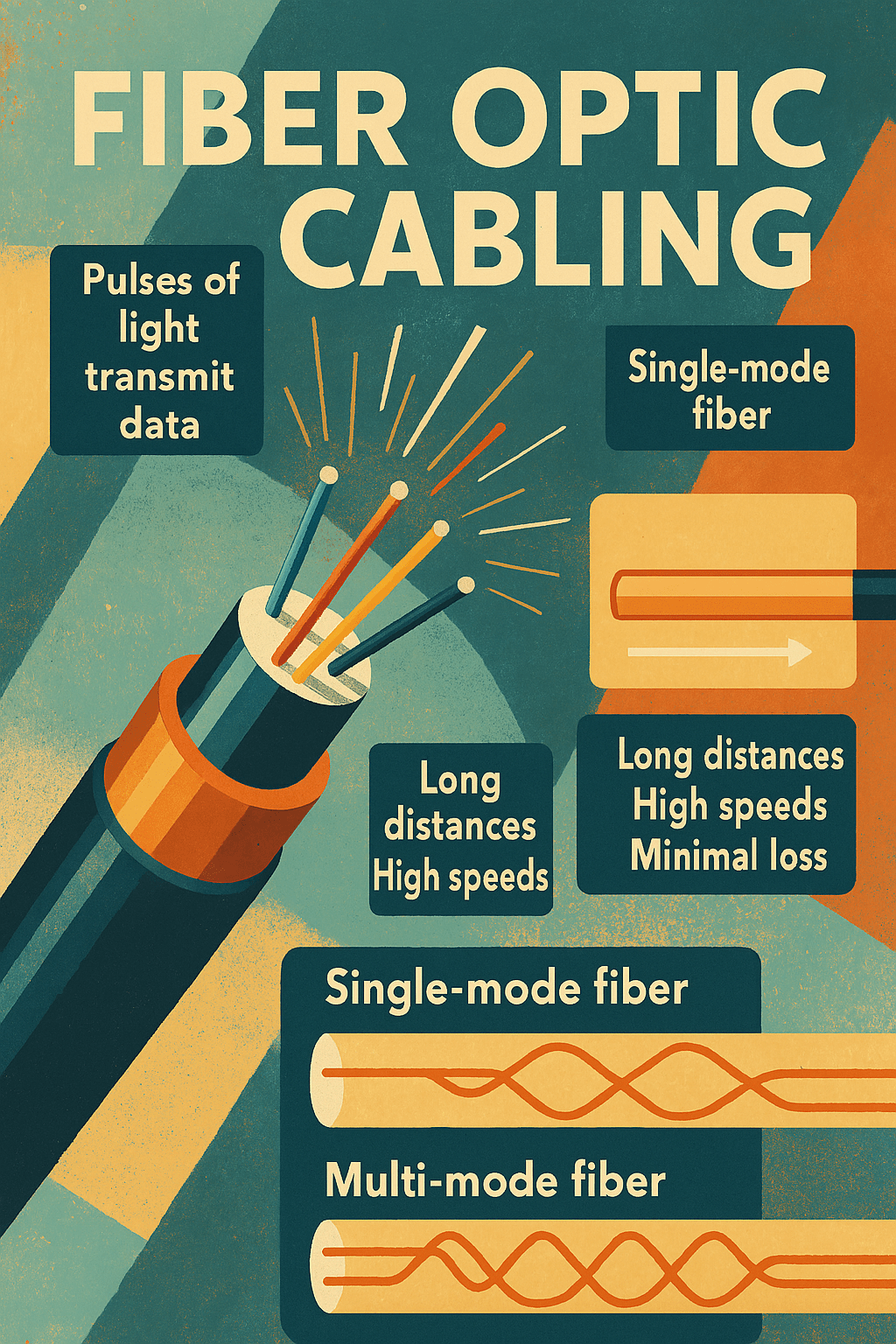
Fiber optic cabling is a high-speed transmission medium that uses pulses of light instead of electrical signals to carry data over glass or plastic strands.
It supports far greater bandwidth and significantly longer transmission distances than copper cabling, making it essential for enterprise backbones, internet service providers, data centers, and long-haul telecommunications.
Two core types exist: single-mode fiber (SMF) and multi-mode fiber (MMF).
Single-mode uses a narrow core (approx. 9 microns) and a single light path, ideal for long-distance, high-speed connections up to 100 km or more.
Multi-mode has a larger core (50–62.5 microns) and allows multiple light paths, which is better suited for shorter distances up to 2 km in LANs and building-to-building links.
Fiber cabling also offers superior immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI), is more secure from signal tapping, and has lower attenuation (signal loss) compared to copper.
However, it is more fragile and expensive, and often requires specialized tools and skills for termination and testing. Connectors like LC, SC, and ST are commonly used depending on the environment.
Installation requires careful consideration of bend radius, connector cleanliness, and splicing technique.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment