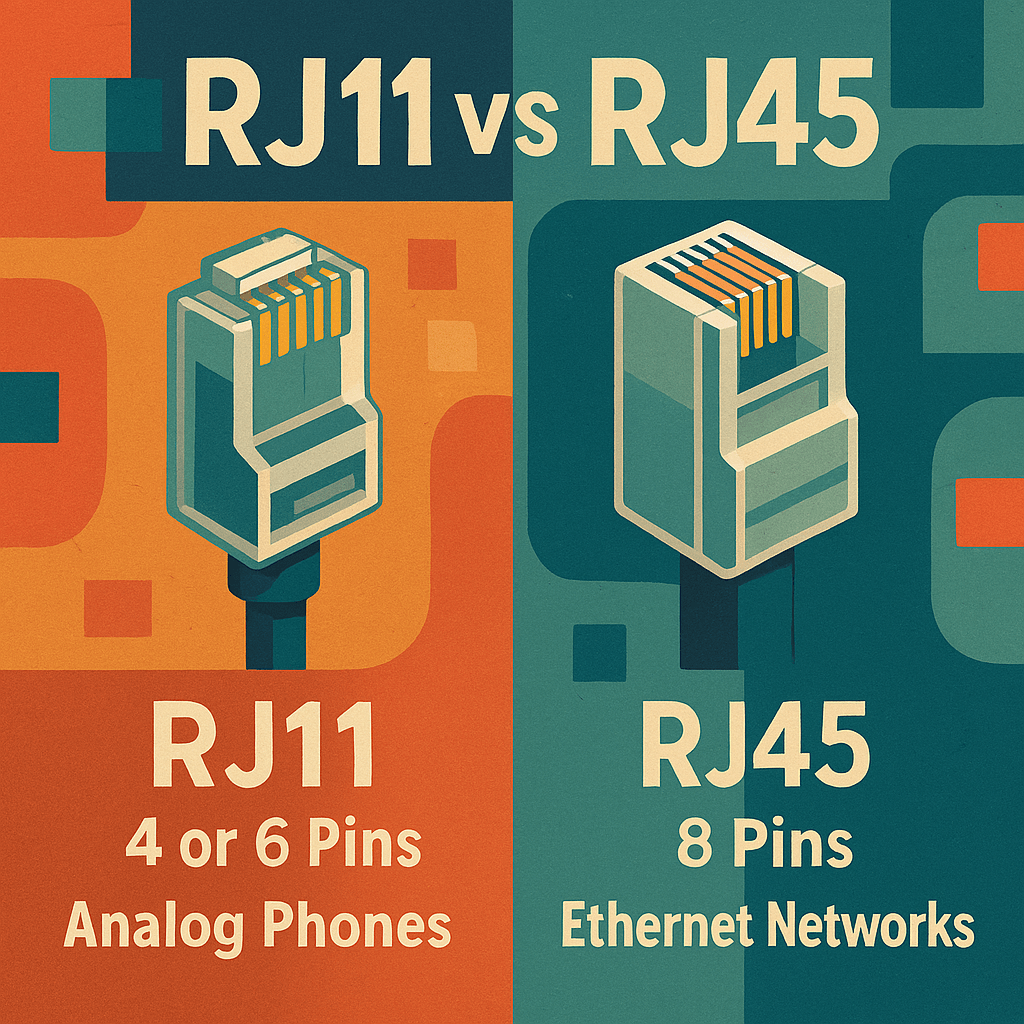
RJ11 and RJ45 are modular connectors used for telecommunications and networking, but they serve distinct purposes and are not interchangeable.
RJ11 is a 4- or 6-pin connector most commonly used for analog telephone lines, fax machines, and DSL connections. It typically carries a single phone line and uses two to four wires, fitting snugly into smaller jacks found on traditional landline equipment.
RJ11 is largely being phased out in favor of VoIP solutions, but it remains relevant in environments where legacy telephony infrastructure still exists.
RJ45, by contrast, is an 8-pin connector used for Ethernet networking.
It supports twisted-pair cabling (Cat5e, Cat6, etc.) and enables data transfer rates ranging from 10 Mbps to 10 Gbps and beyond.
RJ45 connectors are wider and are not physically compatible with RJ11 jacks.
They play a critical role in LANs, structured cabling, switches, routers, and NICs. For CompTIA A+ techs, understanding the physical differences, pin counts, and function of each connector is key to avoiding misinstallation and ensuring proper device connectivity.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment