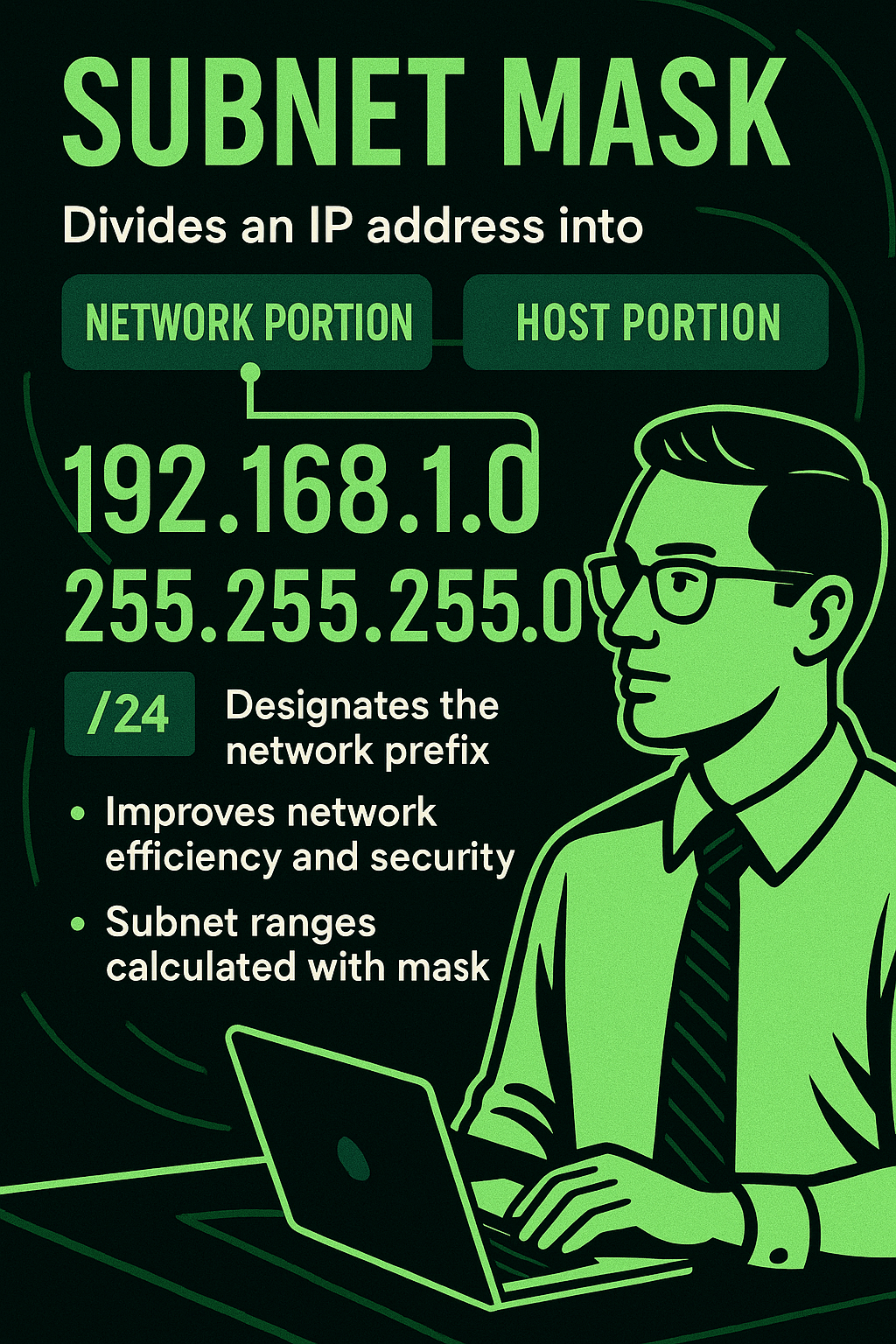
A subnet mask is used in IP networking to divide an IP address into network and host portions, allowing efficient IP address allocation and enhancing routing performance.
For example, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (or /24 in CIDR notation) designates the first 24 bits of the IP address as the network portion, leaving the remaining 8 bits for host identification—supporting up to 254 usable host addresses in that subnet.
Subnet masks are critical in IPv4 addressing schemes, helping routers and switches determine whether a destination IP is local or must be forwarded to a gateway.
Subnetting allows organizations to split large IP address blocks into smaller, more manageable segments, improving network organization, security, and broadcast containment.
A tighter subnet mask (e.g., 255.255.255.240) reduces the number of usable host IPs but increases the number of available subnets, useful in scenarios like VLAN segmentation or IP-based access control.
Properly assigning subnet masks helps prevent IP conflicts and optimizes routing tables.
Understanding how to calculate ranges, identify subnet IDs, and determine broadcast addresses is essential in managing scalable networks.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purpos
Leave a comment