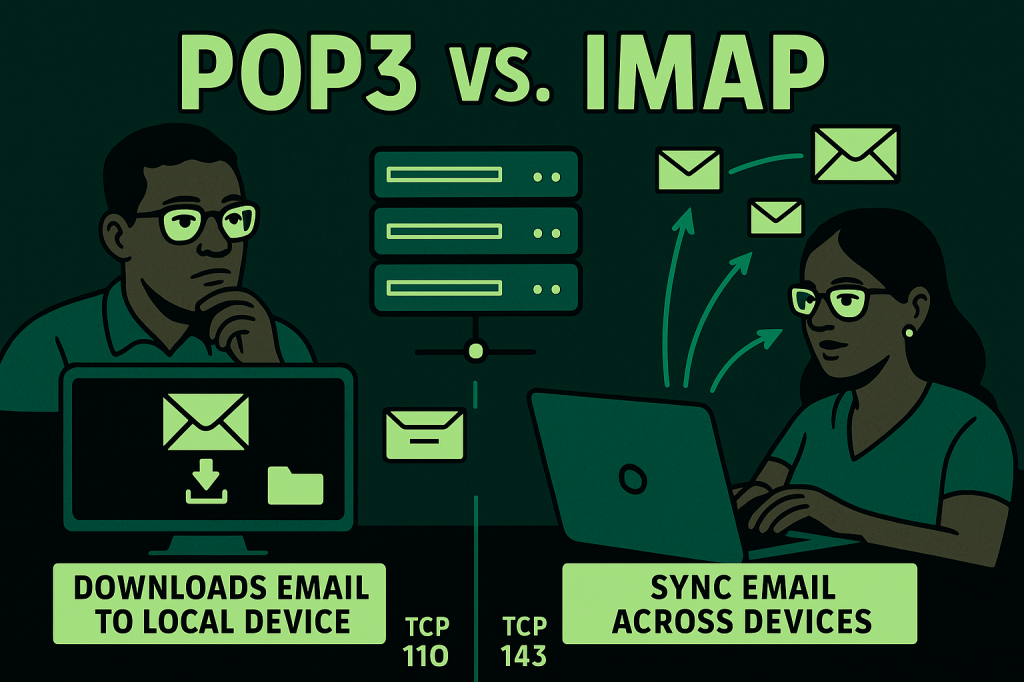
POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) is an email retrieval protocol that allows a client to download messages from a mail server to a local device.
Operating over TCP port 110 (or 995 with SSL/TLS), POP3 typically downloads and then deletes messages from the server unless configured otherwise. It is ideal for users who want to store their emails locally and access them without an internet connection.
However, because POP3 usually doesn’t synchronize changes across multiple devices, actions like reading, deleting, or moving an email on one device won’t reflect elsewhere.
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol), by contrast, operates over TCP port 143 (or 993 with SSL/TLS) and allows clients to view and manage emails directly on the server.
IMAP keeps the email synchronized across multiple devices, ensuring that folders, read status, and actions are consistent whether accessing from a smartphone, tablet, or laptop.
IMAP is the preferred protocol for modern email clients, cloud-based services, and mobile devices where real-time synchronization and server-side storage are essential. Understanding the distinction between POP3 and IMAP is crucial for configuring email clients to match user preferences for storage, accessibility, and synchronization.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment