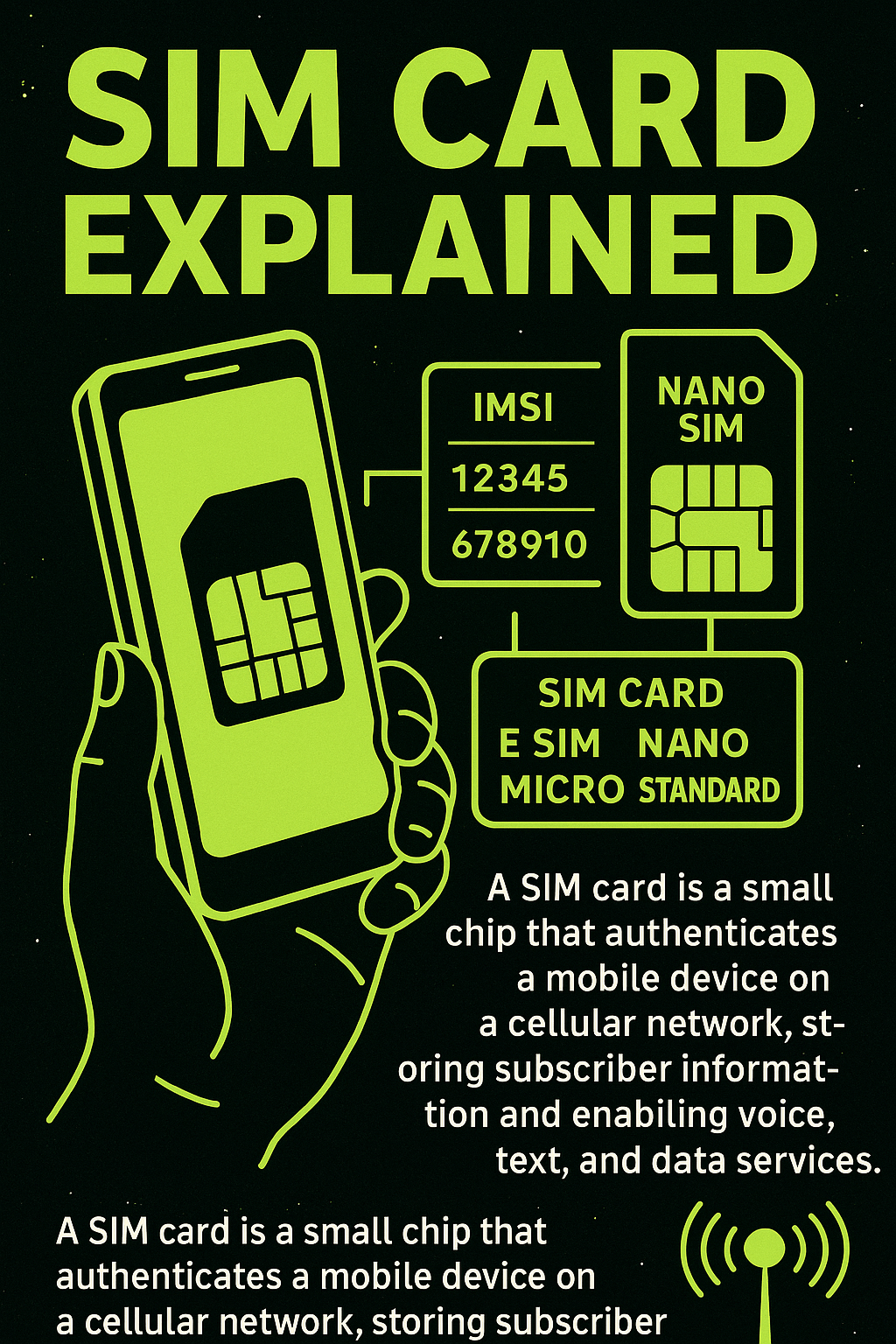
A SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module) is a small, removable smart card used in mobile devices to securely store information that authenticates a user to a mobile carrier’s network. It contains the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) and a secret authentication key, which allows the mobile device to connect to the carrier’s GSM, LTE, or 5G network.
SIM cards can also store limited contact information and SMS messages. They’re essential for voice, SMS, and mobile data access, and they link the device to a specific subscriber account, not the hardware itself—making it easy to switch phones by simply transferring the SIM.
SIM cards come in several form factors: Standard, Micro, Nano, and now eSIM (embedded SIM). Nano-SIM is the most common physical form today, used in modern smartphones. eSIM is a digital version integrated directly into the device, allowing users to activate or switch carriers without swapping cards. A technician may work with SIM cards when troubleshooting cellular connectivity issues, performing carrier unlocks, or provisioning devices for business use.
Proper handling and alignment are important, as SIM trays and contacts are delicate and easily damaged if forced incorrectly.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment