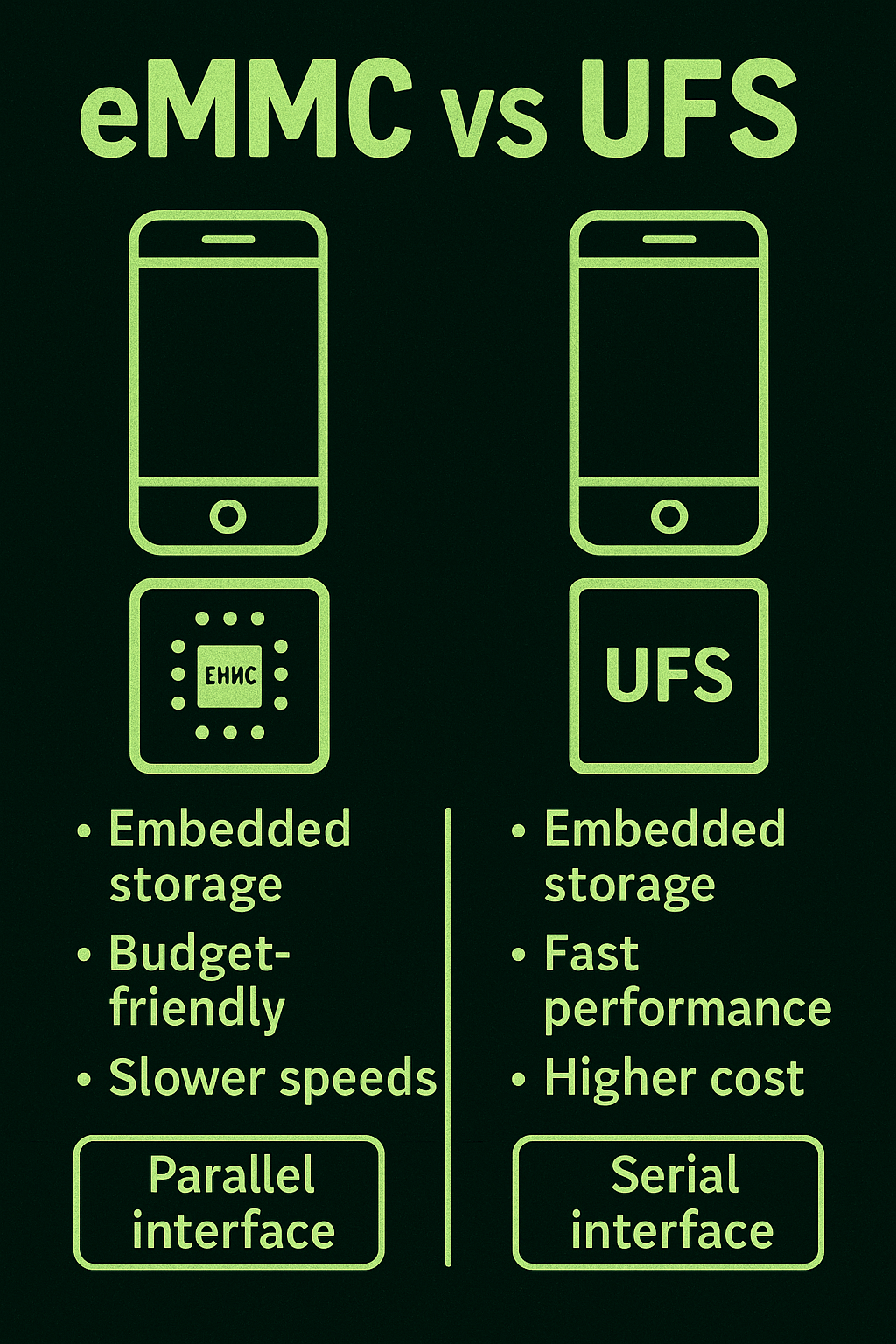
eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) and UFS (Universal Flash Storage) are two types of embedded storage used in smartphones, tablets, and entry-level laptops. eMMC integrates flash memory and a controller into a single package, functioning similarly to an SD card.
It’s affordable, compact, and easy to implement, making it common in budget devices. However, eMMC operates on a parallel interface and uses a single data bus, resulting in lower read/write speeds and slower multitasking performance.
Typical eMMC versions (like 5.1) deliver speeds in the hundreds of MB/s, adequate for light workloads but not optimal for high-performance applications.
UFS, on the other hand, is a newer, faster storage technology that uses a serial interface, allowing simultaneous read/write operations and significantly higher bandwidth.
Found in most flagship Android phones and high-end mobile devices, UFS offers performance closer to that of SSDs, with lower power consumption and reduced latency.
UFS supports features like command queuing, which enhances efficiency in multitasking environments. Understanding the differences between eMMC and UFS is crucial when evaluating a mobile device’s responsiveness, boot time, app load speed, and overall performance potential.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment