Gene editing technology, genetic engineering, and gene therapy are revolutionary fields offering the potential to prevent, treat, and even eliminate diseases while enhancing lifespan.
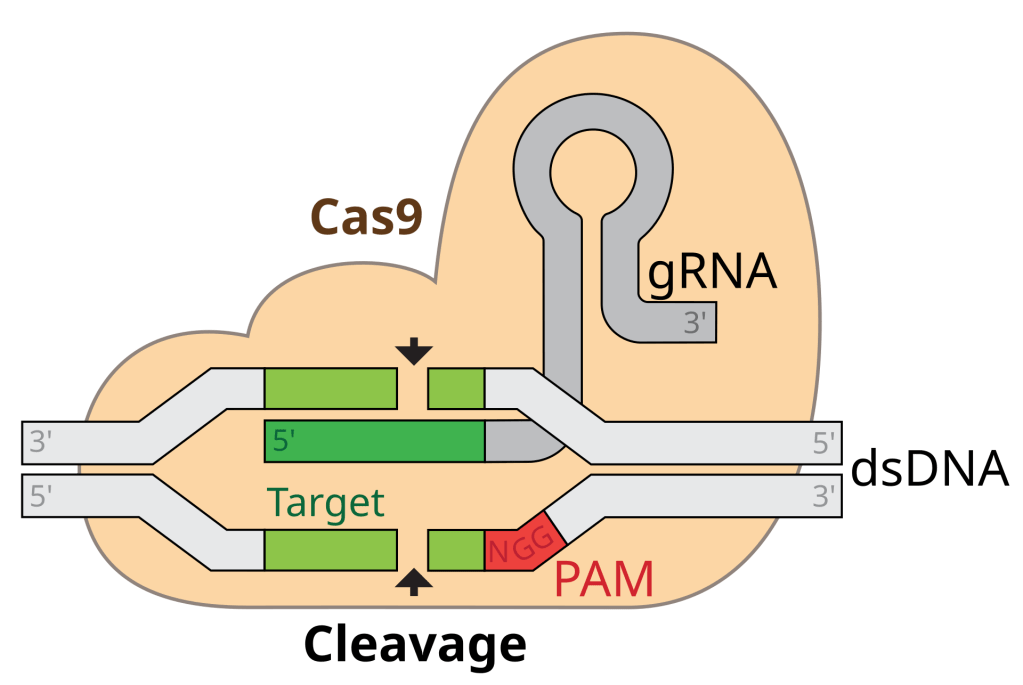
Gene editing, particularly CRISPR-Cas9, enables precise modifications to DNA by “cutting” specific segments and removing, altering, or replacing them. This allows scientists to address genetic disorders at their root, potentially extending human lifespans by targeting genes linked to aging, disease susceptibility, and cellular repair.
As a subset of genetic engineering, gene editing fits into a broader spectrum of methods that modify the genetic makeup of cells to introduce desirable traits or eliminate harmful ones.
Genetic engineering, which has been widely applied in agriculture to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for better yield and pest resistance, shows promise in human health by correcting defective genes that can lead to diseases like cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, and certain cancers. This technology could help people lead healthier lives, free from debilitating genetic conditions.
Gene therapy, meanwhile, is focused specifically on treating or preventing diseases by introducing, removing, or altering genetic material in a patient’s cells. By inserting a healthy gene to replace a faulty one responsible for disease, gene therapy offers a curative approach for conditions such as sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, and immune disorders.
This strategy represents a shift from symptom management to addressing the genetic root causes of disease. Excitingly, gene therapy could also be applied to age-related diseases, potentially enhancing both lifespan and quality of life.
Collectively, these technologies hold remarkable potential for longevity by directly influencing the genes tied to cellular aging and DNA repair. By targeting cellular senescence—the process by which cells lose the ability to divide and function—researchers hope to improve resilience to age-related decline.
Advances in DNA repair mechanisms could help cells maintain functionality, reducing risks for conditions like Alzheimer’s, heart disease, and cancer, which are prevalent in later life. Programming genes for longevity-related traits may eventually enable people to reach their maximum biological lifespan of around 120 years while remaining in better health.
However, ethical, social, and regulatory considerations will play a crucial role as these technologies advance, requiring responsible application to balance the profound benefits with potential risks.
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.

Leave a comment