Fiber optic theory is the foundational science behind the transmission of light through optical fibers, which are thin strands of glass or plastic designed to carry data in the form of light pulses.
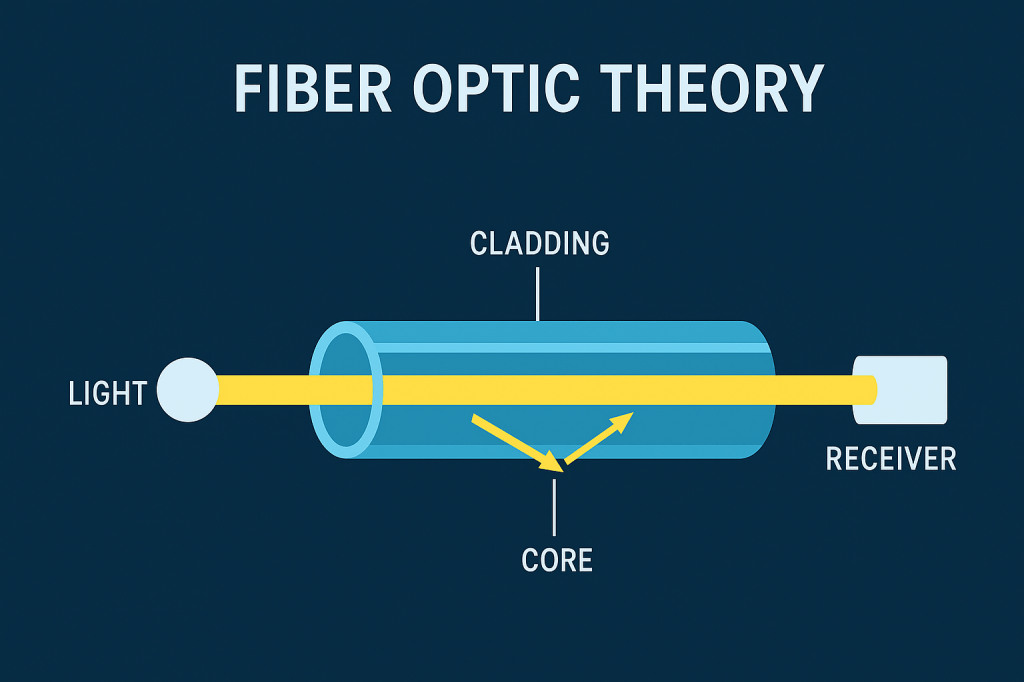
At its core is the principle of total internal reflection, where light entering the fiber core at a specific angle is reflected repeatedly along the boundary between the core and the cladding, allowing it to travel long distances with minimal loss.
The fiber consists of a central core surrounded by cladding with a lower refractive index, which traps the light inside the core. This structure enables the guided propagation of light, even around bends, as long as the critical angle is maintained.
The theory also encompasses the behavior of different modes of light transmission—single-mode fibers carry one light path for long-distance, high-bandwidth applications, while multimode fibers carry multiple paths and are used for shorter distances.
Key concepts include attenuation (signal loss over distance), dispersion (spreading of light pulses), and bandwidth capacity.
The wavelength of the transmitted light—typically in the infrared range around 850 nm, 1310 nm, or 1550 nm—affects how far and how fast data can travel.
Fiber optic theory also addresses the interaction of light with materials, including absorption, scattering, and reflection, which influence fiber design and performance.
This theory underpins the design of modern communication systems, enabling technologies such as internet backbones, high-speed data centers, medical imaging (endoscopy), and industrial sensing.
It represents a convergence of physics, materials science, and engineering, and continues to evolve with advances in photonics and quantum communication.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment