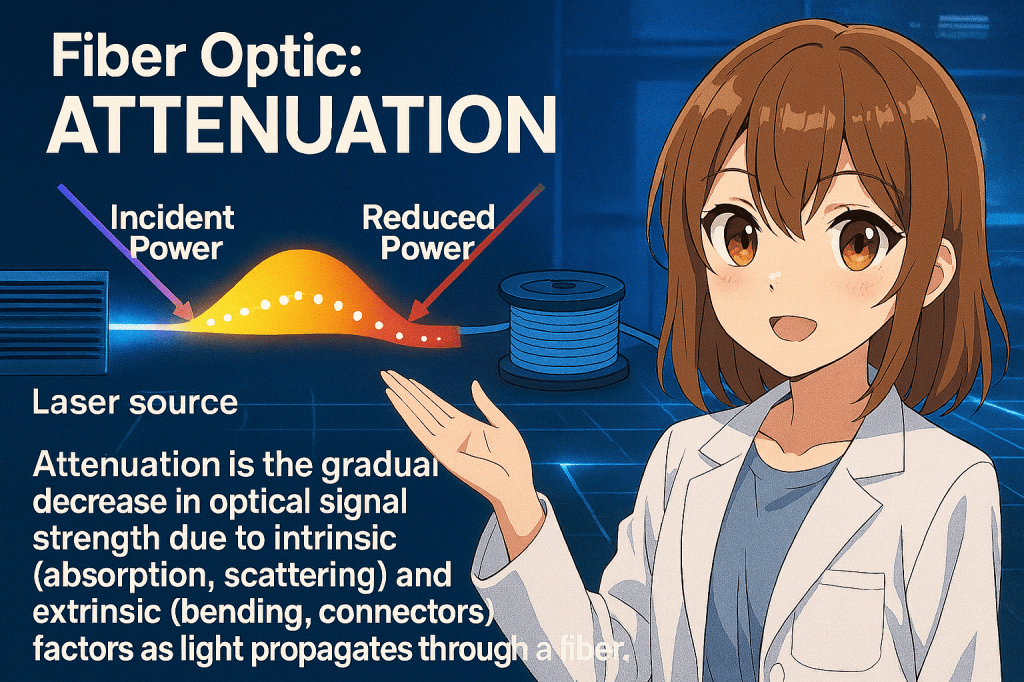
Attenuation in fiber optics refers to the gradual weakening of an optical signal as it travels through the fiber. This loss happens because some of the light energy is absorbed by the glass material or scattered due to microscopic irregularities. It’s measured in decibels per kilometer (dB/km), and the lower the number, the better the fiber is at preserving signal strength over long distances.
For example, single-mode fiber typically has attenuation around 0.2 dB/km at 1550 nm, meaning only a small fraction of the signal is lost every kilometer. Factors like dirty connectors, sharp bends, or poor splices can increase attenuation and degrade performance. Keeping attenuation low is essential for reliable, high-speed communication—especially in long-haul or high-bandwidth network
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True. If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment