Specific contact resistivity is the fundamental measure of how effectively a metal makes an electrical connection to a semiconductor material.
Think of it as a report card for the quality of the contact itself, completely separate from its physical size.
Its value, given in units of Ohm-centimeters squared, tells you how much inherent resistance exists at the tiny interface where the metal and semiconductor meet.
A very low specific contact resistivity means the contact is excellent, allowing electrical current to flow through the junction with minimal obstruction, which is the hallmark of a good “Ohmic contact.”
Conversely, a high value indicates a poor-quality interface where the current faces significant hindrance, leading to wasted power as heat and a poor-performing device.
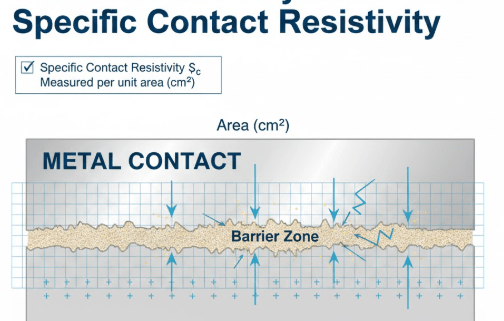
This metric is so vital because it allows engineers to compare different contact materials and manufacturing processes on a fair and standardized basis, focusing purely on the electrical property of the interface itself, regardless of whether the contact is microscopically small or relatively large.
It is the key parameter used to optimize the metal layers and semiconductor surface treatments to create the most efficient and low-resistance connections possible in modern electronics.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True.
If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here: bc1qrved9tfquym6u3age7xhmnkjs2lq8j9aulperagkuhtuk5w5c35ssfpge8
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment