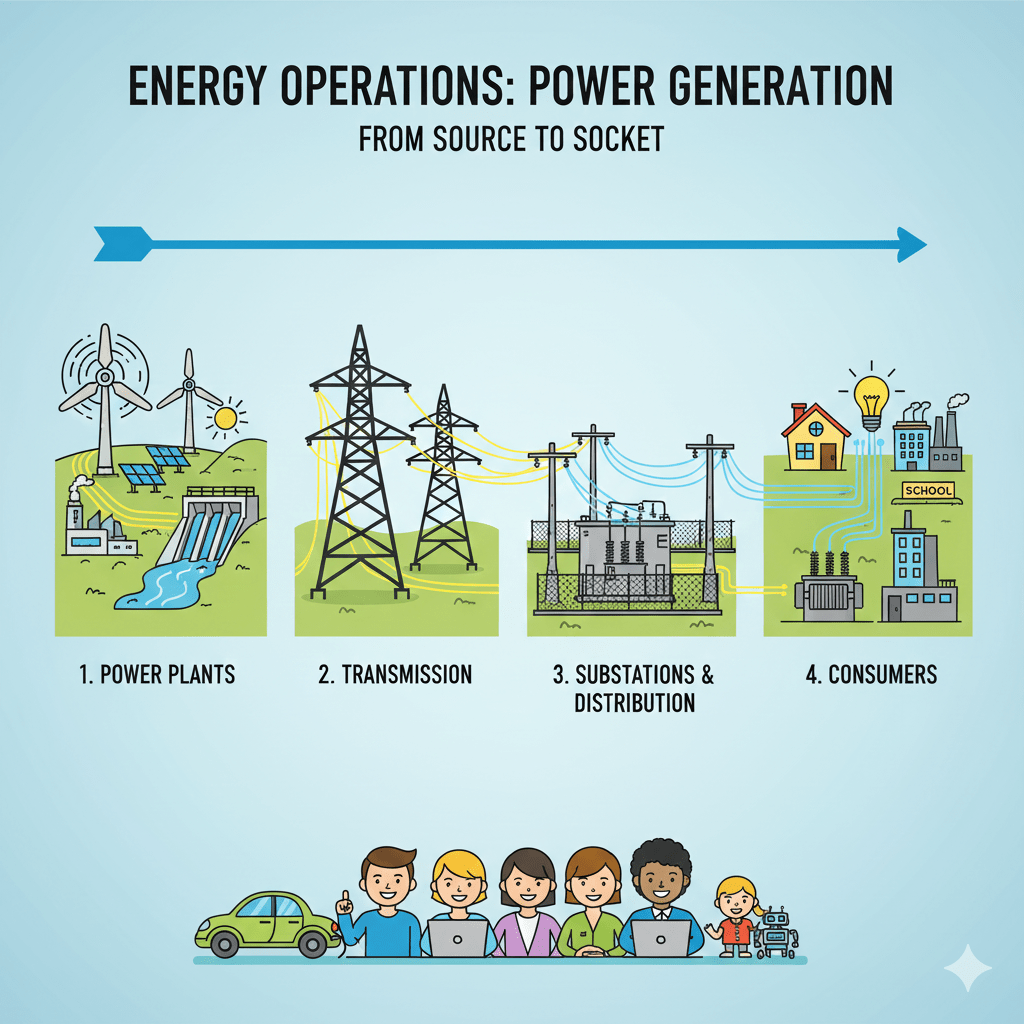
Power generation in terms of the energy grid refers to the process of producing electrical power at power stations or generation assets, which are connected to an interconnected network called the electrical grid.
This grid is a complex system comprising power generation facilities, transmission lines, substations, distribution lines, and consumers.
The power generated comes from various sources such as fossil fuels, nuclear, wind, solar, hydroelectricity, and geothermal energy, and is synchronized and matched to the grid’s frequency of alternating current (AC) to maintain stability. Once generated, the electricity is stepped up in voltage at substations to be efficiently transmitted over long distances through high-voltage transmission lines.
It is then stepped down at distribution substations for safe delivery and use by consumers.
The grid operates to continuously balance power supply and demand, ensuring reliable service, with large centralized plants often providing consistent base load power, while diverse generation assets contribute based on factors like cost and availability. The integration of renewable sources and energy storage solutions continues to modernize this system for enhanced reliability and efficiency in delivering electricity from generation to end users across wide areas.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True.
If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here: bc1qrved9tfquym6u3age7xhmnkjs2lq8j9aulperagkuhtuk5w5c35ssfpge8
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.
Leave a comment