A British Thermal Unit, commonly abbreviated as BTU, is a unit of measurement used to quantify the amount of heat energy.
Specifically, it represents the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit at a constant pressure.
This measurement is crucial in various fields, particularly in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, where understanding heat transfer is essential for designing efficient systems.
The BTU provides a standardized way to compare the energy output of different heating appliances, making it easier for consumers to make informed decisions. In practical terms, the BTU is often used to describe the energy content of fuels, such as natural gas, propane, and heating oil.
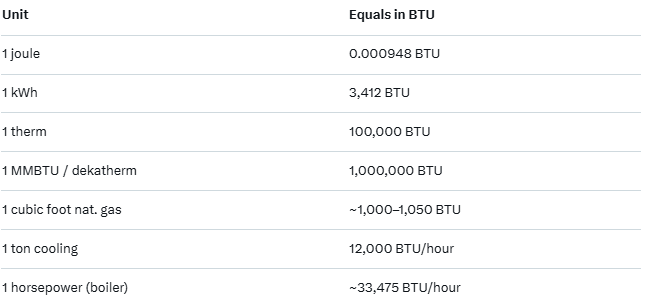
In the natural gas and heating world, the British Thermal Unit (BTU) is the standard measure of heat content. One cubic foot of typical pipeline-quality natural gas delivered to homes and businesses contains roughly 1,000 to 1,050 BTU (often rounded to 1,000 BTU for simplicity and billing).
Larger volumes are expressed in convenient multiples: 100 cubic feet (1 Ccf) equals approximately 100,000–103,000 BTU, a unit called a therm and widely used on household gas bills in the United States and the United Kingdom. One therm is therefore exactly 100,000 BTU.
Commercial and industrial users commonly work with dekatherms (10 therms) or MMBTU (one million BTU), both of which equal 1,000,000 BTU and represent the energy in about 1,000 cubic feet of natural gas.
Furnace and boiler capacities are rated in BTU per hour (e.g., a 100,000 BTU/h furnace can deliver the heat of one therm every hour), while wholesale natural gas trading at hubs like Henry Hub is priced per MMBTU.
These BTU-based units allow direct comparison of the heating value of natural gas regardless of slight regional variations in composition, making the BTU the essential bridge between volume of gas and actual usable heat energy in heating systems worldwide.
A higher BTU rating typically means that the appliance can heat a larger space or provide more hot water in a shorter amount of time.
However, it is important to consider the size of the space being heated and the efficiency of the appliance, as a unit with too high a BTU rating can lead to energy waste and increased costs. Moreover, the BTU is not only relevant in residential settings but also plays a significant role in industrial applications.
In industries that require precise temperature control, such as food processing or chemical manufacturing, understanding BTUs can help optimize energy use and improve overall efficiency.
Additionally, as the world moves towards more sustainable energy practices, the BTU measurement is being adapted to evaluate renewable energy sources, allowing for a better comparison between traditional and alternative energy systems. This versatility makes the British Thermal Unit a fundamental concept in both everyday life and advanced scientific applications.
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note:
We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True.
If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here: bc1qrved9tfquym6u3age7xhmnkjs2lq8j9aulperagkuhtuk5w5c35ssfpge8
BitcoinVersus.tech is not a financial advisor. This media platform reports on financial subjects purely for informational purposes.

Leave a comment