Information Technology
-
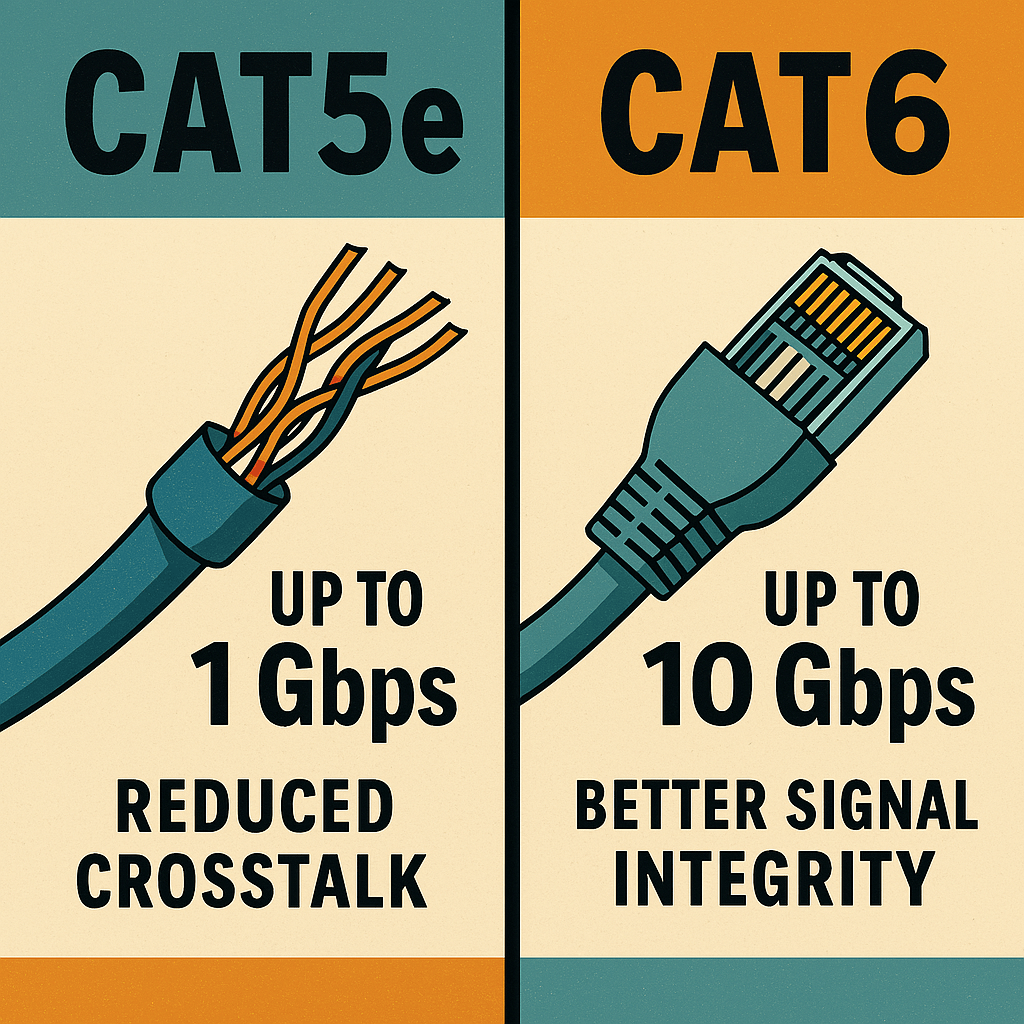
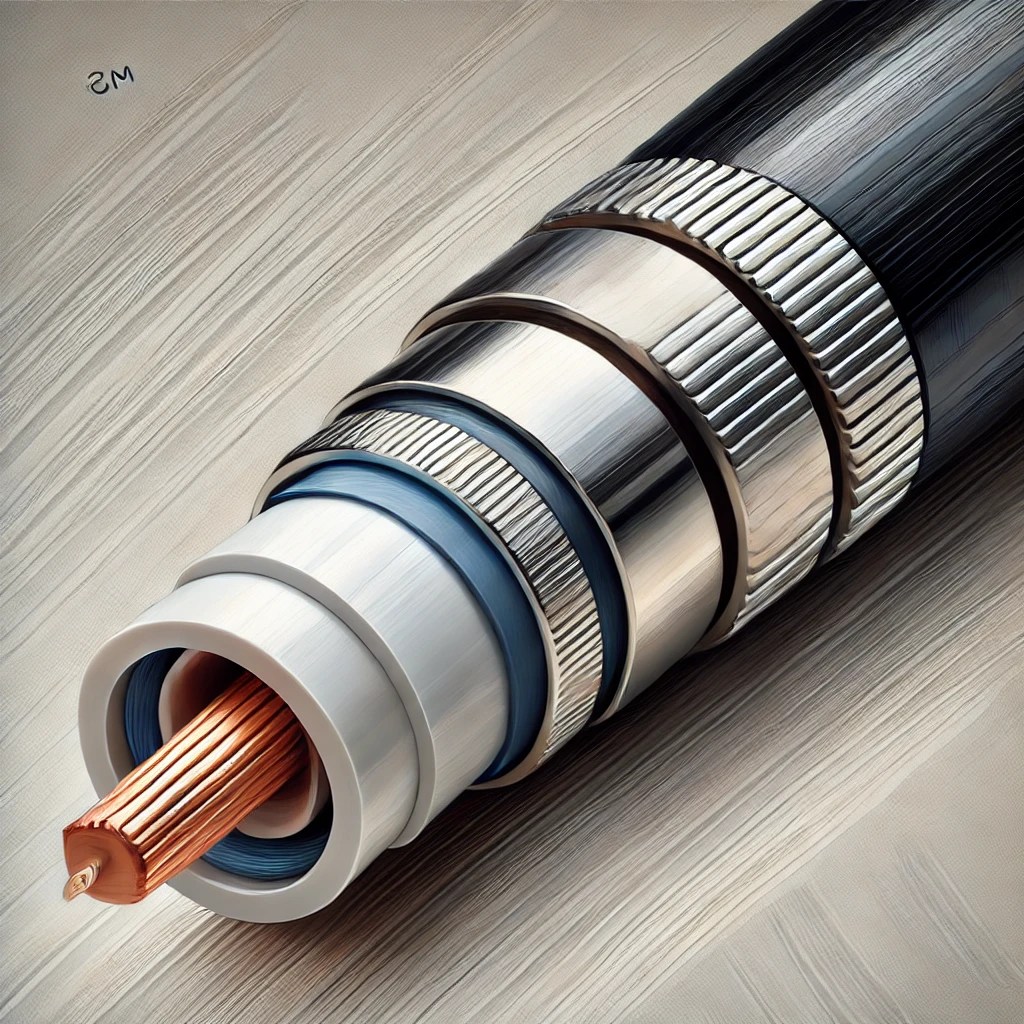
Cat5e (Category 5 Enhanced) and Cat6 (Category 6) Ethernet cables are both unshielded twisted pair (UTP) standards used for wired networking, but they differ in terms of performance, shielding, and signal integrity. Cat5e supports speeds up to 1 Gbps over distances of up to 100 meters and is commonly used in residential networks and small…
-
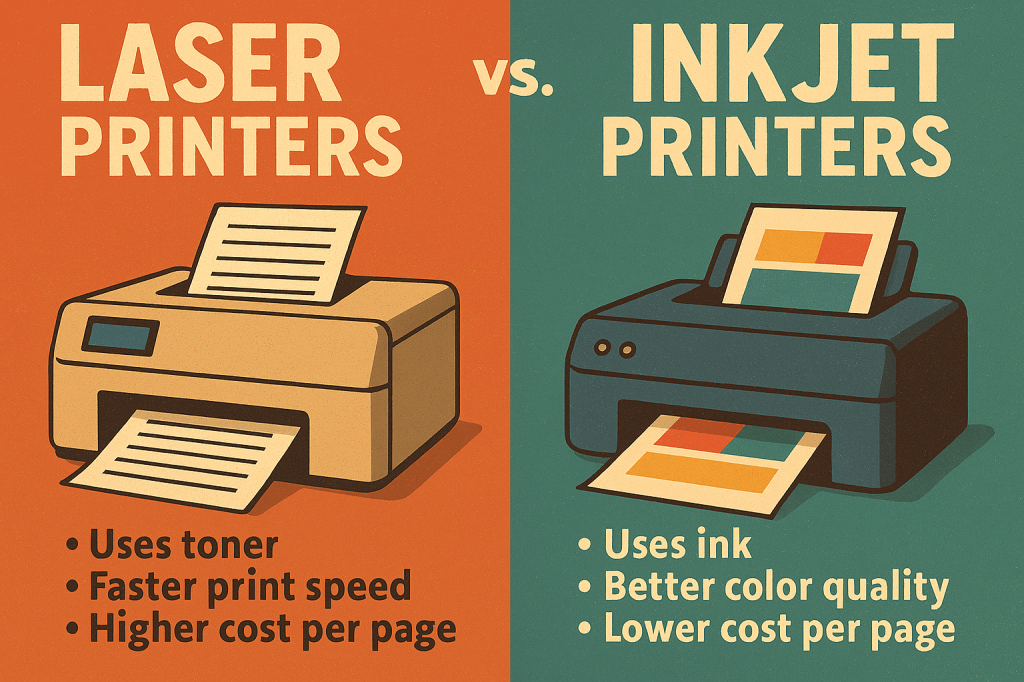
Laser printers and inkjet printers serve similar functions—producing printed output from digital sources—but differ significantly in technology, performance, and cost. Laser printers use a laser beam and toner (powdered ink) fused to the paper using heat, making them ideal for high-volume, fast, and sharp text printing. They are cost-effective per page and commonly used in…
-
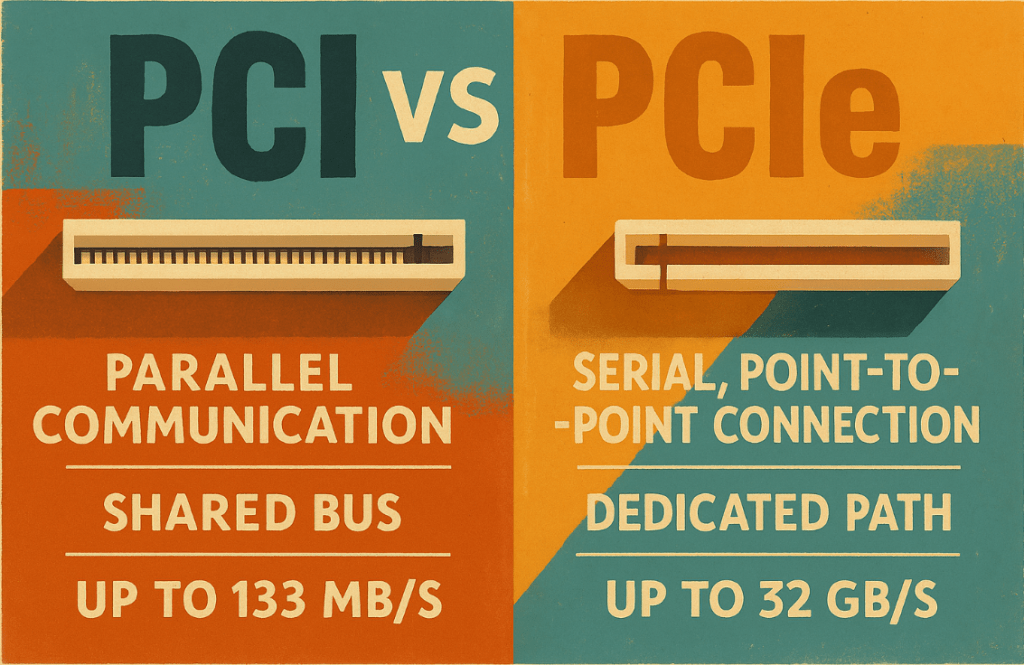
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) and PCIe (PCI Express) are both expansion bus standards used to connect internal hardware components like network cards, sound cards, or GPUs to the motherboard—but their architectures and performance differ greatly. PCI is a parallel communication interface introduced in the early 1990s, capable of transferring data at speeds up to 133…
-
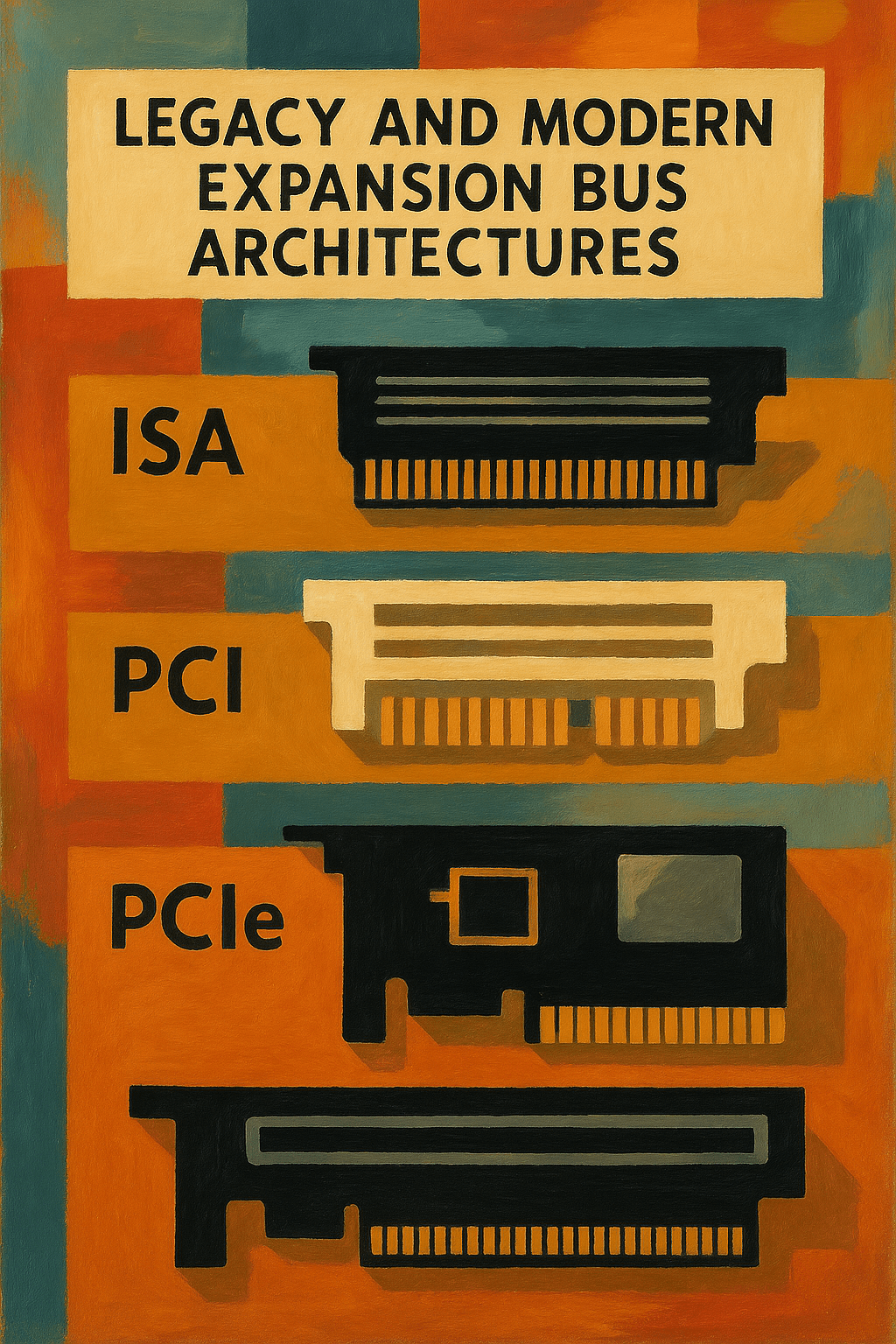
An expansion bus refers to the part of a computer’s internal architecture that allows additional hardware components to communicate with the CPU and other system components. These hardware additions are known as expansion cards, which are installed into the system’s expansion slots. Expansion cards provide specialized functions not handled by the motherboard directly—such as advanced…
-
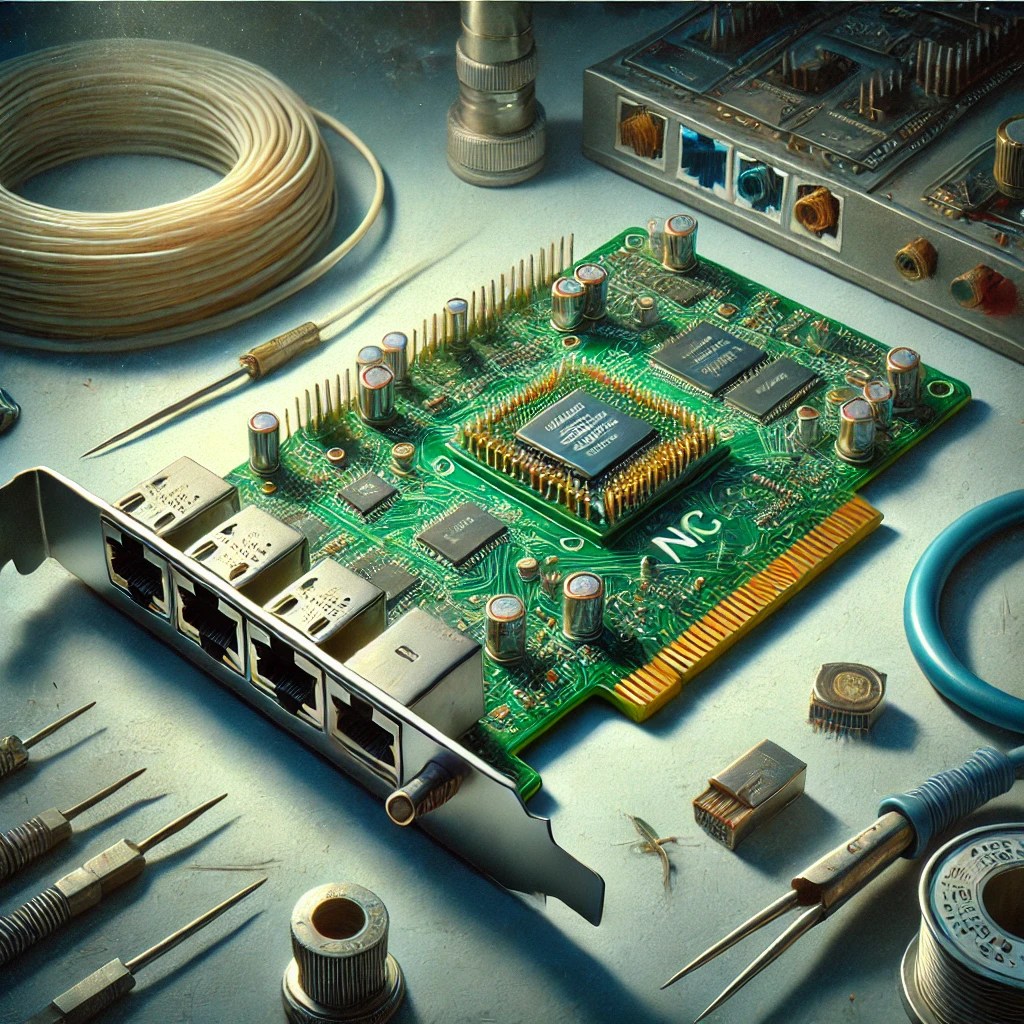
A Network Interface Card (NIC) is a hardware component, either integrated into the motherboard or installed as an expansion card, that enables devices to connect to a network. It provides a physical interface for Ethernet or wireless connections, supporting protocols like TCP/IP for data communication. NICs handle tasks such as framing, error detection, and packet…
-

Printer issues are among the most frequent hardware-related problems in both home and business environments. Symptoms include paper jams, poor print quality, printer not found errors, or no print output at all. Initial troubleshooting should start with physical inspection. Check for paper jams in the feed path, output tray, or duplex unit, and remove any…
-

SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) SMTP is the standard protocol for sending emails. It governs how messages are transmitted from the sender’s email client to the recipient’s email server. SMTP operates as a “push” protocol, meaning it pushes emails from the sender’s device to the server and between servers during mail relaying. SMTP uses commands…
-

Access Points (APs) are networking devices that extend the wireless coverage of a network by acting as a relay between wired and wireless devices. Unlike routers, which manage entire network traffic, access points focus specifically on connecting Wi-Fi-enabled devices to a wired network infrastructure. They are essential in environments requiring wide and reliable wireless coverage,…
-
Network issues can significantly impact productivity and user experience and often present as no connectivity, slow performance, intermittent dropouts, or limited network access. Wired network troubleshooting should always begin by verifying physical layer components—inspect Ethernet cables for damage, confirm they are rated properly (Cat5e, Cat6, etc.), and ensure that connectors are fully seated. Examine link…
-

Laptop display assemblies house several critical components beyond just the LCD or LED screen itself. These components typically include the screen panel, inverter (older models), backlight, digitizer (in touchscreens), webcam, microphone, Wi-Fi antennas, and sometimes even the IR sensor or ambient light sensor. Each of these components serves a specific function—LCDs/LEDs handle visual output, webcams…
-
Mobile device synchronization ensures that user data such as contacts, emails, calendars, media files, and application data remain consistent across multiple platforms. Synchronization can be conducted through several methods including cloud-based sync, local sync, and enterprise-level synchronization. Popular cloud services include Google Account Sync for Android devices and Apple iCloud for iOS devices, which automatically…
-

CompTIA, short for the Computing Technology Industry Association, is a globally recognized nonprofit trade organization that issues professional IT certifications. It is best known for certifications like A+, Network+, and Linux+, which validate foundational and specialized tech skills. CompTIA plays a major role in setting industry standards for information technology education and workforce development. I…
-

Cables serve as the physical medium that transmits data, power, and signals between devices in computing and networking environments. In IT, the most common data cables include Ethernet cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables. Ethernet cables, or twisted pair cables, are the most widely used in local area networks (LANs) and come in categories…
-

When building a custom PC, the first step is understanding the user’s specific requirements. A basic family desktop is typically used for web browsing, document creation, streaming media, light photo editing, and running basic productivity applications. For such a system, a budget-friendly quad-core processor (such as an Intel Core i3 or AMD Ryzen 3) will…
-

The Windows Firewall, officially known as Windows Defender Firewall, is a built-in security feature included with modern versions of the Windows operating system. It provides both inbound and outbound traffic filtering based on customizable rules, protecting devices from unauthorized access and common network threats. By default, Windows Firewall operates with a balanced set of pre-configured…
-

Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and more—over the internet rather than through local infrastructure. It offers organizations flexibility, scalability, and reduced upfront costs by eliminating the need for physical hardware. The most common cloud computing types are public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud.…
-
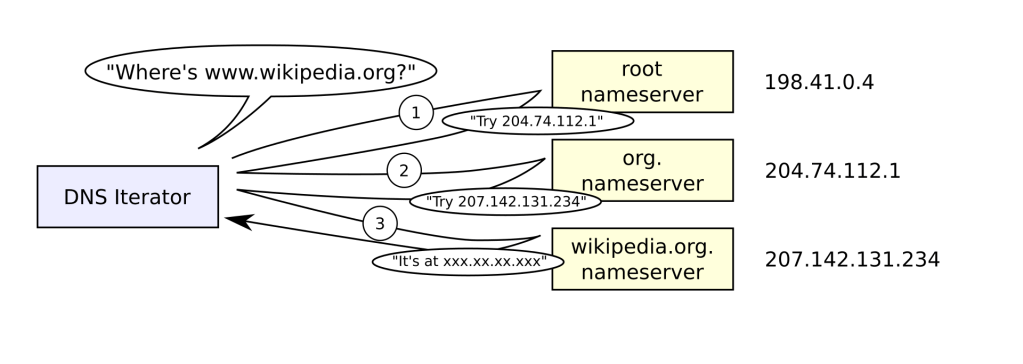
The Domain Name System (DNS) is like the phonebook of the internet. It translates human-friendly domain names such as www.google.com into IP addresses like 142.250.190.78, which computers use to locate and communicate with each other across networks. Without DNS, users would need to memorize long strings of numbers to access websites, making the internet much…
-
Add-on cards, also known as expansion cards, are hardware components inserted into expansion slots on a motherboard—typically PCIe slots—to extend a server’s functionality. These cards enable specialized performance beyond the system’s native capabilities, including enhanced network connectivity, accelerated processing, and advanced storage management. Common types include GPU cards for high-performance computing, network interface cards (NICs)…
-

Storage devices are critical components in computing, used to retain digital information permanently or temporarily. The two most common types of internal storage are Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs). HDDs use spinning magnetic platters and read/write heads to store data and are valued for their high storage capacities at lower cost per…
-
Selecting and installing RAM (Random Access Memory) starts with identifying the system’s compatibility requirements. The first step is to determine the form factor—most desktop motherboards use DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module), while laptops use the smaller SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM). Next, determine the DDR generation your system supports—DDR3, DDR4, or DDR5. These are not backward…
-

Understanding cable types and their respective connectors is essential in modern IT environments, where the efficiency of data transmission depends on the correct physical medium. Common cable types include twisted pair (Ethernet), fiber optic, coaxial, HDMI, and USB, each serving unique roles in networking and communication systems. Ethernet cables, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a,…
-

Setting up a Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) network requires a balance of reliability, security, and scalability. Wired networks offer stability and speed, typically using Ethernet cables (Cat5e, Cat6, or Cat6a) connected to a router or switch. The installation process involves configuring the router’s LAN settings, assigning static or dynamic IP addresses through DHCP, and ensuring…
-
Networked hosts provide essential services that enable communication, resource sharing, and security within a network. One of the most fundamental services is web hosting, where web servers deliver websites using HTTP and HTTPS protocols, ensuring content is accessible globally. File hosting and sharing services, such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SMB (Server Message Block), and…
-
Network configuration involves assigning and managing how devices connect and communicate across a network. IP addressing is a fundamental concept—devices can be assigned static IP addresses (manually set and unchanging) or dynamic IP addresses (automatically assigned by a DHCP server). Static IPs are often used for devices like servers or printers to ensure consistent accessibility,…
-

RISC, or Reduced Instruction Set Computer, represents a CPU architecture designed with simplified instructions, enabling processors to execute instructions at high speeds with fewer cycles per operation. According to IBM, RISC architectures streamline instruction processing by reducing complexity, enabling faster and more efficient performance at lower power consumption. ARM processors are built on RISC principles,…
-

Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are two core transport-layer protocols that facilitate network communication, each serving distinct purposes. TCP is connection-oriented, meaning it establishes a reliable session between devices before data is transmitted. It uses a three-way handshake (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK) to ensure that both sender and receiver are ready to…
-
Understanding how to use networking tools in real-world scenarios is a core part of CompTIA A+ training. Each tool has a specific purpose, from diagnosing connection issues to testing cables or analyzing network traffic. Below is a breakdown of essential tools and how they would be used when given a practical situation: Cable Tester A…
-

Ensuring seamless network connectivity on mobile devices requires proper configuration of Wi-Fi, cellular data, and Bluetooth settings. Wi-Fi connections should be set up using the appropriate security protocols, such as WPA2 or WPA3, to prevent unauthorized access. When configuring cellular data, users must input the correct Access Point Name (APN) settings, which define how the…
-

Effective troubleshooting is essential for maintaining system reliability and performance. The CompTIA A+ certification outlines a structured approach to problem-solving, ensuring that IT professionals can systematically identify and resolve issues. 1. Identify the Problem The initial step involves gathering comprehensive information about the issue. Technicians should consult system logs, engage with end-users to understand the…
-

Installing and configuring laptop hardware involves replacing or upgrading essential components such as memory (RAM), storage drives, and batteries. When upgrading RAM, the laptop must be powered off, and the correct type and size of memory modules must be installed in the designated slots. Storage upgrades often involve swapping out traditional hard disk drives (HDDs)…
-
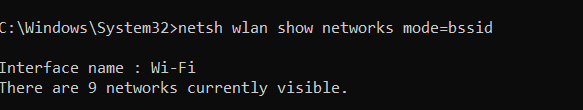
The command netsh wlan show networks mode=bssid is a Windows command-line instruction used to display detailed information about wireless networks available within range of the computer’s Wi-Fi router or adapter. The netsh utility, short for Network Shell, allows users to configure and monitor network settings from the command prompt. In this case, the command queries…
-
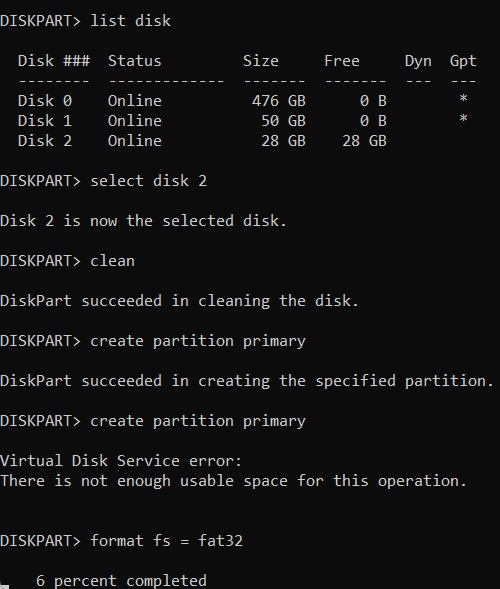
DiskPart is a command-line disk partitioning tool built into the Windows operating system. It allows users to manage their storage devices such as hard drives, SSDs, USB flash drives, and SD cards. DiskPart provides more control and flexibility over disk management compared to the GUI Disk Management utility in Windows. BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note: We volunteer…
-

The tasklist command is a Windows utility that lists all currently running processes on the system, along with key details like Process IDs (PIDs), memory usage, and executable names. It is commonly used for monitoring and troubleshooting processes. For instance, it can be combined with filters to locate specific tasks, such as running tasklist |…
-
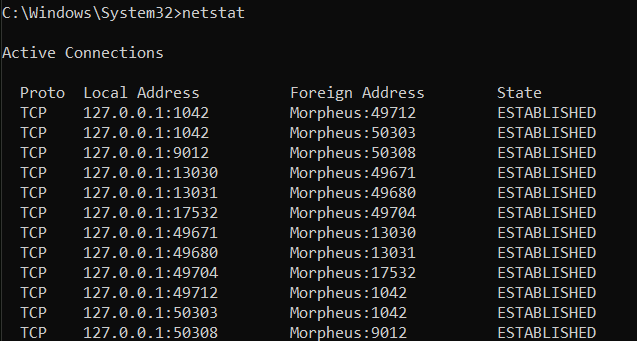
The netstat command provides statistics on current network connections and listening ports, offering insight into which applications are communicating over the network. Running netstat -a displays all active connections and ports. Netstat -b reveals the applications associated with each connection, valuable for security assessments (you need admin privileges for the “netstat -b” command). This command is used to detect suspicious…
-
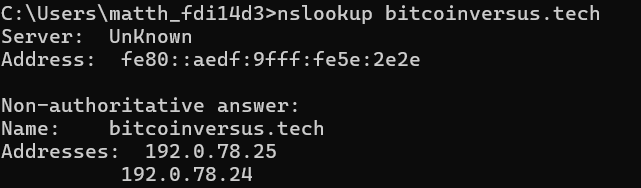
Nslookup (Name Server Lookup) is a command-line tool for querying Domain Name System (DNS) servers. It allows users to obtain the IP address associated with a domain name, or vice versa, helping in diagnosing DNS-related issues. For instance, nslookup google.com will show the IP addresses linked to bitcoinversus.tech This command is useful for troubleshooting DNS…
-
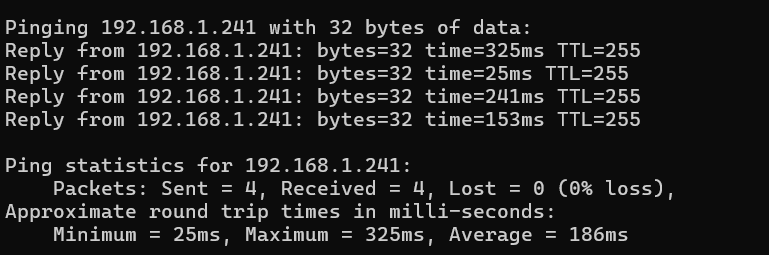
BitcoinVersus.Tech Editor’s Note: We volunteer daily to ensure the credibility of the information on this platform is Verifiably True.If you would like to support to help further secure the integrity of our research initiatives, please donate here The ping command is a fundamental network utility used to test the reachability of a host on an…
-

The ‘tracert’ command, short for ‘Trace Route,’ is a network diagnostic tool that tracks the path data packets take from your device to a specified IP address or domain. By listing each hop and measuring the time it takes to travel between them, ‘tracert’ helps identify delays or connection issues along the route. For instance,…
-

The ipconfig command in Windows OS provides essential network configuration details, helping users view IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways, vital for resolving connectivity issues. Running ipconfig /all offers extended data such as DNS servers, DHCP settings, and MAC addresses. This command is commonly used in troubleshooting scenarios where network connectivity is interrupted or…
-
The reason I had to change the color of the cursor was simply because I kept having a recurring issue with the cursor “disappearing” on different platforms. Changing your mouse color on Windows can improve cursor visibility, making it easier to locate on a complex screen and reducing eye strain. It also adds a personal…
-
-

Network topology is essential for network design and performance, as it determines data transfer efficiency, scalability, and maintenance costs. Physical and logical topologies play vital roles, with key types including star, bus, ring, mesh, tree, and hybrid topologies. Understanding these is crucial for effective network management and resilience.