linux
-
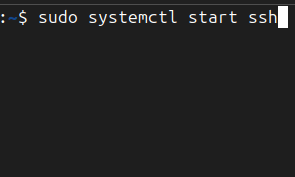
Secure Shell, commonly known as SSH, is a cryptographic network protocol used to establish secure and encrypted communication between two systems over an unsecured network. It allows users to remotely access and control another computer, typically through a command-line interface. SSH ensures that all data, including login credentials and command outputs, are encrypted to prevent…
-
The /bin directory is where Linux keeps many of its most essential commands that are available to all users, whether they are administrators or regular users. Inside /bin, you will find programs like ls for listing directory contents, cp for copying files, and mv for moving or renaming files. These commands are so vital that…
-

The Linux root directory (/) is the highest-level directory in the entire file system, acting as the central point from which everything else originates. To further clarify, the root directory (/) is the top-level of the entire Linux file system hierarchy, whereas /root is specifically the private home directory for the root (administrator) user. All…
-

The snmpwalk command is used to perform a series of network management requests to a specific device using an IP address(example: 10.31.10.101),starting from the OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1, using SNMPv3. Reference record for OID: Website to interpret OID Adresses snmpwalk -v3 -l authPriv -u l1monitor -a MD5 -A GEe9bb8h -x DES -X 4ixay7su 10.36.10.108 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1snmpwalk: This is…
-

Secure Shell, commonly known as SSH, is a cryptographic network protocol used to establish secure and encrypted communication between two systems over an unsecured network. It allows users to remotely access and control another computer, typically through a command-line interface. SSH ensures that all data, including login credentials and command outputs, are encrypted to prevent…
-

Before writing C++ programs on a Linux system, it’s essential to make sure the compiler is properly installed. G++ is the GNU Compiler Collection’s tool specifically for compiling C++ code. The screenshot demonstrates the process of checking and confirming that G++ is installed and ready to use. The screenshot shows that the user successfully confirmed…
-
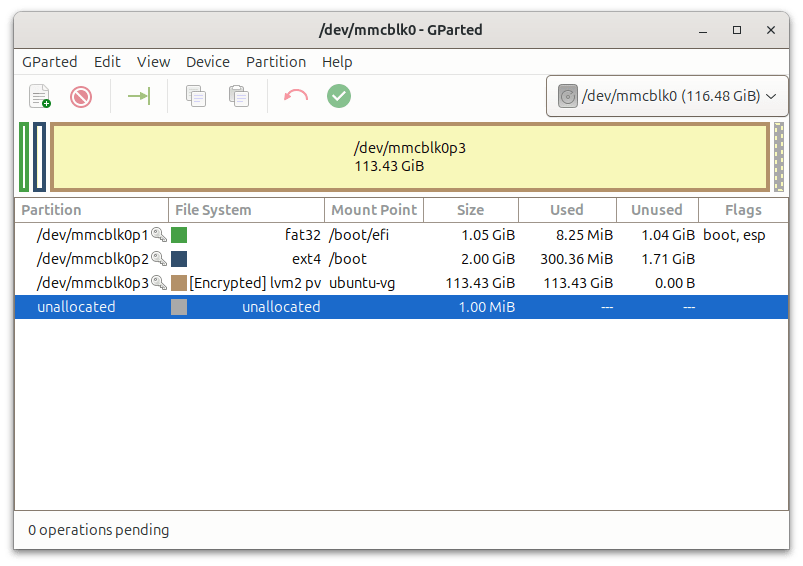
According to Linux.com, GParted—short for GNOME Partition Editor—remains one of the most trusted tools in the Linux ecosystem for managing disk partitions, especially in systems using EFI bootloaders and encrypted logical volume management (LVM). sers can graphically create, resize, format, and delete partitions across a wide range of file systems including ext4, fat32, and NTFS.…
-

The sed command in Linux is a powerful stream editor used to filter, find, and modify text within files or input streams. Short for “stream editor,” sed operates line-by-line and can perform operations like search-and-replace, deletion, insertion, or even complex pattern matching using regular expressions. It is commonly used for parsing and transforming text in…
-
The mkfifo command in Linux is used to create named pipes, also known as FIFOs (First In, First Out). Unlike regular files, a FIFO behaves like a pipe that allows data to flow between processes. You can think of it as a communication tunnel where one process writes data and another reads it. For example,…
-

The locate command in Linux is used to quickly search for files by name across the entire filesystem. Unlike the find command, which actively searches through directories in real-time, locate uses a prebuilt index from a database (usually updated with the updatedb command). This makes it incredibly fast and efficient. For example, typing locate passwd…
-
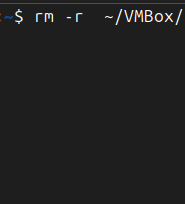
The rm command in Linux is used to remove (delete) files and directories from the filesystem. It stands for “remove” and is one of the most powerful and potentially destructive commands if used without care. A basic usage like rm file.txt deletes the specified file permanently — there’s no trash or recycle bin involved. To…
-
The /opt directory is used in Linux for installing optional or third-party software that is not part of the default package management system. Many commercial applications or special-purpose tools are installed into /opt to keep them separate from system-managed software. If you install proprietary software like VMware or a custom application, it may place its…
-

The /mnt directory in Linux serves as a traditional location for temporarily mounting filesystems. Unlike /media, which is mostly used for automatic mounting of USBs and other external devices, /mnt is primarily used by system administrators for manual mounts during maintenance, recovery, or troubleshooting. When you need to access another drive or partition for testing…
-

The /media directory is used in Linux to automatically mount removable storage devices such as USB drives, DVDs, and external hard drives. When you insert a USB or plug in a storage device, most Linux distributions will automatically create a subdirectory inside /media and mount the device there. This helps users access external drives easily…
-

The /bin directory is where Linux keeps many of its most essential commands that are available to all users, whether they are administrators or regular users. Inside /bin, you will find programs like ls for listing directory contents, cp for copying files, and mv for moving or renaming files. These commands are so vital that…
-

The Linux root directory (/) is the highest-level directory in the entire file system, acting as the central point from which everything else originates. To further clarify, the root directory (/) is the top-level of the entire Linux file system hierarchy, whereas /root is specifically the private home directory for the root (administrator) user. All…
-

Setting up an Ubuntu Virtual Machine (VM) using Oracle VirtualBox begins with downloading the latest ISO file from Ubuntu’s official site. For Ubuntu 24.04, users typically select the desktop version compatible with their hardware architecture, commonly “amd64.” After downloading, users open Oracle VirtualBox, create a new VM, name it, select the Linux operating system type,…
-

LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is an open, vendor-neutral protocol used to access and maintain distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. LDAP is widely used for storing and managing information about users, groups, computers, and other resources in a centralized database, known as a directory. The protocol allows clients to connect…
-

When a Linux machine starts feeling slower than normal, it’s often a sign that system resources are strained. In this case, the user decided to troubleshoot by checking memory usage and cleaning up unused files. After running the free command to get a snapshot of RAM and swap usage, they used find to delete all…
-

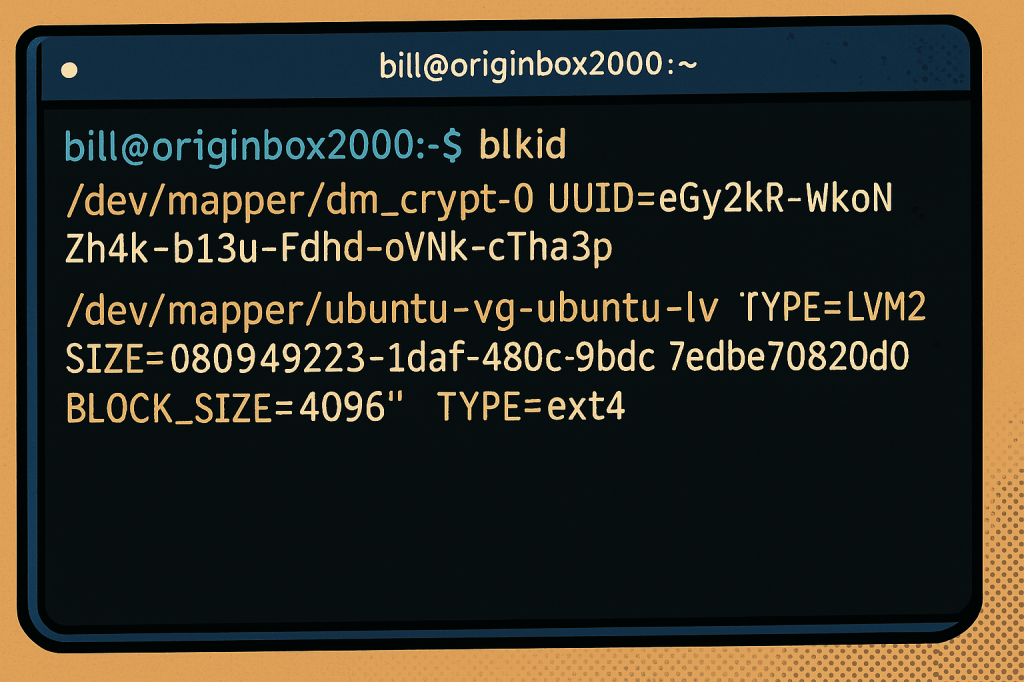
To set up logical volume management in Linux, the first step is creating a physical volume (PV). A physical volume is typically a disk partition (like /dev/sdb1) that is initialized for use by the Logical Volume Manager. This is done using the pvcreate command, which prepares the partition to be added into a volume group.…
-
A swap file in Linux is a special file on the disk that acts as virtual memory when the system’s physical RAM becomes full. Instead of immediately failing or killing processes when memory runs low, the kernel moves less-used data from RAM into the swap file to free up space for active applications. This ensures…
-
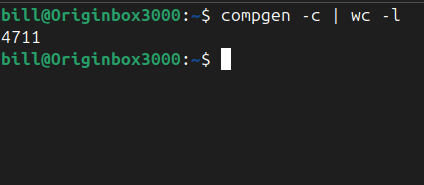
The compgen command in Linux is a built-in feature of the Bash shell used to display a list of available commands, functions, aliases, and reserved words. It’s part of the programmable completion system and is mainly used to introspect what the shell knows. For example, running compgen -c outputs all executable commands that the shell…
-
In Linux, mount refers to the process of attaching a storage device or partition—such as a hard drive, USB stick, or network share—to the system’s directory tree so that its contents become accessible. Unlike operating systems that assign drive letters, Linux integrates storage into a single hierarchical file system. When a device is mounted, it…
-

Creating a filesystem means formatting a partition or volume with a specific structure that the operating system can understand—such as ext2, ext3, ext4, xfs, or fat32. This is often done on a new partition using the mkfs (make filesystem) family of commands. For example, formatting a device with ext4 can be done with: sudo mkfs.ext4…
-
The file command in Linux is used to determine the true type of a file by inspecting its contents, not just its name or extension. Unlike many operating systems that rely on file extensions (like .jpg, .txt, or .mp3), Linux doesn’t depend on naming alone. The file command reads the internal binary signatures of the…
-
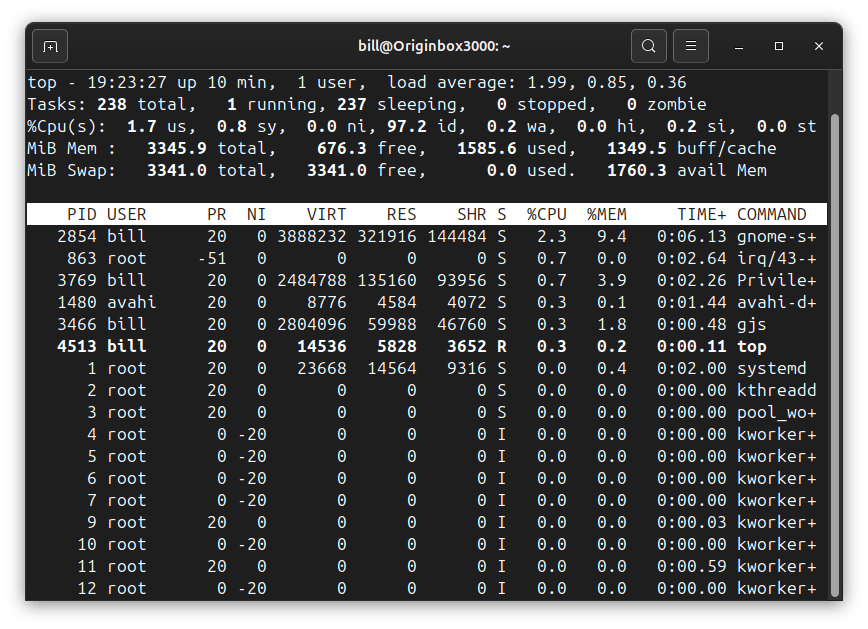
The top command in Linux provides real-time monitoring of system processes, resource usage, and performance metrics directly from the terminal. It dynamically displays essential information, including CPU utilization, memory consumption, swap usage, and running tasks. The interactive output updates automatically, offering an immediate overview of the system’s operational state, making it invaluable for troubleshooting, performance…
-

Linux systems commonly rely on iptables and its modern replacement nftables as core utilities for firewall configuration. These tools allow administrators to create and manage firewall rules that filter traffic based on IP addresses, ports, protocols, and connection states. Linux firewalls operate at a very low level, offering fine-grained control of packet filtering and network…
-
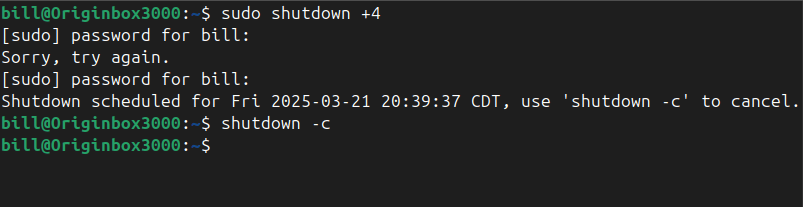
The shutdown command in Linux safely powers off or reboots a system, allowing users and administrators to schedule the shutdown after a certain time interval or at a specific time. It ensures the system terminates all processes correctly and prevents data corruption. The command accepts various parameters to specify time and behavior, with the option…
-
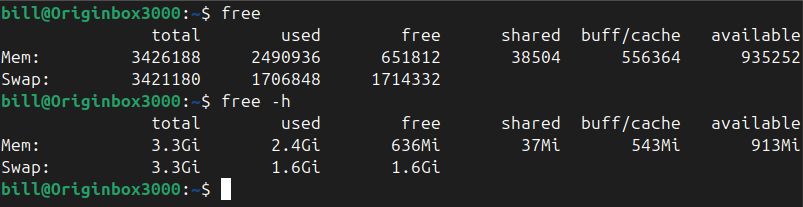
The free command in Linux is used to display comprehensive memory usage information, reporting the total, used, free, shared, buffer/cache, and available memory, including both RAM and swap space. It provides essential insights for system administrators and users to efficiently monitor and manage resources. By default, running the command free outputs memory details numerically in…
-
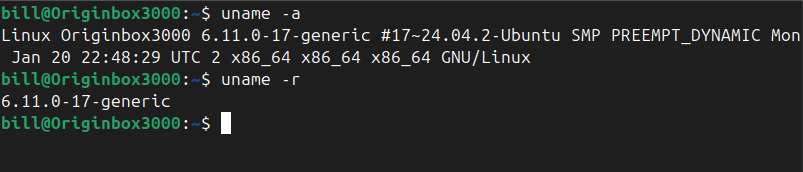
The uname command in Linux prints system information about the current machine. Specifically, it reports details such as the kernel name, kernel release, kernel version, machine hardware name, and the operating system. This command is commonly used by administrators and users alike to quickly determine system details for troubleshooting, software compatibility checks, or documenting system…
-
Understanding how to use networking tools in real-world scenarios is a core part of CompTIA A+ training. Each tool has a specific purpose, from diagnosing connection issues to testing cables or analyzing network traffic. Below is a breakdown of essential tools and how they would be used when given a practical situation: Cable Tester A…
-
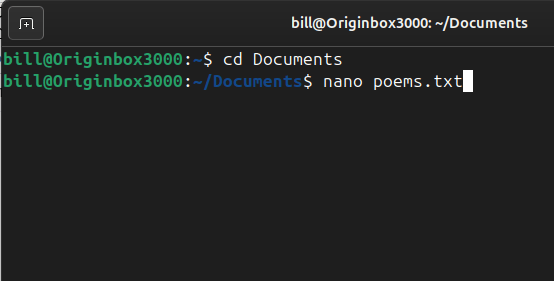
Nano is a simple and user-friendly command-line text editor for Unix-based systems, including Linux. It is designed to be easy to use, even for beginners, with a straightforward interface and on-screen shortcuts. Unlike more complex editors like Vim or Emacs, Nano does not require users to learn advanced keybindings or modes, making it an accessible…
-
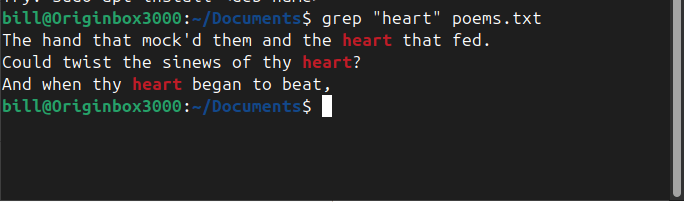
The grep command in Linux is a powerful text-search utility used to find specific patterns within files. In the screenshot, the command grep “heart” poems.txt was executed, instructing the system to search for the word “heart” inside poems.txt and display all matching lines. The output highlights instances where “heart” appears within the poem, helping the…
-

Links in Linux are essential for managing files efficiently, offering flexibility in how files are referenced and accessed. Two primary types exist: hard links and symbolic links (also called soft links). While both serve as references to files, they function differently in how they store and manage data. A hard link is a direct reference…
-
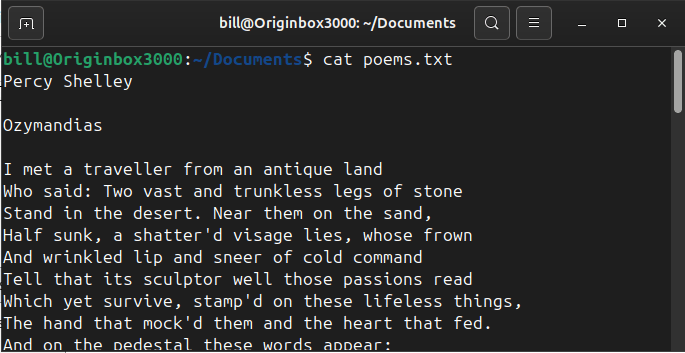
The cat command in Linux is used to display the contents of a file directly in the terminal. In the screenshot, the command cat poems.txt was executed from the ~/Documents directory. The cat command instructs the system to read the file poems.txt and print its contents line by line on the screen. The output shows…
-
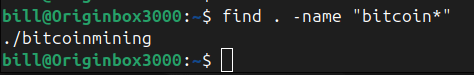
The find command in Linux is a powerful and versatile tool designed to search through files and directories based on specific criteria. It helps users efficiently locate files within a file system, filtering searches by name, file type, modification date, size, or even permissions. A typical syntax for using find includes specifying a starting directory,…
-

The apropos command searches manual page names and descriptions for a given keyword, helping users quickly discover relevant commands for a task. The apropos command helps Linux users find commands related to a keyword quickly. For example, typing apropos copy lists commands involving copying files or directories. Similarly, apropos network shows commands associated with network…
-
File System Hierarchy Standard (FHS): The File System Hierarchy Standard defines a consistent directory structure for Linux systems, specifying locations for system files, user files, and application data. FHS ensures predictability and uniformity across distributions, facilitating easier management and maintenance. Standard directories include /etc for configuration files, /var for variable data, /bin for essential binaries,…
-
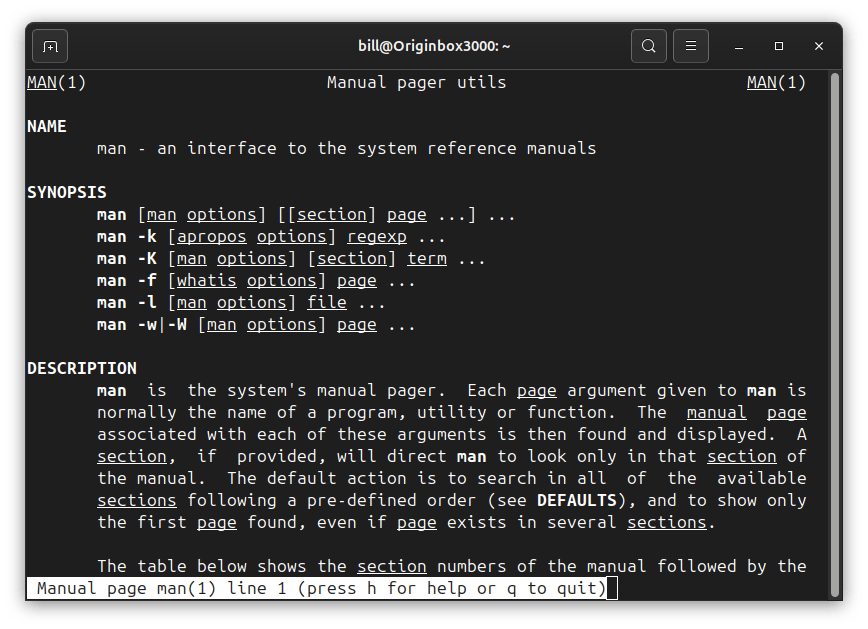
The man command, short for ‘manual’, is an essential tool in Linux, offering detailed documentation on virtually every command and program. By typing man followed by a specific command name, users gain immediate access to comprehensive manuals covering syntax, usage options, and practical examples. Ideal for beginners and seasoned professionals alike, the man command fosters…
-
Network ports serve as essential communication endpoints, allowing devices to exchange data over the internet and private networks. These numerical identifiers, assigned to specific services and applications, ensure proper data routing between devices. The IT industry relies on well-defined port numbers to facilitate secure and efficient networking operations across various protocols and services. Commonly Used…
-
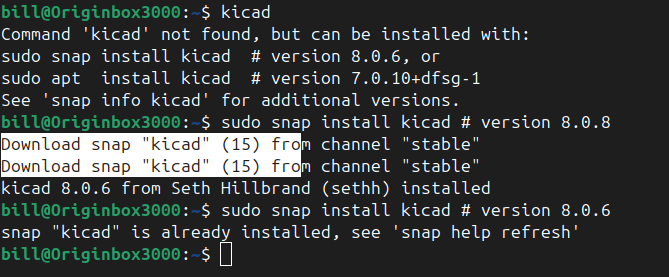
KiCad is a powerful open-source software suite used for designing printed circuit boards (PCBs). It offers a comprehensive set of tools for schematic capture, PCB layout, and 3D visualization, making it a go-to choice for both hobbyists and professional engineers. The software supports industry-standard formats and integrates essential features such as Gerber file export and…
-

The snmpwalk command is used to perform a series of network management requests to a specific device using an IP address(example: 10.31.10.101),starting from the OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1, using SNMPv3. Reference record for OID: Website to interpret OID Adresses snmpwalk -v3 -l authPriv -u l1monitor -a MD5 -A GEe9bb8h -x DES -X 4ixay7su 10.36.10.108 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1snmpwalk: This is…
-
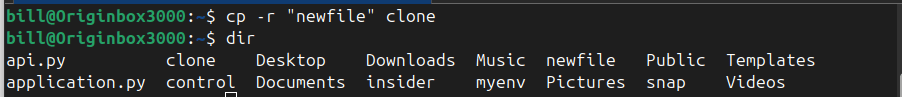
The cp command in Linux is used to copy files and directories. It’s a powerful utility that can create copies of data from one location to another, either within the same directory or across different directories. Adding the -r (recursive) flag allows you to copy entire directories, including their contents. This command copies the newfile…
-
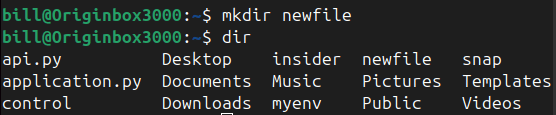
The mkdir command, an abbreviation for “make directory,” is a foundational tool for Linux users, enabling the creation of directories directly within the terminal. According to Linux documentation, the command is widely used to organize files systematically, promoting efficient file management practices for both personal and professional projects. Users simply type mkdir <directory_name> to create…
-
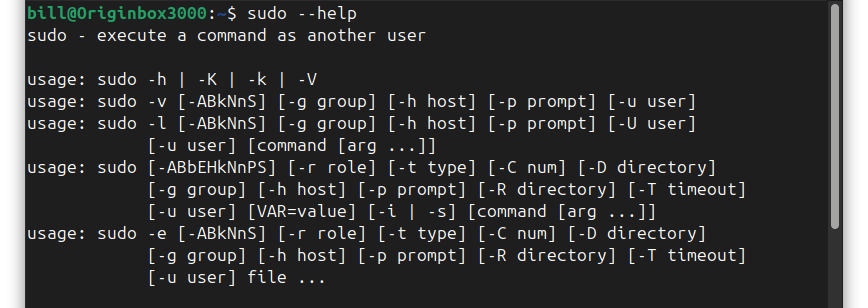
The sudo command in Linux enables authorized users to execute commands with superuser privileges, facilitating essential administrative tasks such as software installation, system configuration modifications, and service management. Key benefits of using sudo include enhanced security by requiring explicit permission before executing potentially harmful commands, accountability through logging each use for traceability, and controlled access…
-
Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) is a widely used serial communication protocol developed by Schneider Electric in 1979 for industrial applications. It’s designed for communication between various devices such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and other industrial electronic devices. Modbus RTU uses a Commander/Executor architecture, where one device (Commander) initiates communication and controls one…
-