Tech Docs
-
-
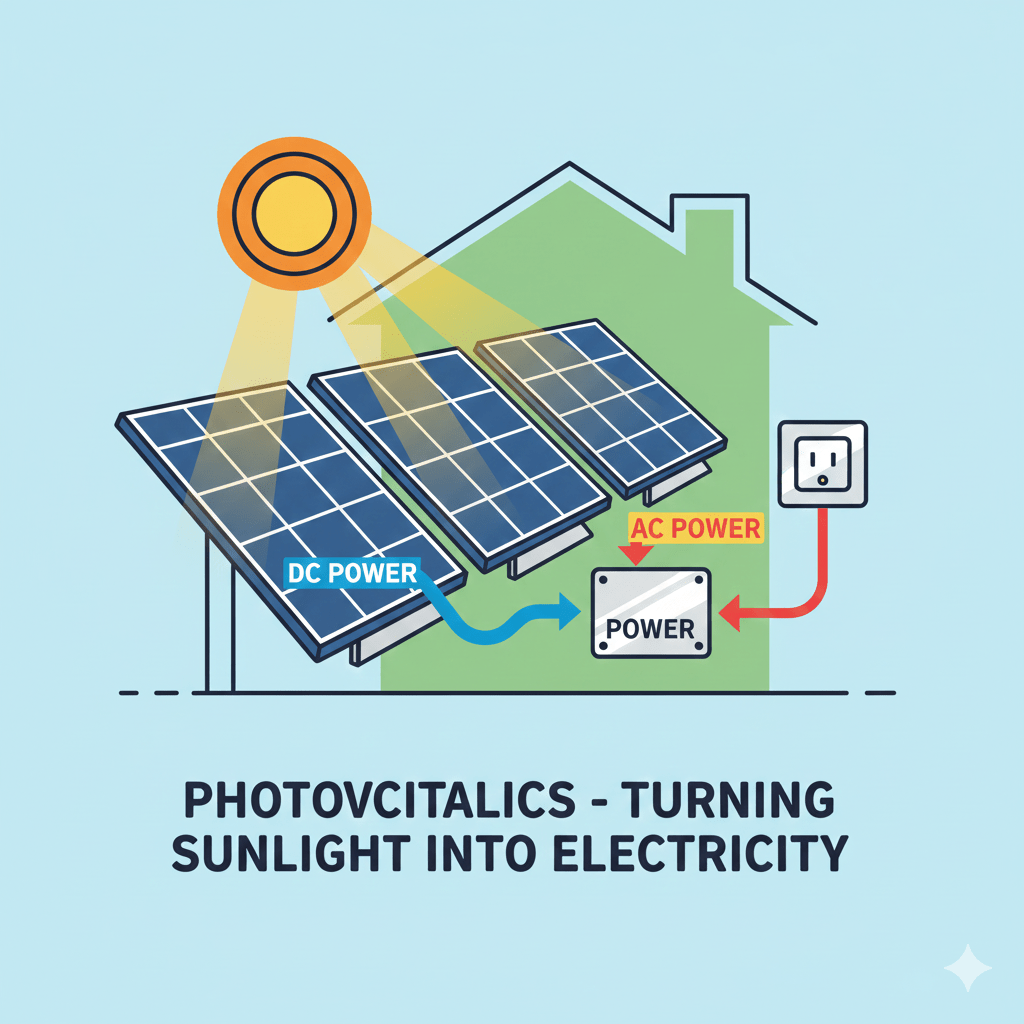
Photovoltaics is the technological principle and scientific field concerned with the direct conversion of light energy, specifically photons from sunlight, into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect, a physical and chemical process that occurs within a class of materials known as semiconductors, most commonly crystalline silicon. The fundamental unit of this conversion is the photovoltaic cell,…
-
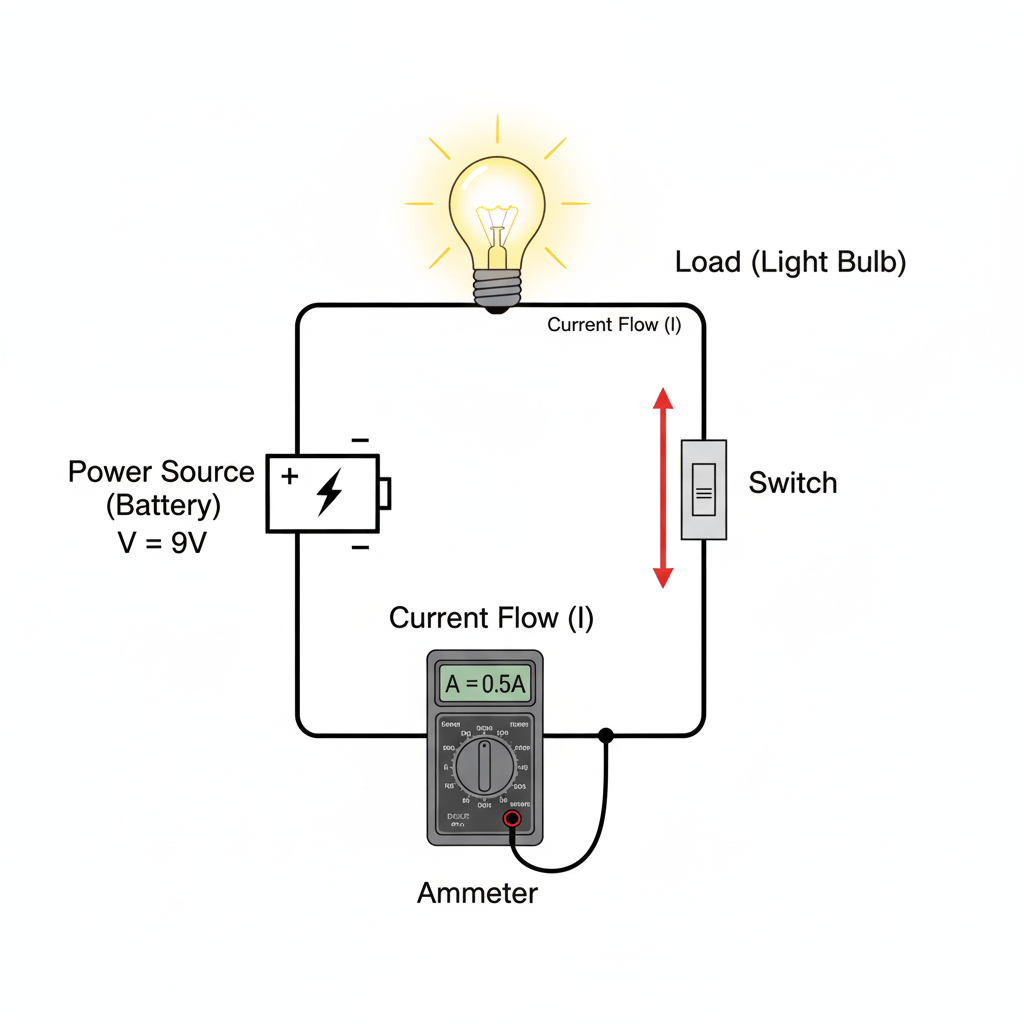
A simple circuit is an electrical circuit that consists of just a few basic components, creating a closed loop through which electric current flows. Typically, it includes a power source like a battery, a conductive path such as wires, and a load, which can be a device like a light bulb or resistor that uses…
-

Semiconductors are materials whose electrical conductivity lies between that of conductors and insulators, and they are unique because their properties can be controlled and modified. Semiconductors are chemically diverse materials whose electrical conductivity lies between that of conductors and insulators, and their behavior can be precisely engineered. The most common elemental semiconductors are silicon (Si),…
-
Industrial robots are highly versatile automation systems designed for a wide range of tasks in manufacturing and production environments. They are freely programmable, meaning their operations can be customized and reconfigured for different applications. These robots are also freely positionable, allowing them to be installed in various locations within a facility. Their universal applicability makes…
-

Direct burial in fiber optics refers to the installation of specially designed fiber optic cables directly into the ground without the need for protective conduits or ducts. These cables are engineered to withstand harsh underground conditions for long-term, maintenance-free operation. Direct burial fiber optic cables are constructed with multiple protective layers to endure soil pressure,…
-
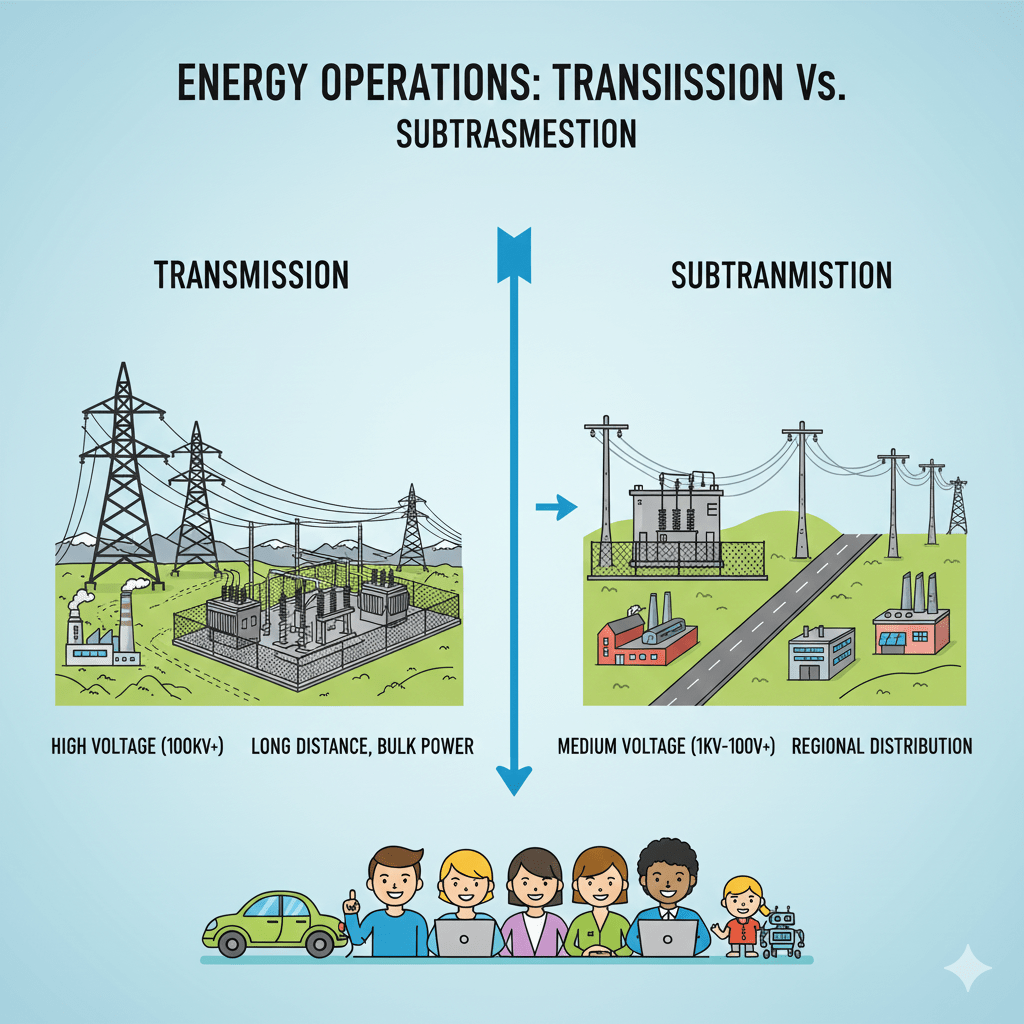
Transmission in electric power systems refers to the bulk transfer of electrical energy at very high voltages (typically 115 kV to 765 kV or higher) from generating stations to major substations, using interconnected networks of overhead or underground lines designed to move large amounts of power efficiently over long distances with minimal losses. Subtransmission, by…
-
-

An optical power meter is a precision instrument used in fiber optic networks to quantify the optical signal power transmitted through a fiber. It operates by converting incoming light—usually in the infrared range—into an electrical signal using a calibrated photodetector, then displaying the power level in decibel-milliwatts (dBm) or milliwatts (mW). This measurement is critical…
-
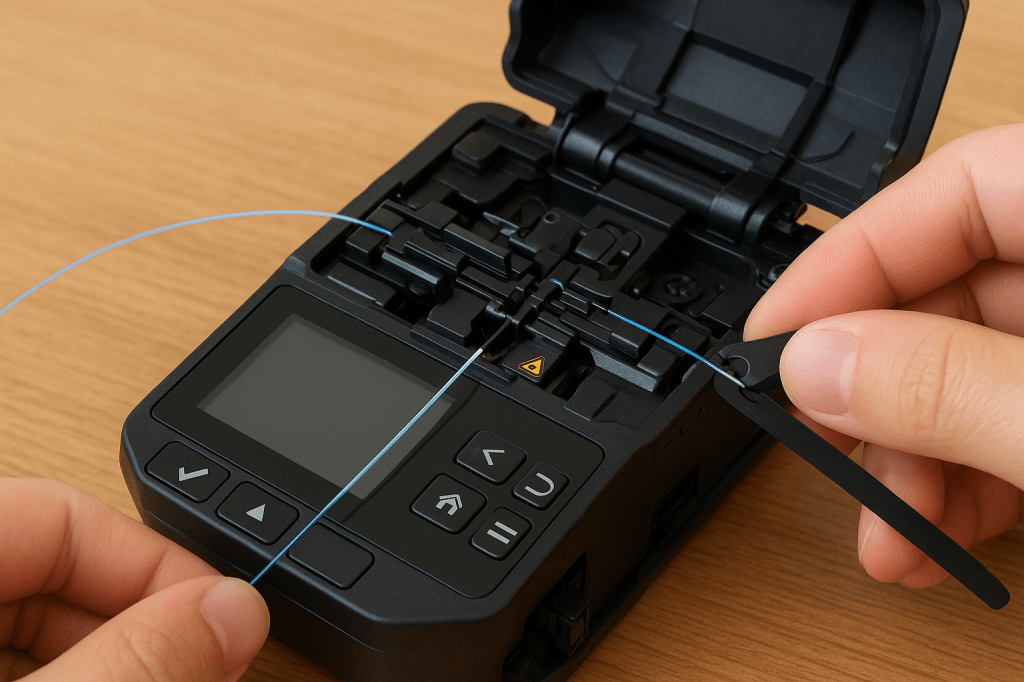

Fiber optic splicing is a precision technique used to connect two optical fibers end-to-end, allowing light signals to pass through with minimal loss and reflection. This process is fundamental in building, repairing, and extending fiber optic networks, especially in long-haul telecommunications, data centers, and FTTH installations. The most common method is fusion splicing, which uses…
-
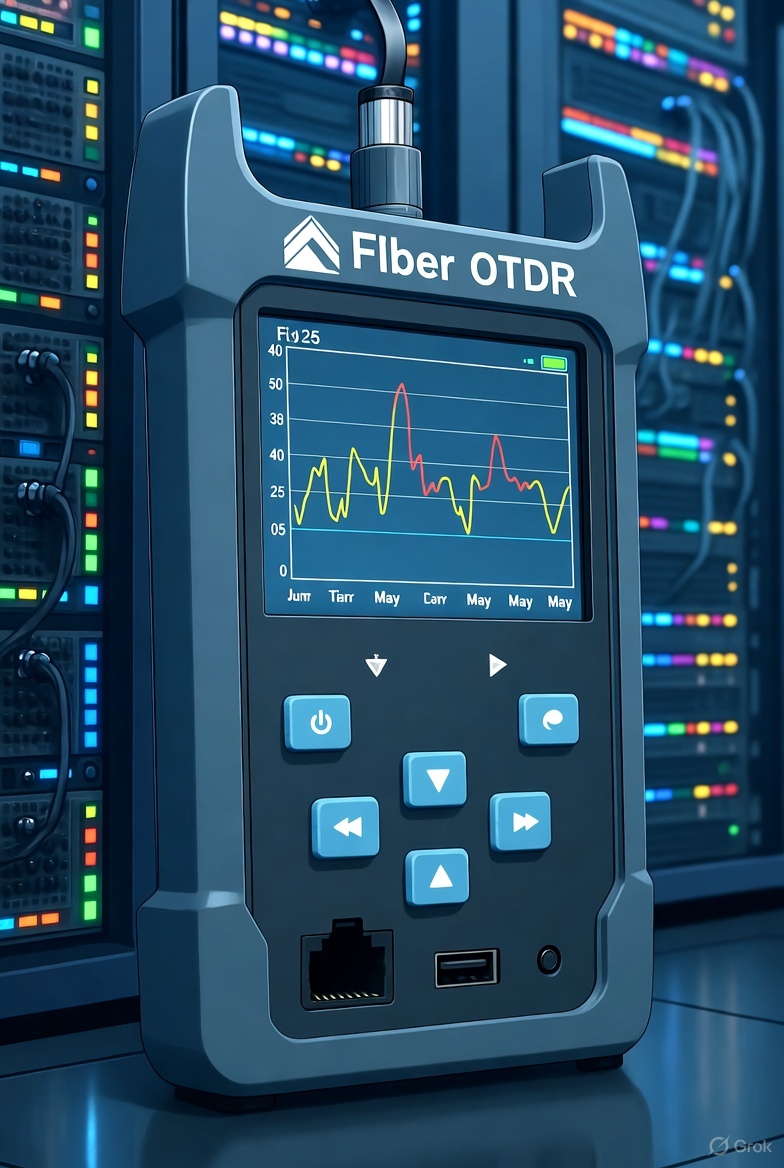
OTDR, or Optical Time Domain Reflectometer, operates by injecting a series of short laser pulses into one end of an optical fiber and measuring the light that is scattered or reflected back from points along the fiber. This backscattered light—primarily due to Rayleigh scattering and Fresnel reflections—is captured by a photodetector within the OTDR, and…
-
Cleaving fiber is a controlled mechanical process used to prepare optical fibers for splicing or termination by creating a clean, flat break at the end of the fiber. The goal is to produce an end face that is perpendicular to the fiber’s axis with minimal surface defects, which is critical for achieving low insertion loss…
-
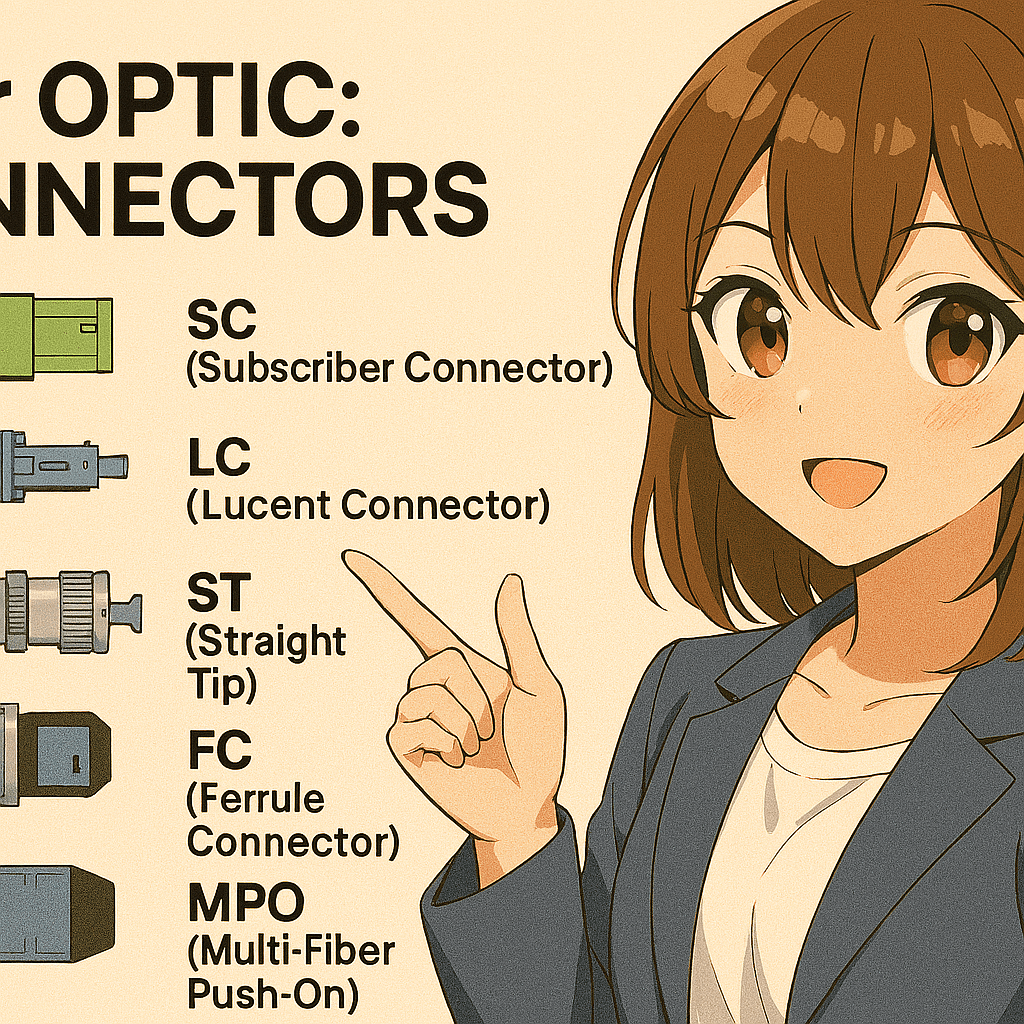
The most commonly known fiber connectors among fiber optic technicians are SC, LC, ST, FC, and MPO. Each has distinct physical characteristics and use cases, with SC and LC dominating modern deployments. SC (Subscriber Connector)The SC connector is a square-shaped, push-pull style fiber optic connector with a 2.5 mm ferrule. It’s widely used in telecom…
-
A splice-on connector is a type of fiber optic connector that allows technicians to fusion splice a pre-polished fiber stub housed within the connector body directly to a field fiber, combining the precision and low-loss performance of factory-terminated connectors with the flexibility of on-site installation. Splice-on connectors are ideal for high-performance environments where mechanical splicing…
-
Fusion splicing is the process of permanently joining two optical fibers end-to-end by fusing them together using an electric arc. The goal is to align the fiber cores precisely and create a continuous optical path that minimizes signal loss and reflection. When properly done, the joint is almost as strong as the original fiber and…
-

An OTDR, or Optical Time Domain Reflectometer, is a diagnostic instrument used to analyze the integrity and performance of fiber optic cables. It works by launching a series of high-speed optical pulses into the fiber and measuring the light that is scattered or reflected back due to imperfections, splices, connectors, or breaks. By calculating the…
-

Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated chip embedded on a computer’s motherboard, designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. It stores sensitive information such as encryption keys, digital certificates, and passwords in a tamper-resistant environment. TPM is commonly used for: The current standard is TPM 2.0, which is required by modern operating systems…
-

A thermal printer uses heat to transfer images onto paper. It comes in two types: Consumables and Maintenance Direct thermal printers require only thermal paper, while thermal transfer printers need both ribbon and label stock.Maintenance includes: Technicians must also check for signs of printhead wear, incorrect temperatures, or paper with poor heat response when troubleshooting…
-

Every desktop computer relies on a Power Supply Unit (PSU) to convert wall electricity into usable voltage levels that safely power internal components. The PSU takes in AC (Alternating Current) and outputs DC (Direct Current) in multiple voltages—typically +12V, +5V, and +3.3V—distributed to the motherboard, CPU, storage devices, and GPU. Without proper power regulation, even…
-

The snmpwalk command is used to perform a series of network management requests to a specific device using an IP address(example: 10.31.10.101),starting from the OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1, using SNMPv3. Reference record for OID: Website to interpret OID Adresses snmpwalk -v3 -l authPriv -u l1monitor -a MD5 -A GEe9bb8h -x DES -X 4ixay7su 10.36.10.108 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1snmpwalk: This is…
-
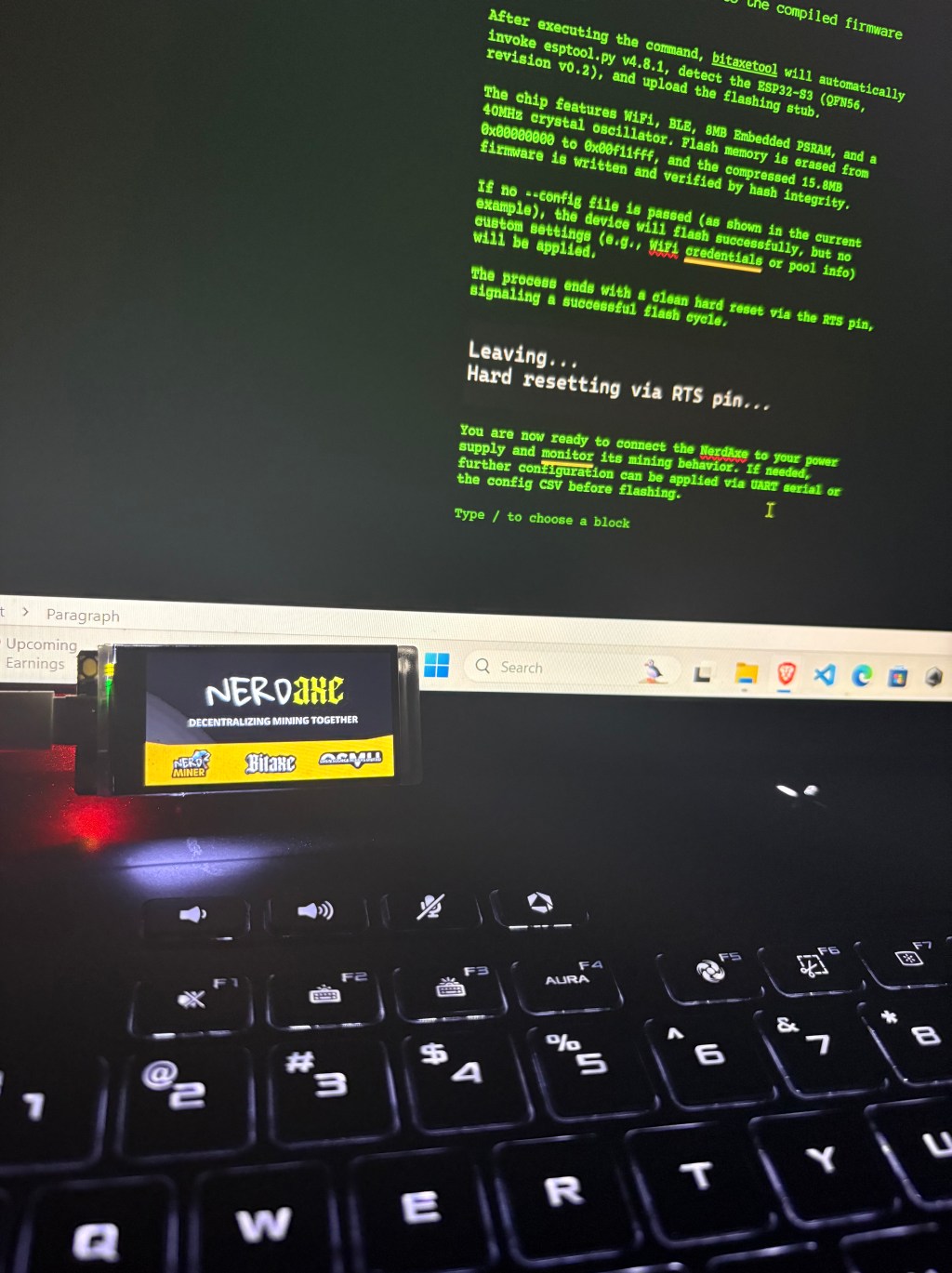
Esptool.py is a Python-based utility created by Espressif for flashing firmware onto ESP8266 and ESP32 chips. It operates cross-platform—working on Windows, Linux, and macOS—and is executed from the command line using Python. Although its name ends in .py, users interact with it using simple terminal commands, not actual Python code. The command-line arguments passed to…
-

ERCOT (The Electric Reliability Council of Texas) is the independent system operator that manages the flow of power for about 90 percent of Texas, serving more than 27 million customers and coordinating more than 54,100 miles of transmission and roughly 1,250 generation units; it oversees real time dispatch and market settlement for the state’s competitive…
-

The taskkill command is a powerful Windows OS CLI tool that allows users to forcefully terminate running processes directly from the terminal. Unlike the Task Manager’s graphical interface, taskkill gives users precise control over which processes to end, either by using the process name (also called the image name) or its unique process ID (PID).…
-
-
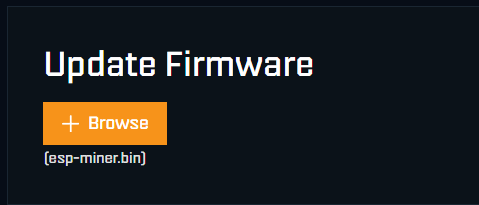
If your SupraHex unit is not appearing on your mining pool dashboard, it’s likely due to outdated or incompatible firmware. To resolve this issue: Check for the latest firmware release by clicking the Check in the settings section of your miners graphical user interface (GUI). After the Download of the “esp-miner.bin” and “www.bin” files upload…
-

Economist Peter Schiff has publicly criticized Michael Saylor’s characterization of Bitcoin as “digital energy.” Schiff questioned the practicality of using Bitcoin to generate power, contrasting it with crude oil’s essential role in preventing mass starvation. Michael Saylor, Executive Chairman of MicroStrategy, has previously described Bitcoin as “digital energy,” suggesting that it conserves energy in cyberspace…
-
The mkfifo command in Linux is used to create named pipes, also known as FIFOs (First In, First Out). Unlike regular files, a FIFO behaves like a pipe that allows data to flow between processes. You can think of it as a communication tunnel where one process writes data and another reads it. For example,…
-

The locate command in Linux is used to quickly search for files by name across the entire filesystem. Unlike the find command, which actively searches through directories in real-time, locate uses a prebuilt index from a database (usually updated with the updatedb command). This makes it incredibly fast and efficient. For example, typing locate passwd…
-

The /media directory is used in Linux to automatically mount removable storage devices such as USB drives, DVDs, and external hard drives. When you insert a USB or plug in a storage device, most Linux distributions will automatically create a subdirectory inside /media and mount the device there. This helps users access external drives easily…
-

Impact printers, such as dot matrix printers, use a physical print head that strikes an ink-soaked ribbon against the paper—similar to a typewriter. These devices are primarily used in environments where multi-part forms, carbon copies, or durability in dusty conditions are required, such as warehouses, industrial settings, and point-of-sale systems. A key feature of impact…
-
.cpp vs .cc in Modern C++ Development C++ source files do not merely represent lines of code—they serve as compiled units of meaning. Their naming convention affects build pipelines, toolchain integration, and developer consistency. Among C++ developers, the two dominant extensions used to denote source files are .cpp and .cc. Both are fully supported by…
-

Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated chip embedded on a computer’s motherboard, designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. It stores sensitive information such as encryption keys, digital certificates, and passwords in a tamper-resistant environment. TPM is commonly used for: The current standard is TPM 2.0, which is required by modern operating systems…
-

A thermal printer uses heat to transfer images onto paper. It comes in two types: Consumables and Maintenance Direct thermal printers require only thermal paper, while thermal transfer printers need both ribbon and label stock.Maintenance includes: Technicians must also check for signs of printhead wear, incorrect temperatures, or paper with poor heat response when troubleshooting…
-

Every desktop computer relies on a Power Supply Unit (PSU) to convert wall electricity into usable voltage levels that safely power internal components. The PSU takes in AC (Alternating Current) and outputs DC (Direct Current) in multiple voltages—typically +12V, +5V, and +3.3V—distributed to the motherboard, CPU, storage devices, and GPU. Without proper power regulation, even…
-
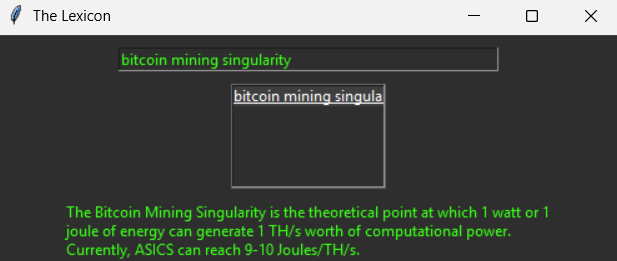
This study proposes a new theoretical framework: the Bitcoin Mining Singularity, defined as the point at which one joule of energy yields one terahash per second (1 J/TH) of cryptographic computation. This convergence of energy efficiency and computational output in Bitcoin mining represents a potential milestone in the global evolution of post-industrial labor, energy monetization,…
-

Inkjet printers are among the most common types of consumer and small office printers, known for their ability to produce detailed color images and sharp text on a variety of media. They function by spraying tiny droplets of ink directly onto paper through nozzles in the printhead. These droplets are controlled with extreme precision, often…
-

LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is an open, vendor-neutral protocol used to access and maintain distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. LDAP is widely used for storing and managing information about users, groups, computers, and other resources in a centralized database, known as a directory. The protocol allows clients to connect…
-
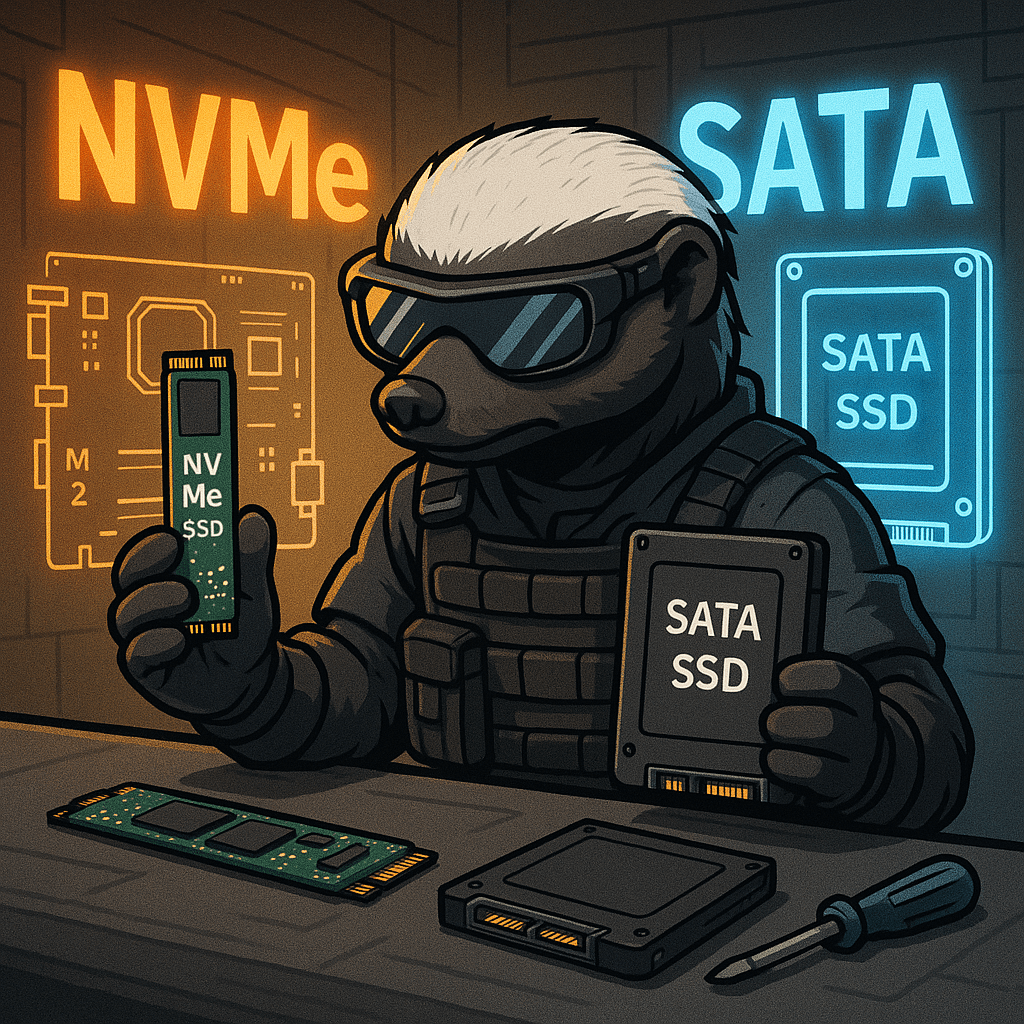
In modern computing, Solid State Drives (SSDs) have largely replaced traditional spinning hard drives due to their superior speed and reliability. Among SSD types, two interfaces dominate: SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs. Both offer fast performance compared to HDDs, but the underlying technology and connection methods set them apart significantly. SATA SSDs use the Serial…
-

When a Linux machine starts feeling slower than normal, it’s often a sign that system resources are strained. In this case, the user decided to troubleshoot by checking memory usage and cleaning up unused files. After running the free command to get a snapshot of RAM and swap usage, they used find to delete all…
-

To set up logical volume management in Linux, the first step is creating a physical volume (PV). A physical volume is typically a disk partition (like /dev/sdb1) that is initialized for use by the Logical Volume Manager. This is done using the pvcreate command, which prepares the partition to be added into a volume group.…
-
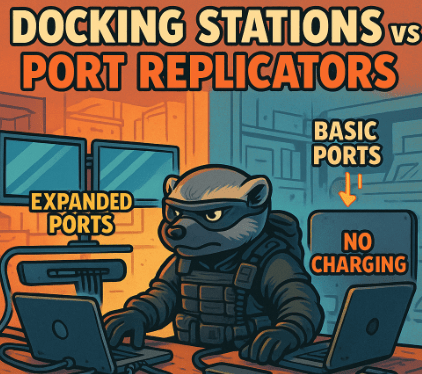
What Is a Docking Station? A docking station is a physical expansion unit that connects to a laptop and transforms it into a full desktop workstation. It adds additional ports such as USB, Ethernet, HDMI, DisplayPort, audio jacks, and charging capabilities, often through a single USB-C or proprietary connector. Docking stations typically: Used in corporate…
-

The IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) is a unique 15-digit number assigned to every mobile device that connects to a cellular network. Unlike a SIM card, which identifies the user, the IMEI identifies the device itself. It is used by carriers to track stolen devices, block lost phones from network access, and enforce blacklists. IMEI…
-
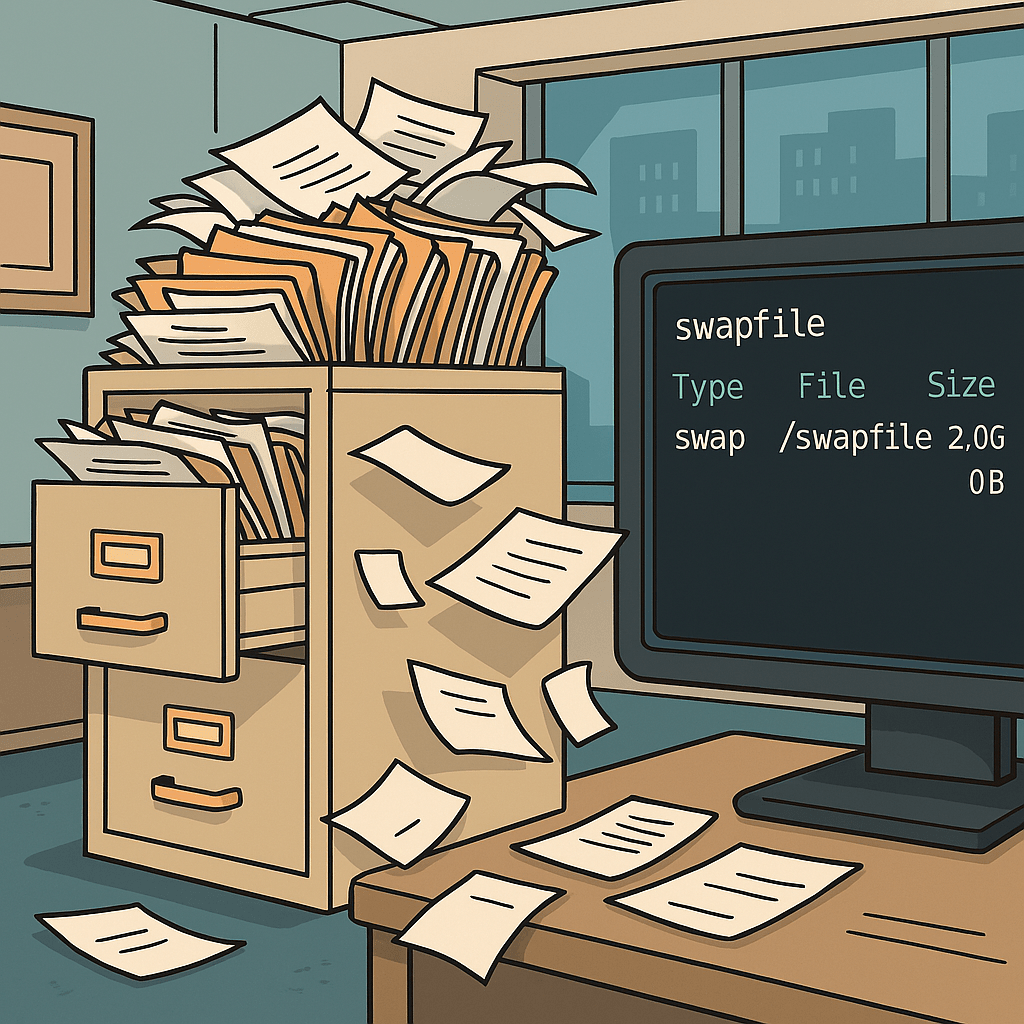
A swap file in Linux is a special file on the disk that acts as virtual memory when the system’s physical RAM becomes full. Instead of immediately failing or killing processes when memory runs low, the kernel moves less-used data from RAM into the swap file to free up space for active applications. This ensures…
-

Creating a filesystem means formatting a partition or volume with a specific structure that the operating system can understand—such as ext2, ext3, ext4, xfs, or fat32. This is often done on a new partition using the mkfs (make filesystem) family of commands. For example, formatting a device with ext4 can be done with: sudo mkfs.ext4…
-
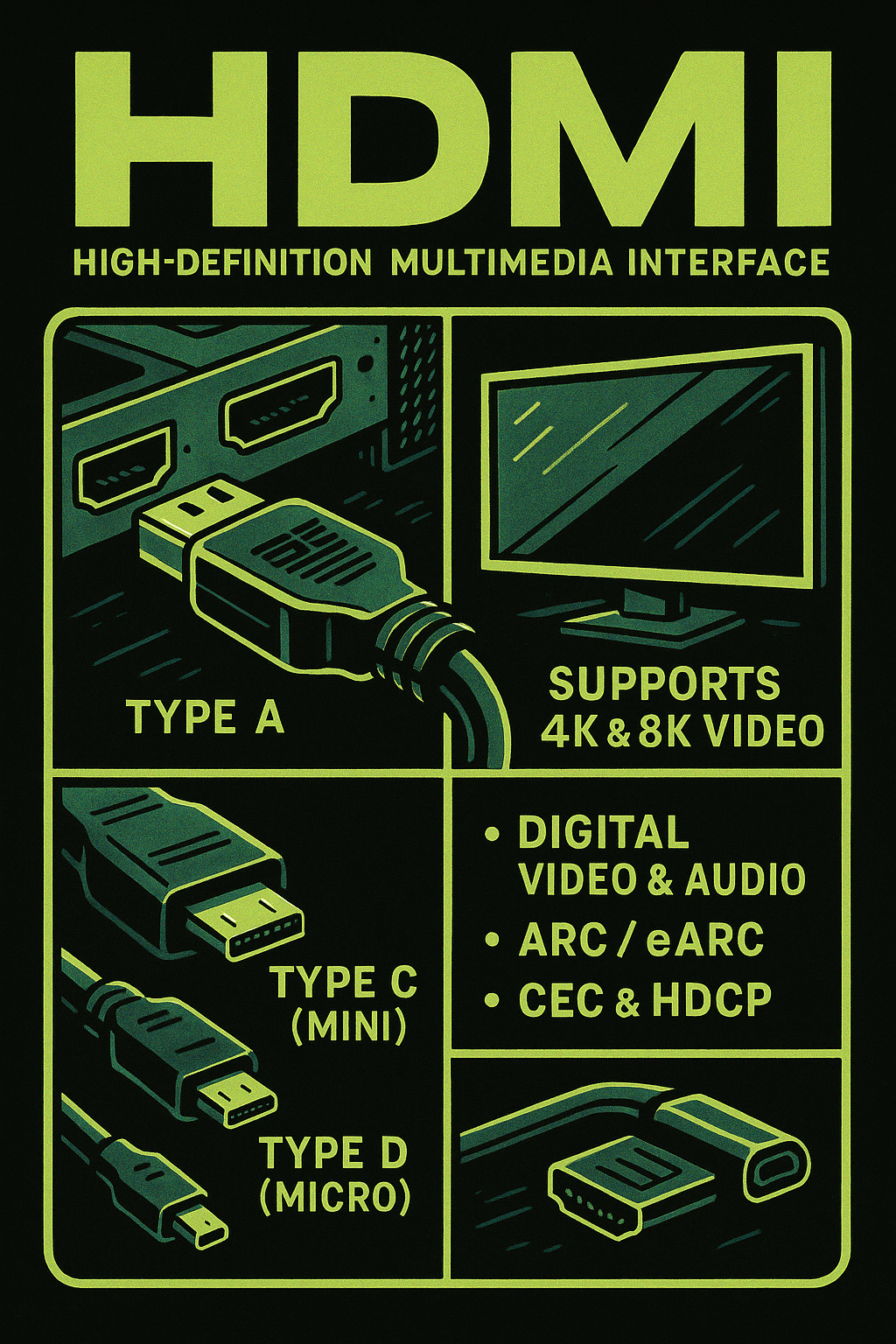
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a proprietary audio/video interface designed to transmit uncompressed digital video and audio from a source device to a display or audio receiver. It supports a wide range of high-resolution formats, including 1080p, 4K, and even 8K video, along with multi-channel digital audio—all through a single cable. HDMI connectors come in…
-
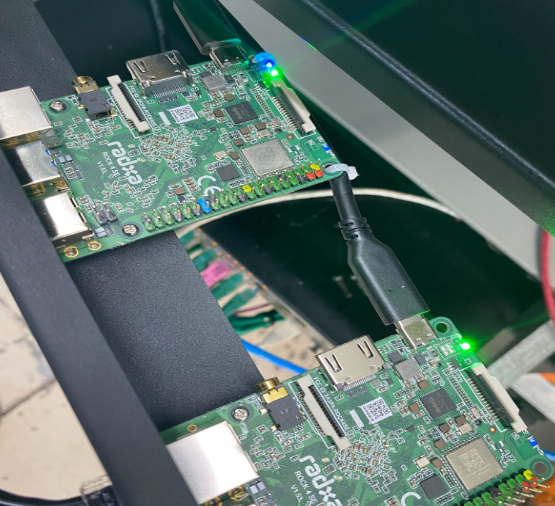

The Rockpi 4 SE is essentially a computer that you can program. The Rockpi has capabilities for various management, monitoring, and automation tasks to further optimize operations at a bitcoin mining facility. Software Overview Retrofitting “Brains”’ on a Rock Pi involves first opening a Fedora terminal to develop u-boot for the Rock Pi. Once the…
-
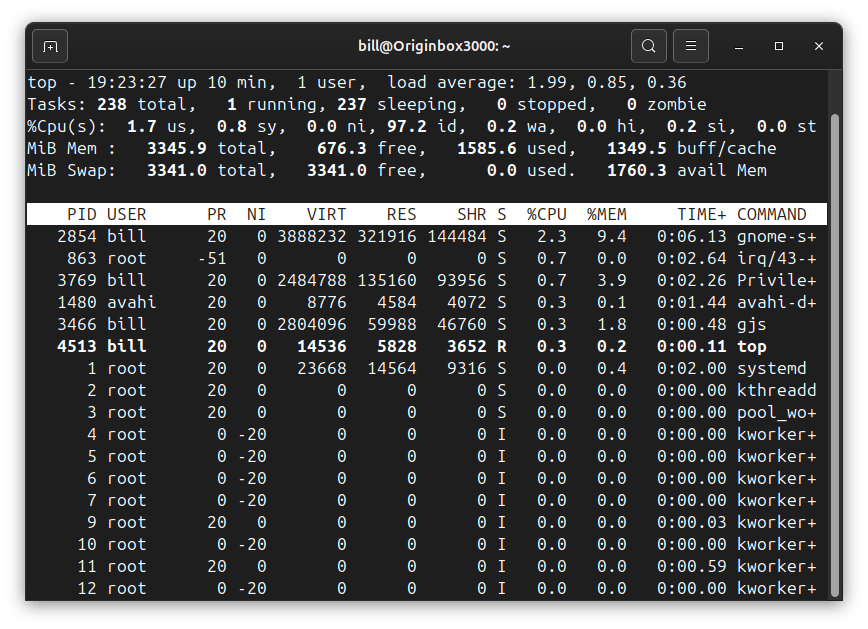
The top command in Linux provides real-time monitoring of system processes, resource usage, and performance metrics directly from the terminal. It dynamically displays essential information, including CPU utilization, memory consumption, swap usage, and running tasks. The interactive output updates automatically, offering an immediate overview of the system’s operational state, making it invaluable for troubleshooting, performance…
-
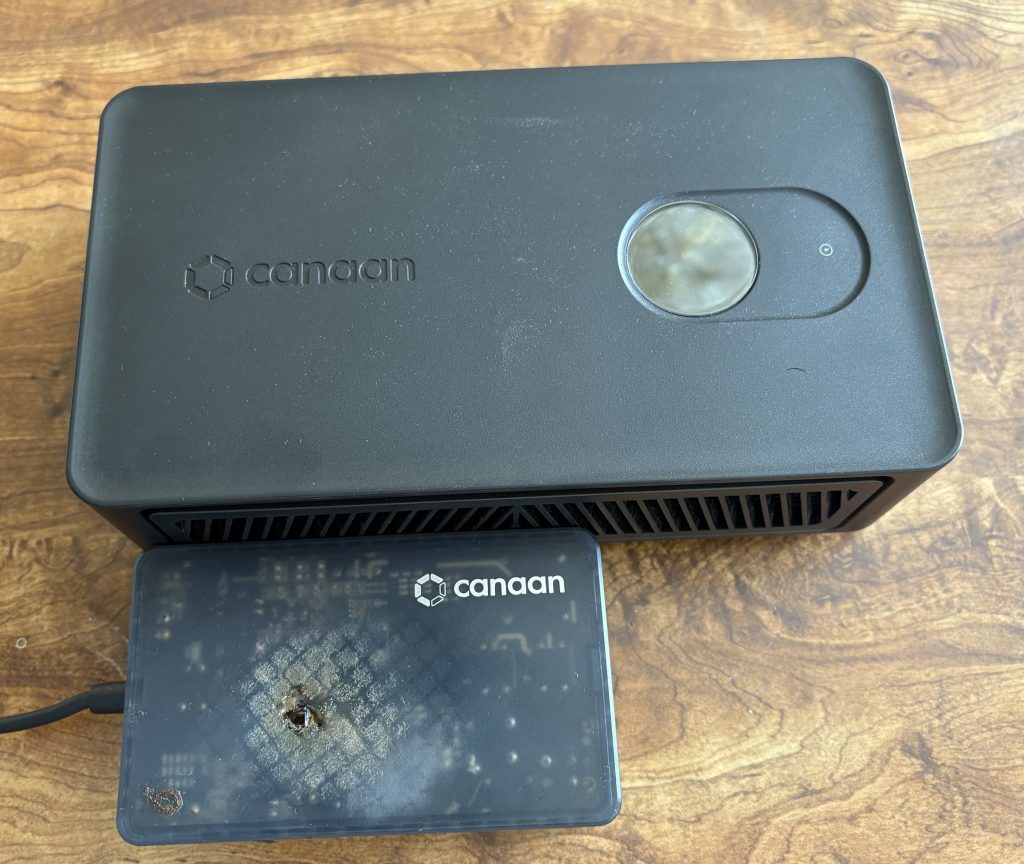

A Canaan Bitcoin miner experienced a power supply unit (PSU) failure, leading to significant damage. An analysis suggests two primary causes: inadequate power delivery from an extension cord and the use of a non-compliant USB-C cable. Theory 1: Inadequate Power Delivery from Extension Cord The PSU was connected via an extension cord, which may not…
-
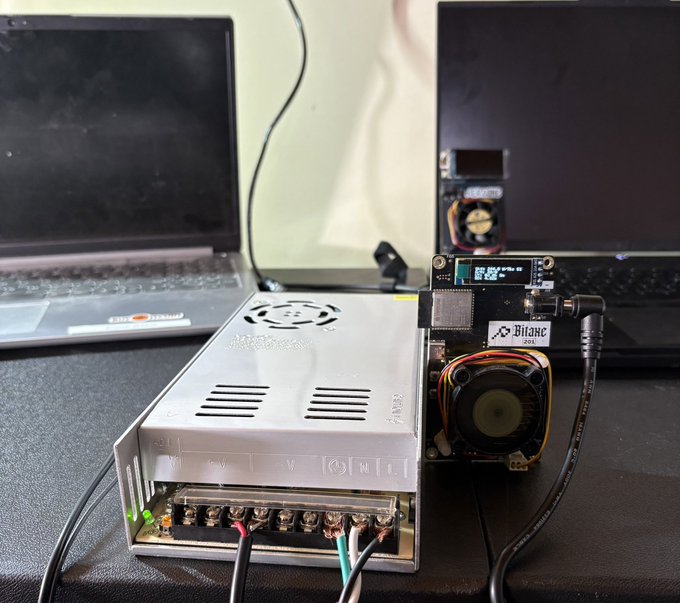

Industrial-grade Bitcoin mining machines require robust and efficient power supplies to convert alternating current (AC) from the grid into the direct current (DC) necessary for their operation. Selecting the appropriate AC to DC power supply is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of the mining equipment. Power Requirements and Efficiency Each mining machine model has…
-
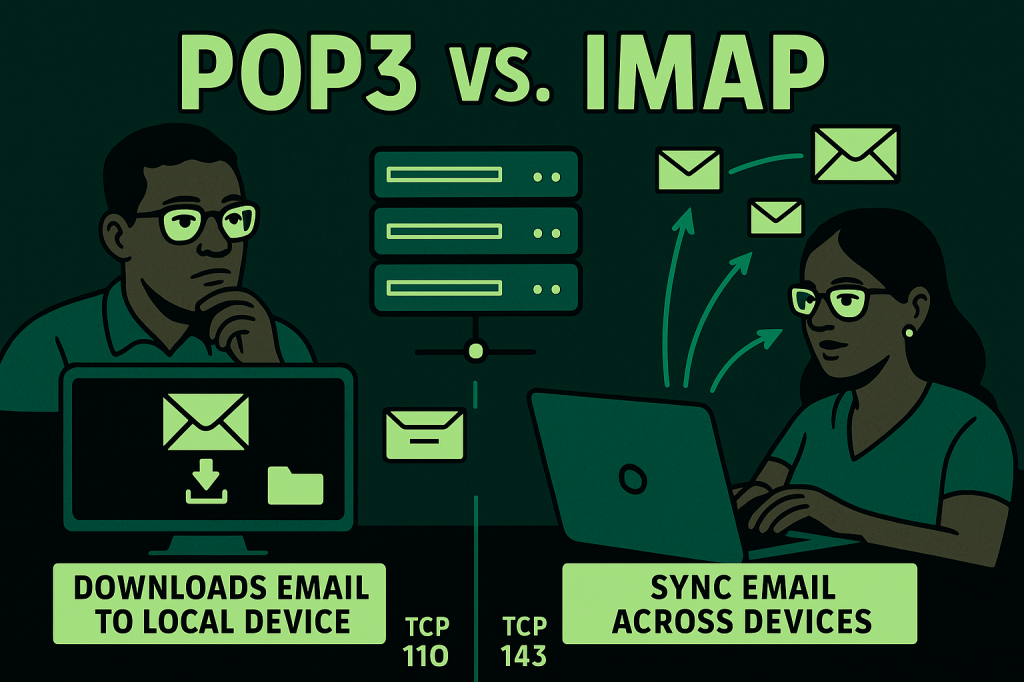
POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) is an email retrieval protocol that allows a client to download messages from a mail server to a local device. Operating over TCP port 110 (or 995 with SSL/TLS), POP3 typically downloads and then deletes messages from the server unless configured otherwise. It is ideal for users who want…
-
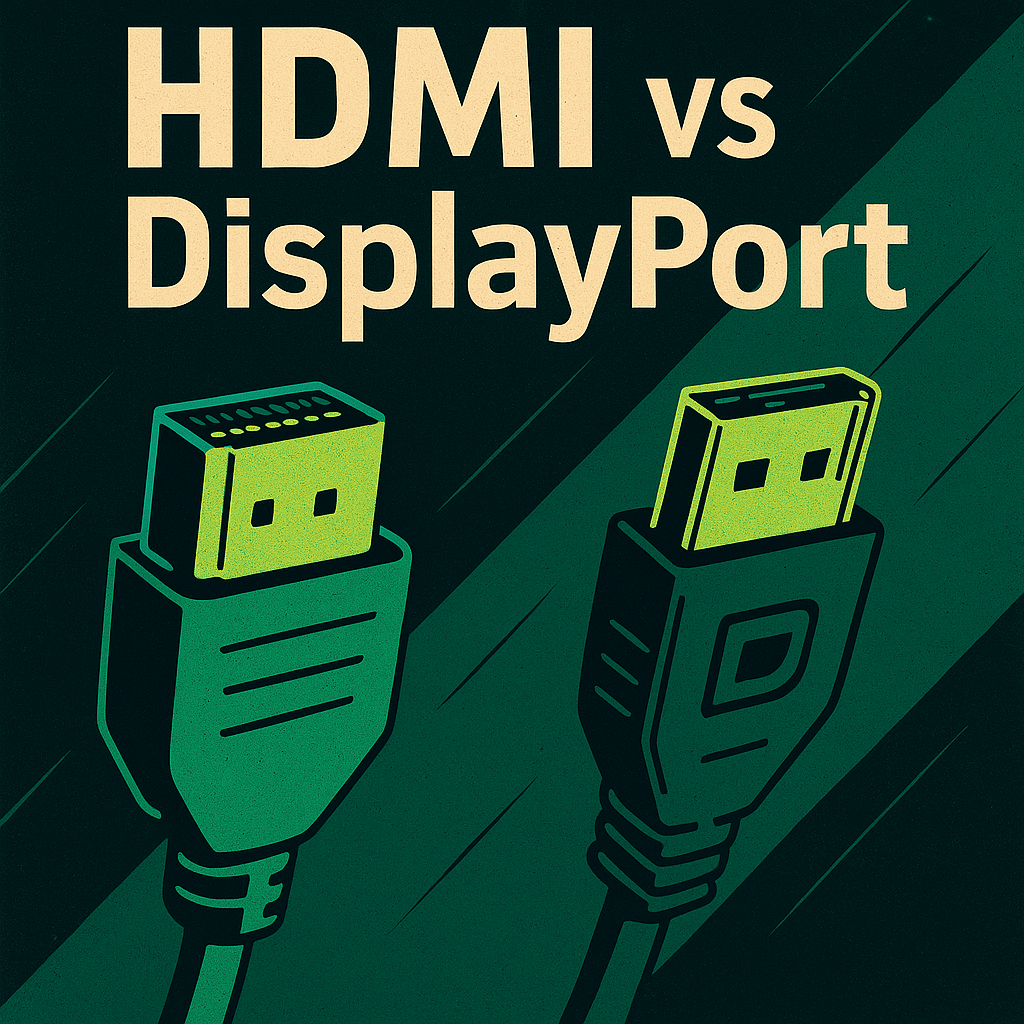
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) and DisplayPort are two widely adopted digital display interfaces, but they are optimized for different environments. HDMI is the standard for consumer electronics, including TVs, projectors, game consoles, and media players. It supports both audio and video in a single cable and includes features like CEC (Consumer Electronics Control) and ARC…
-

Esptool.py is a Python-based utility created by Espressif for flashing firmware onto ESP8266 and ESP32 chips. It operates cross-platform—working on Windows, Linux, and macOS—and is executed from the command line using Python. Although its name ends in .py, users interact with it using simple terminal commands, not actual Python code. The command-line arguments passed to…
-

BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) are closely related components in PC architecture, but they serve distinct functions. BIOS is firmware stored on a chip on the motherboard, responsible for initializing hardware during boot-up, performing POST (Power-On Self-Test), and launching the operating system. It also provides a configuration interface where users can…
-
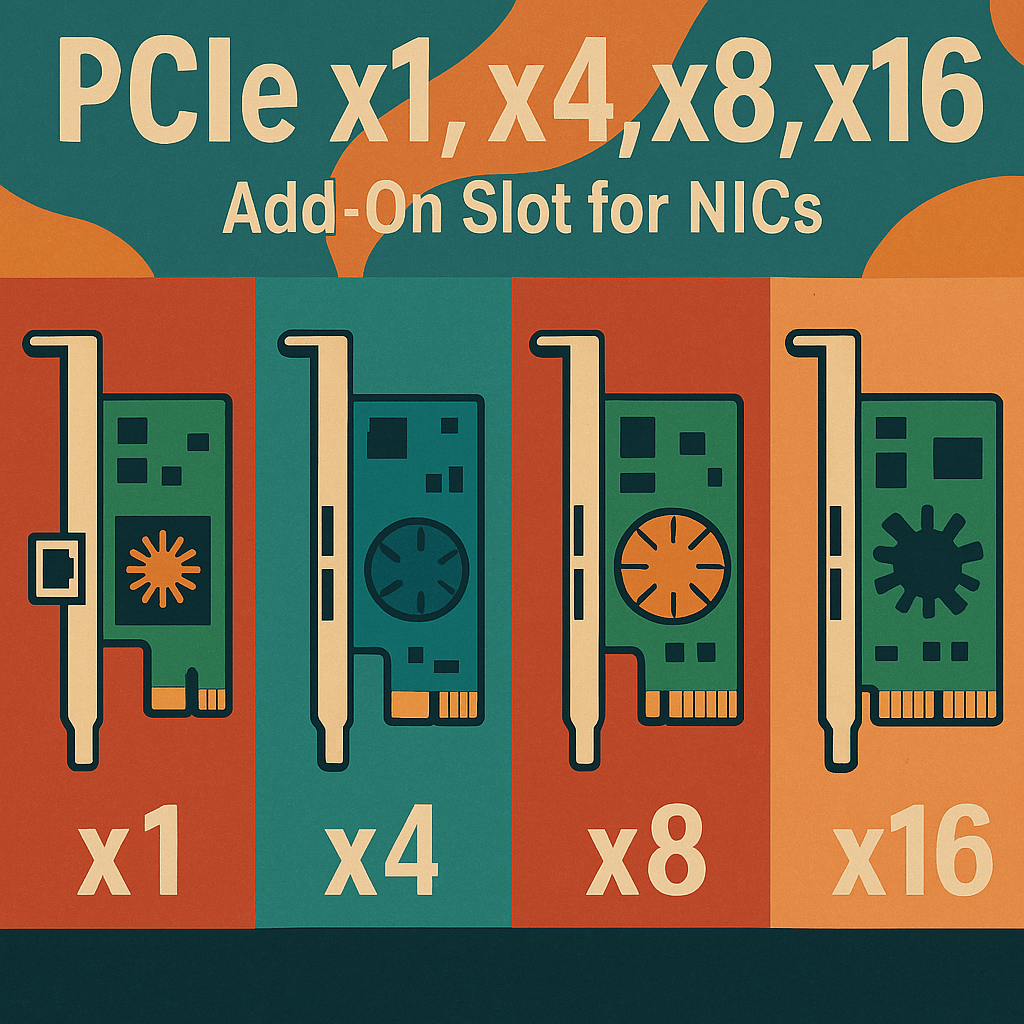
PCI Express (PCIe) is the industry-standard high-speed interface used to connect add-on components—like network interface cards (NICs)—to a computer’s motherboard. For NICs, PCIe offers dedicated data lanes to the CPU or chipset, ensuring low-latency, high-throughput, and scalable bandwidth. PCIe slots are designated by their lane count: x1, x4, x8, and x16. Each lane consists of…
-
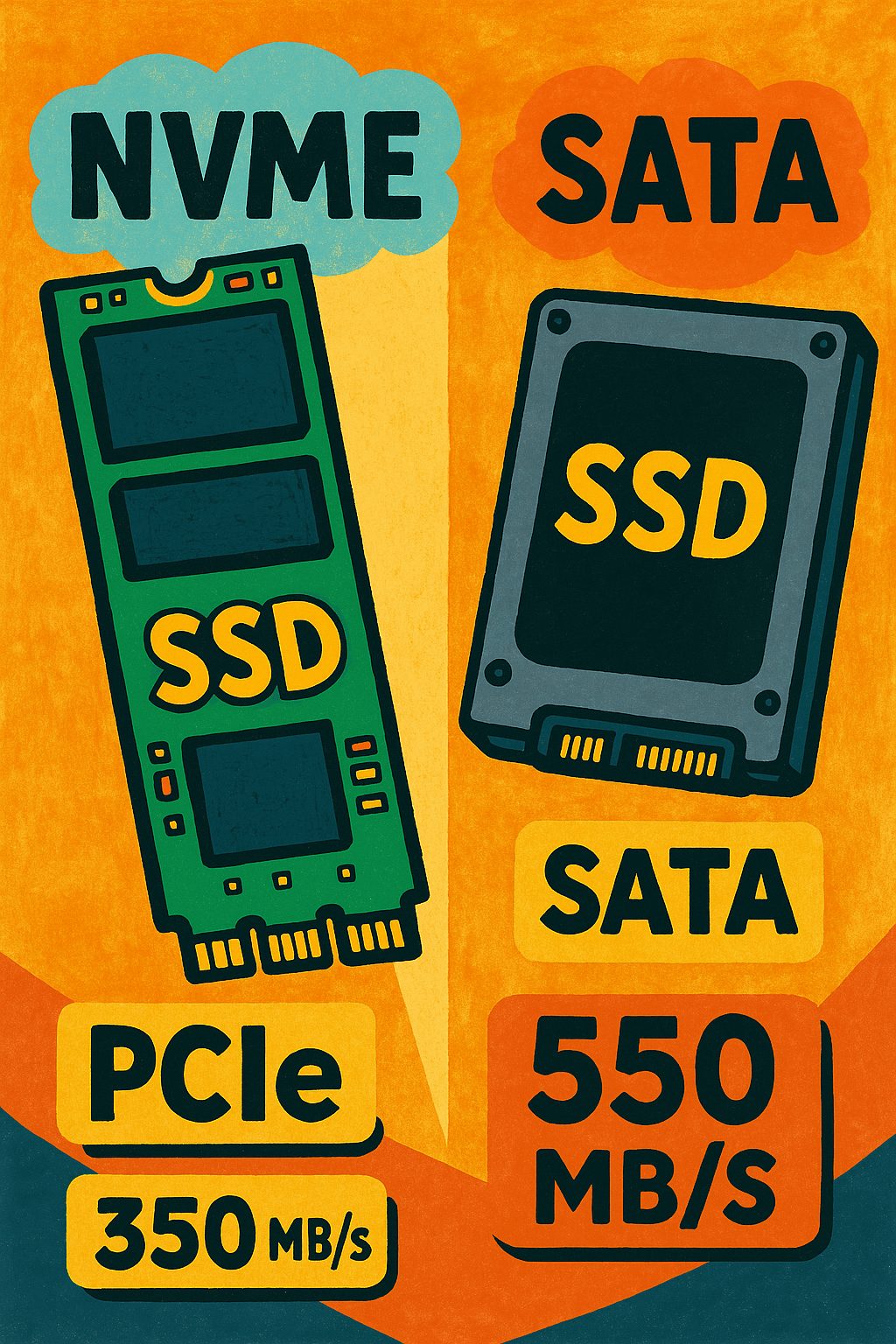
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) and SATA (Serial ATA) are two types of interfaces used to connect SSDs to a system, and while both offer significant advantages over traditional HDDs, their performance differences are critical. SATA SSDs, which use the older AHCI protocol and connect via the SATA III interface, typically max out at 550 MB/s…
-
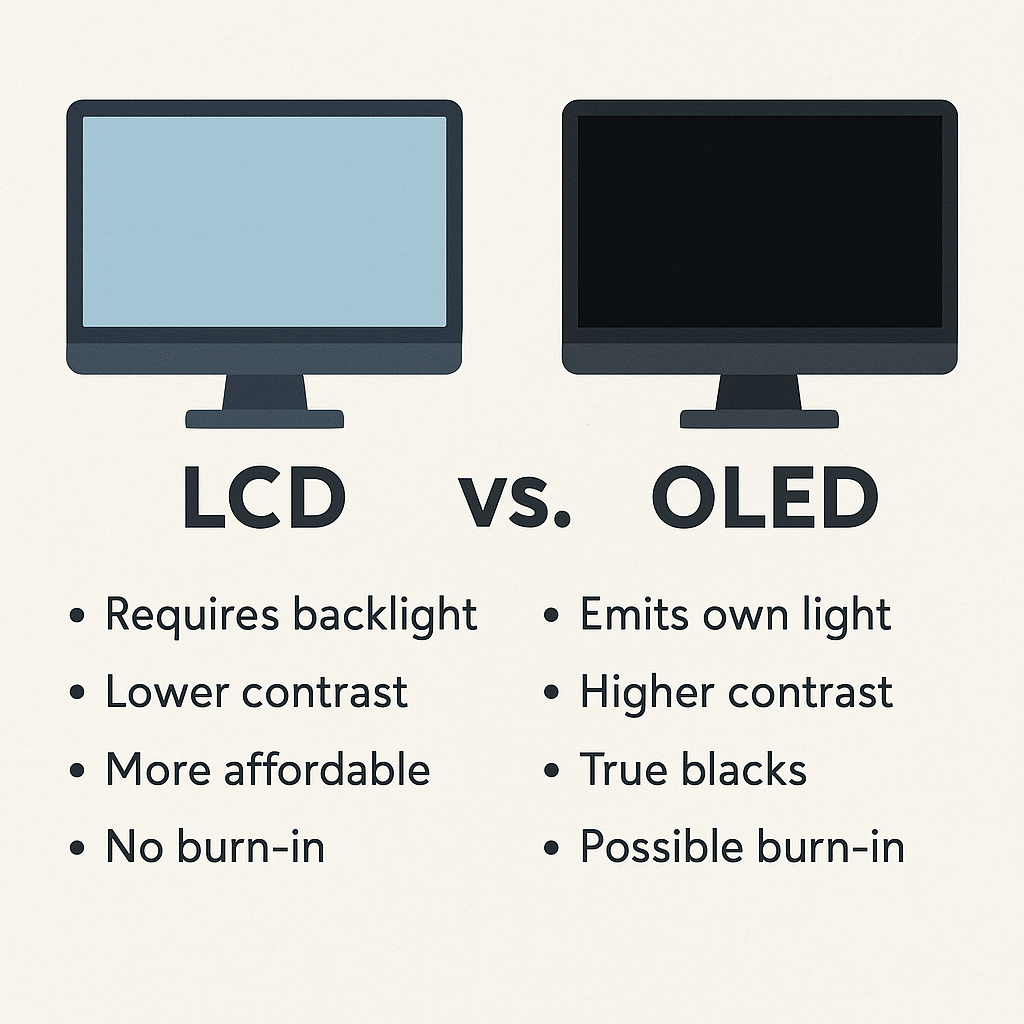
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) technologies are two widely used screen types in modern devices, each with distinct characteristics. LCDs require a backlight to illuminate pixels, which means blacks can appear grayish, but they offer consistent brightness and are generally more affordable. OLED displays, on the other hand, emit their…
-
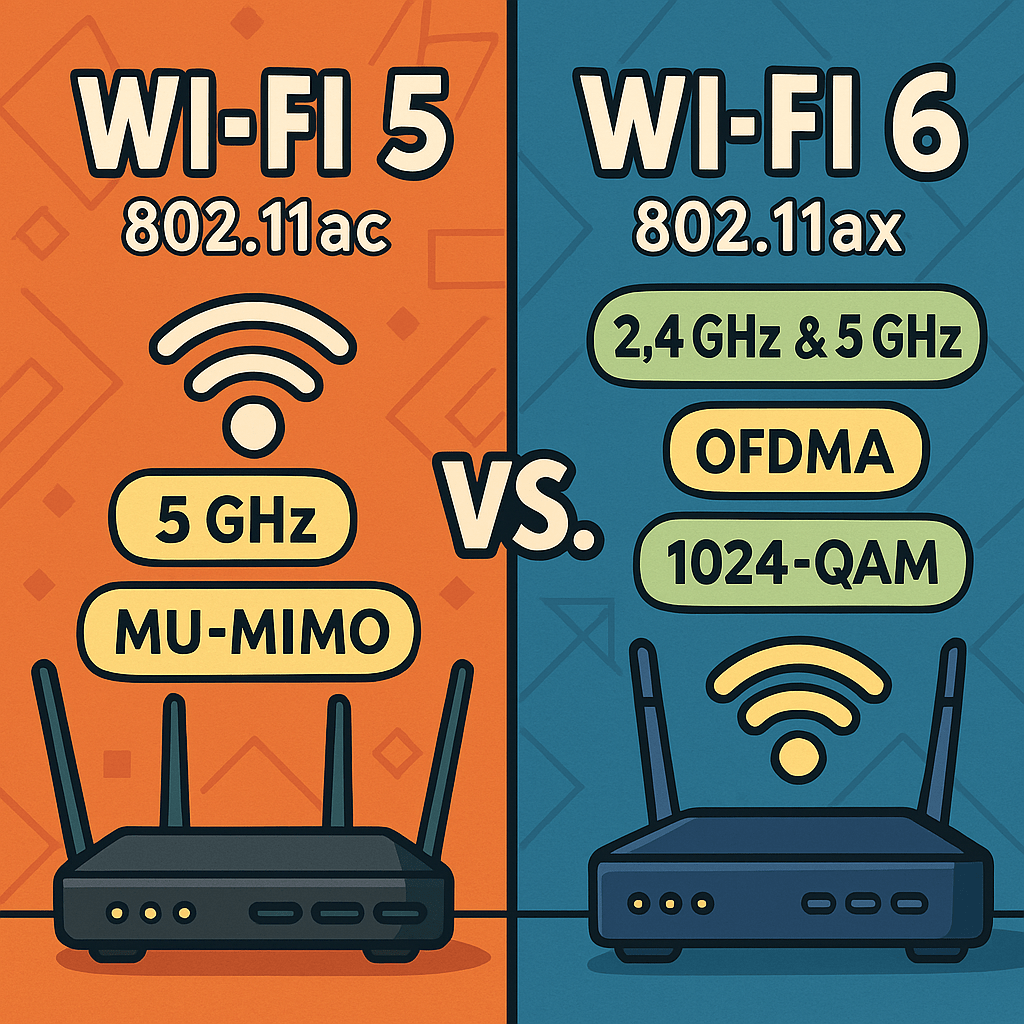
Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) and Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) are two prevalent standards that IT professionals should be familiar with. Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac): Wi-Fi 5, introduced in 2013, operates exclusively on the 5 GHz frequency band. It brought significant improvements over its predecessor, 802.11n, by offering higher data rates and enhanced performance. The standard supports channel widths…
-
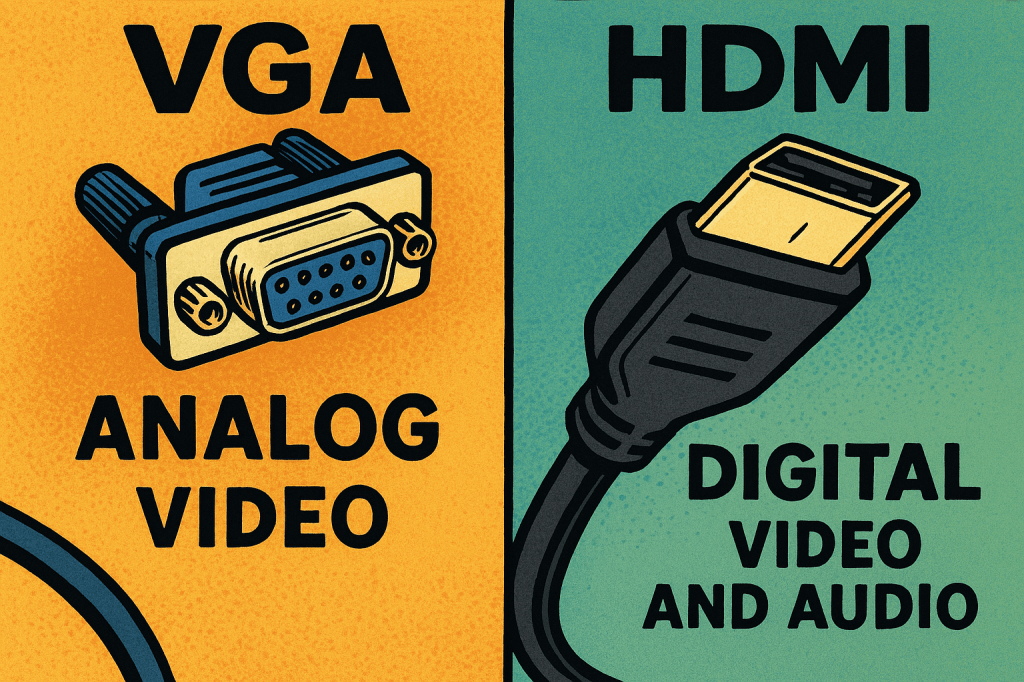
VGA (Video Graphics Array) and HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) are both used to connect displays to computers, but they differ in signal type, quality, and capabilities. VGA is an older analog interface introduced in the late 1980s that transmits video only. It uses a 15-pin D-sub connector and is prone to signal degradation over long…
-
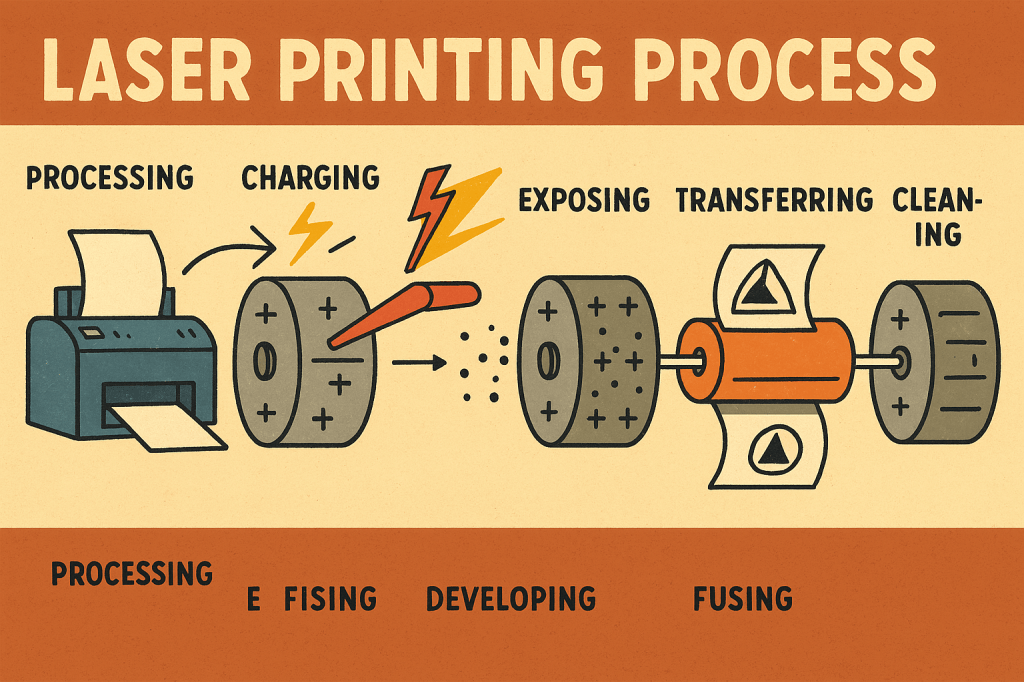
The laser printing process is a precise, multi-step method that relies on electrostatics, heat, and toner to produce high-quality prints quickly and efficiently. It begins with the processing stage, where the printer receives the data from the computer and organizes it into printable instructions. In the charging phase, a primary corona wire or roller applies…
-

Mobile device issues are diverse and may involve power problems, unresponsive screens, charging failures, or connectivity issues. The first step is verifying the basics—does the device power on, is the battery charged, and is the power adapter functioning correctly? A common issue is a dead battery or a faulty charging cable, which can easily be…
-
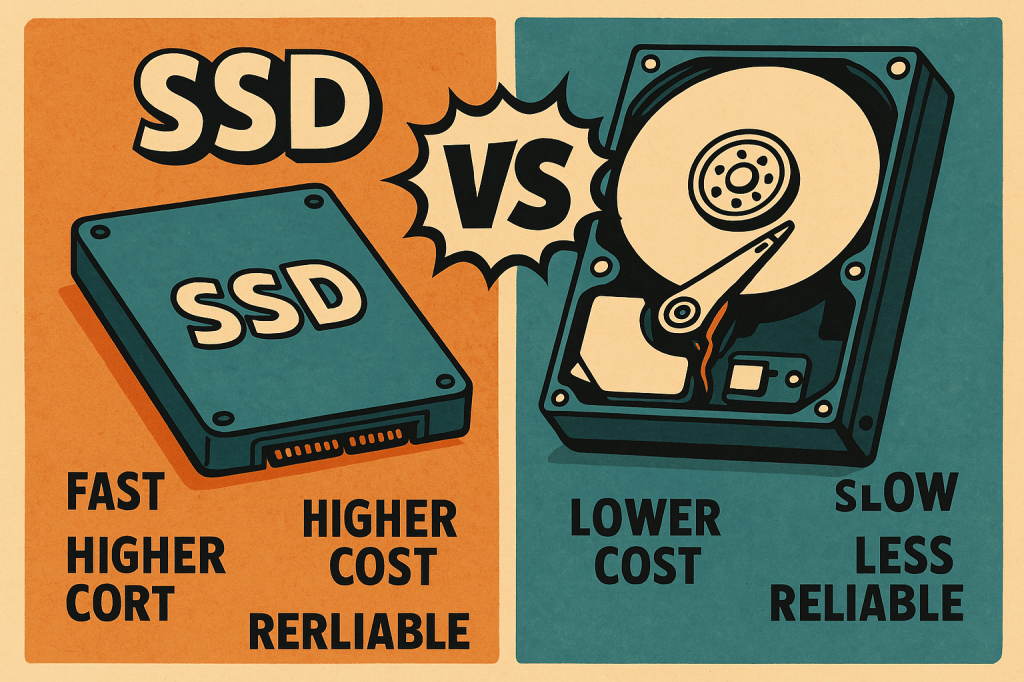
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are two primary forms of internal and external storage used in desktops, laptops, and servers, each with distinct characteristics. SSDs store data on flash memory chips, offering lightning-fast read/write speeds, lower latency, and greater durability due to the absence of moving parts. They’re ideal for operating systems,…
-
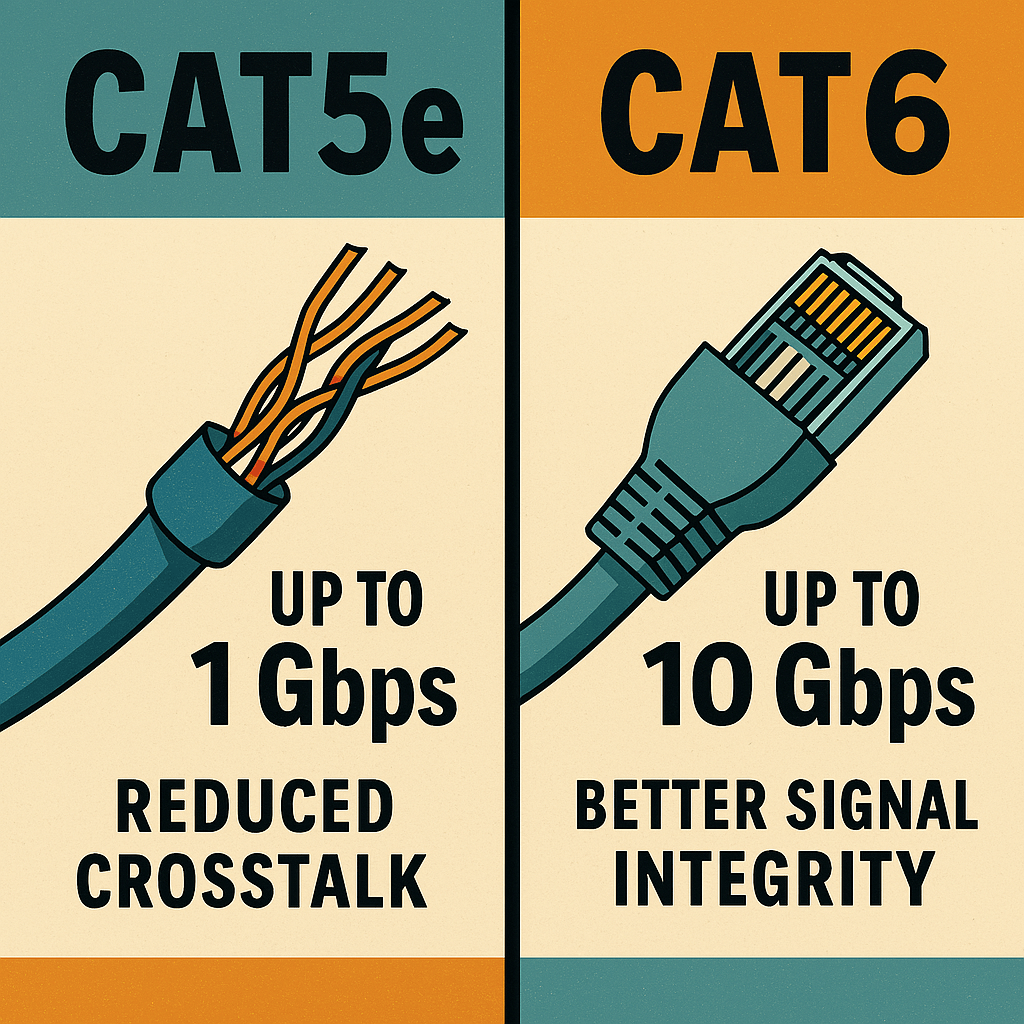
Cat5e (Category 5 Enhanced) and Cat6 (Category 6) Ethernet cables are both unshielded twisted pair (UTP) standards used for wired networking, but they differ in terms of performance, shielding, and signal integrity. Cat5e supports speeds up to 1 Gbps over distances of up to 100 meters and is commonly used in residential networks and small…
-
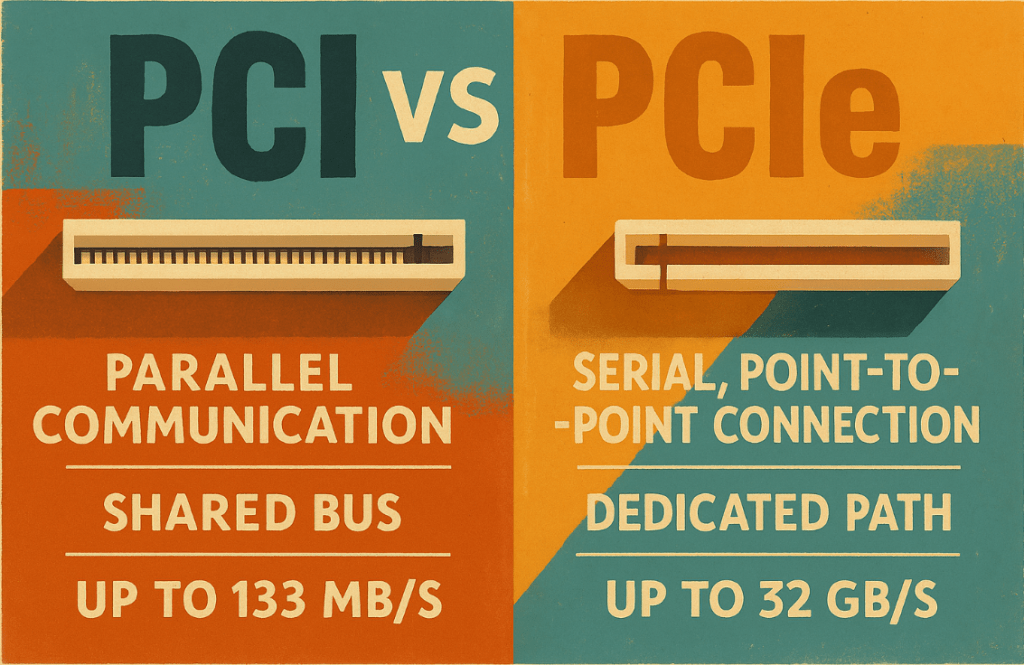
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) and PCIe (PCI Express) are both expansion bus standards used to connect internal hardware components like network cards, sound cards, or GPUs to the motherboard—but their architectures and performance differ greatly. PCI is a parallel communication interface introduced in the early 1990s, capable of transferring data at speeds up to 133…
-
Bitcoin mining business development now stretches far beyond just energy costs or hardware deployment. It includes brokering long-term power agreements with utilities, acquiring land with favorable zoning laws, and forming strategic partnerships with ASIC manufacturers, firmware teams, and AI compute providers. Leading mining firms are also building relationships with lawmakers to navigate permitting hurdles, access…
-
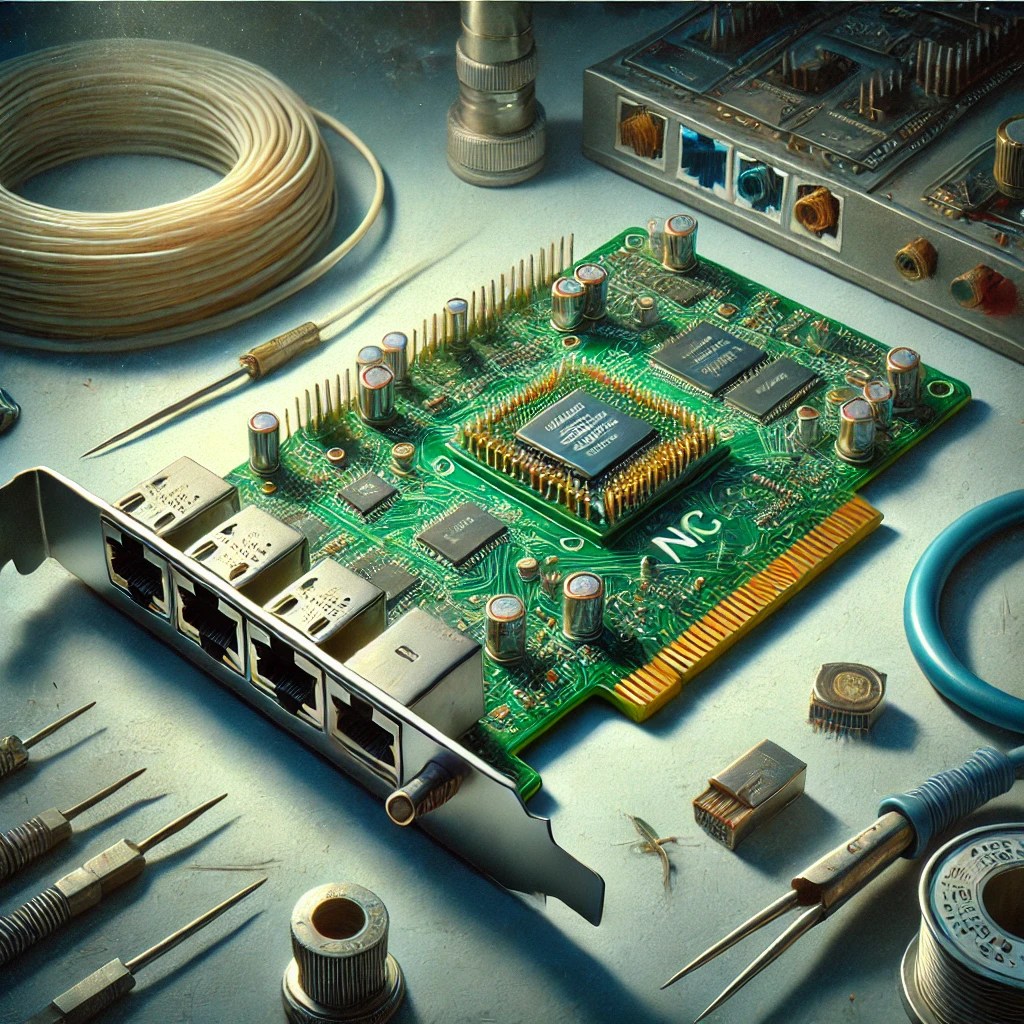
A Network Interface Card (NIC) is a hardware component, either integrated into the motherboard or installed as an expansion card, that enables devices to connect to a network. It provides a physical interface for Ethernet or wireless connections, supporting protocols like TCP/IP for data communication. NICs handle tasks such as framing, error detection, and packet…
-

Printer issues are among the most frequent hardware-related problems in both home and business environments. Symptoms include paper jams, poor print quality, printer not found errors, or no print output at all. Initial troubleshooting should start with physical inspection. Check for paper jams in the feed path, output tray, or duplex unit, and remove any…
-

Access Points (APs) are networking devices that extend the wireless coverage of a network by acting as a relay between wired and wireless devices. Unlike routers, which manage entire network traffic, access points focus specifically on connecting Wi-Fi-enabled devices to a wired network infrastructure. They are essential in environments requiring wide and reliable wireless coverage,…
-

The Windows Firewall, officially known as Windows Defender Firewall, is a built-in security feature included with modern versions of the Windows operating system. It provides both inbound and outbound traffic filtering based on customizable rules, protecting devices from unauthorized access and common network threats. By default, Windows Firewall operates with a balanced set of pre-configured…
-

Linux systems commonly rely on iptables and its modern replacement nftables as core utilities for firewall configuration. These tools allow administrators to create and manage firewall rules that filter traffic based on IP addresses, ports, protocols, and connection states. Linux firewalls operate at a very low level, offering fine-grained control of packet filtering and network…
-

Client-side virtualization is the practice of running virtual machines (VMs) directly on a user’s local device, such as a desktop or laptop, instead of relying on remote servers. This is made possible through the use of hypervisor software, such as Type 2 hypervisors (hosted), which run on top of a host operating system. Common examples…
-
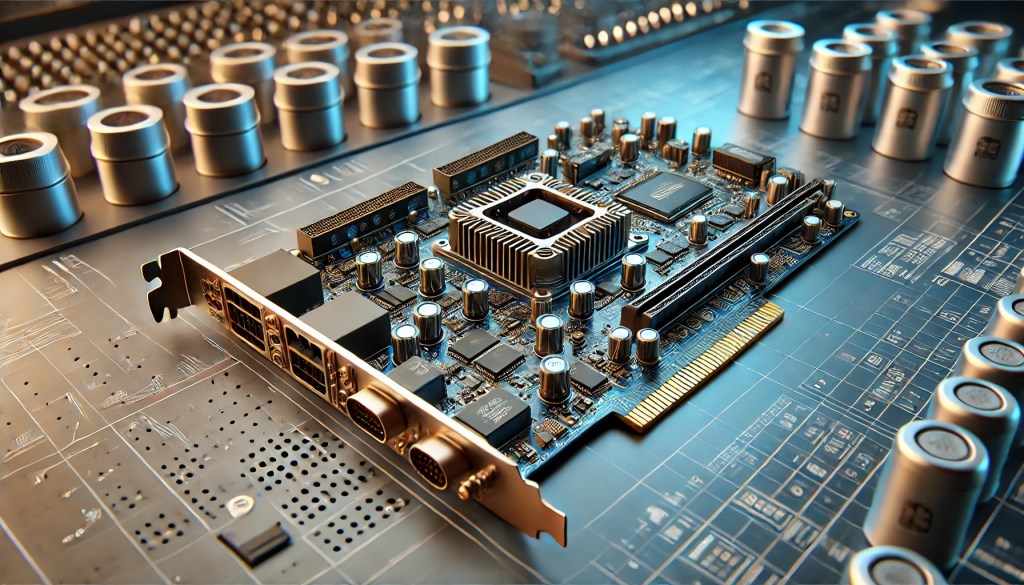
Add-on cards, also known as expansion cards, are hardware components inserted into expansion slots on a motherboard—typically PCIe slots—to extend a server’s functionality. These cards enable specialized performance beyond the system’s native capabilities, including enhanced network connectivity, accelerated processing, and advanced storage management. Common types include GPU cards for high-performance computing, network interface cards (NICs)…
-

Storage devices are critical components in computing, used to retain digital information permanently or temporarily. The two most common types of internal storage are Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs). HDDs use spinning magnetic platters and read/write heads to store data and are valued for their high storage capacities at lower cost per…
-

Understanding cable types and their respective connectors is essential in modern IT environments, where the efficiency of data transmission depends on the correct physical medium. Common cable types include twisted pair (Ethernet), fiber optic, coaxial, HDMI, and USB, each serving unique roles in networking and communication systems. Ethernet cables, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a,…
-
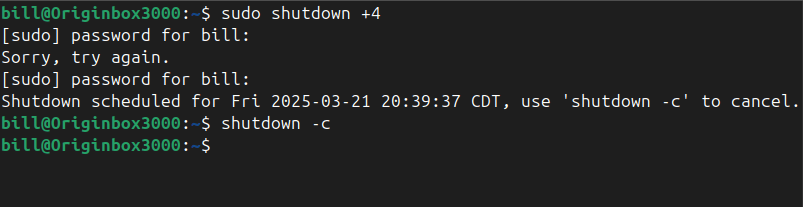
The shutdown command in Linux safely powers off or reboots a system, allowing users and administrators to schedule the shutdown after a certain time interval or at a specific time. It ensures the system terminates all processes correctly and prevents data corruption. The command accepts various parameters to specify time and behavior, with the option…
-
Networked hosts provide essential services that enable communication, resource sharing, and security within a network. One of the most fundamental services is web hosting, where web servers deliver websites using HTTP and HTTPS protocols, ensuring content is accessible globally. File hosting and sharing services, such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SMB (Server Message Block), and…
-
Network configuration involves assigning and managing how devices connect and communicate across a network. IP addressing is a fundamental concept—devices can be assigned static IP addresses (manually set and unchanging) or dynamic IP addresses (automatically assigned by a DHCP server). Static IPs are often used for devices like servers or printers to ensure consistent accessibility,…
-
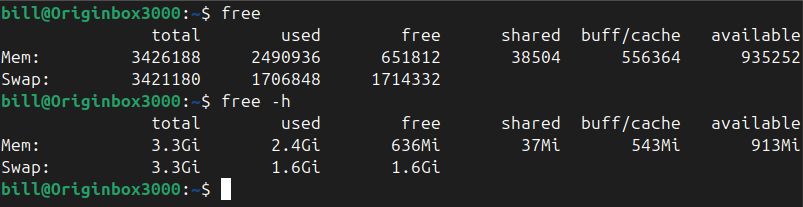
The free command in Linux is used to display comprehensive memory usage information, reporting the total, used, free, shared, buffer/cache, and available memory, including both RAM and swap space. It provides essential insights for system administrators and users to efficiently monitor and manage resources. By default, running the command free outputs memory details numerically in…
-

Mobile devices rely on a variety of accessories and ports to enhance functionality and improve user experience. Properly setting up and configuring these peripherals ensures seamless connectivity and optimized performance. Common accessories include external keyboards, wireless headphones, docking stations, and styluses, each requiring correct pairing and settings adjustments. Bluetooth-enabled accessories must be paired through the…
-
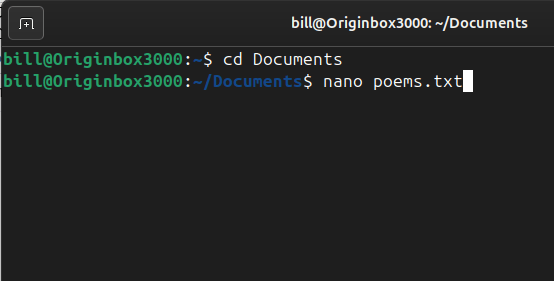
Nano is a simple and user-friendly command-line text editor for Unix-based systems, including Linux. It is designed to be easy to use, even for beginners, with a straightforward interface and on-screen shortcuts. Unlike more complex editors like Vim or Emacs, Nano does not require users to learn advanced keybindings or modes, making it an accessible…
-
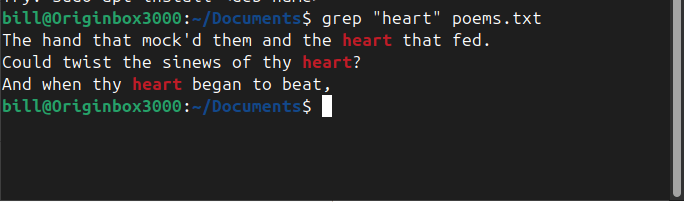
The grep command in Linux is a powerful text-search utility used to find specific patterns within files. In the screenshot, the command grep “heart” poems.txt was executed, instructing the system to search for the word “heart” inside poems.txt and display all matching lines. The output highlights instances where “heart” appears within the poem, helping the…
-

Links in Linux are essential for managing files efficiently, offering flexibility in how files are referenced and accessed. Two primary types exist: hard links and symbolic links (also called soft links). While both serve as references to files, they function differently in how they store and manage data. A hard link is a direct reference…
-

The Small Computer System Interface (SCSI), pronounced “scuzzy,” is a set of standards for connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. Introduced in the 1980s, SCSI became a prevalent interface for hard drives, scanners, printers, and other peripherals, especially in high-performance and server environments. Despite the advent of newer interfaces like USB and…
-

Installing and configuring laptop hardware involves replacing or upgrading essential components such as memory (RAM), storage drives, and batteries. When upgrading RAM, the laptop must be powered off, and the correct type and size of memory modules must be installed in the designated slots. Storage upgrades often involve swapping out traditional hard disk drives (HDDs)…
-
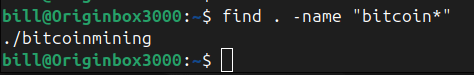
The find command in Linux is a powerful and versatile tool designed to search through files and directories based on specific criteria. It helps users efficiently locate files within a file system, filtering searches by name, file type, modification date, size, or even permissions. A typical syntax for using find includes specifying a starting directory,…
-

Data centers, the backbone of our digital world, employ various cooling methods to maintain optimal operating temperatures for their equipment. One such method is immersion cooling, where IT components are submerged in thermally conductive, dielectric liquids. technique allows for efficient heat dissipation, as the liquid directly contacts heat-generating components, reducing the need for traditional air…
-

Molex connectors are standardized electrical connectors widely used in power and signal applications across various industries, including computing, consumer electronics, and automotive systems. They are known for their durability, ease of use, and reliable connectivity, often featuring plastic housings with metal contacts that enable secure electrical connections. These connectors originated from Molex Incorporated, a company…
-

The apropos command searches manual page names and descriptions for a given keyword, helping users quickly discover relevant commands for a task. The apropos command helps Linux users find commands related to a keyword quickly. For example, typing apropos copy lists commands involving copying files or directories. Similarly, apropos network shows commands associated with network…
-
File System Hierarchy Standard (FHS): The File System Hierarchy Standard defines a consistent directory structure for Linux systems, specifying locations for system files, user files, and application data. FHS ensures predictability and uniformity across distributions, facilitating easier management and maintenance. Standard directories include /etc for configuration files, /var for variable data, /bin for essential binaries,…
-
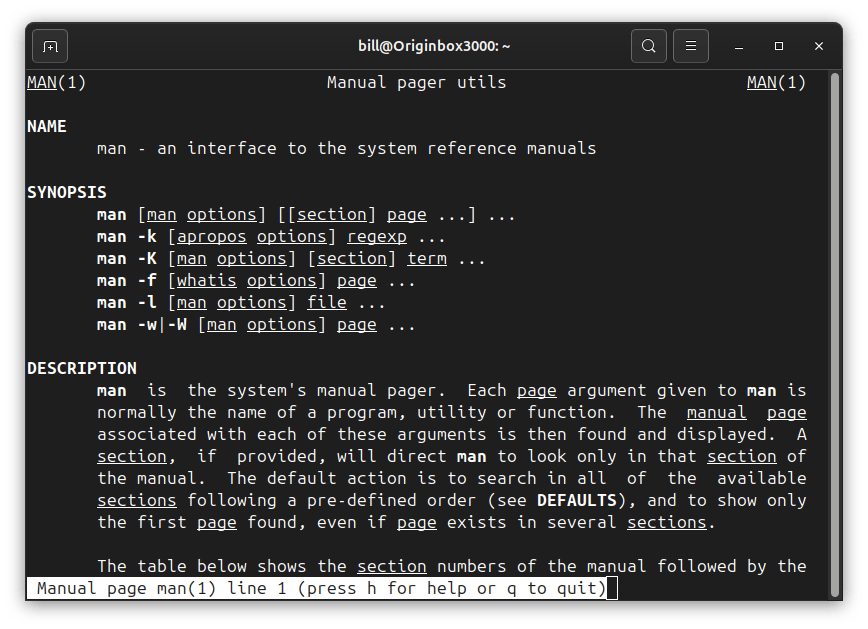
The man command, short for ‘manual’, is an essential tool in Linux, offering detailed documentation on virtually every command and program. By typing man followed by a specific command name, users gain immediate access to comprehensive manuals covering syntax, usage options, and practical examples. Ideal for beginners and seasoned professionals alike, the man command fosters…
-

Definition and FunctionalitySerial communication refers to the process of transmitting data one bit at a time over a communication channel or computer bus. Unlike parallel communication, which sends multiple bits simultaneously, serial communication reduces signal interference and supports long-distance data transfer with fewer wires. It is widely used in telecommunications, industrial automation, and computer networking…
-

The Power-On Self-Test (POST) is a fundamental diagnostic process performed by computers immediately after they are powered on. This procedure verifies the functionality and integrity of essential hardware components before the operating system loads, ensuring that the system operates correctly. During POST, the system’s firmware—commonly the BIOS or UEFI—conducts a series of checks on…
-

Overclocking involves increasing a computer component’s clock rate beyond the manufacturer’s specifications to boost performance. This practice is commonly applied to processors and graphics cards, allowing them to execute more operations per second. While overclocking can lead to significant performance gains, it also raises power consumption and heat output, necessitating improved cooling solutions to maintain…
-

Client-side virtualization enables users to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single physical machine, enhancing flexibility and resource utilization. This technology allows each virtual machine (VM) to operate independently, with its own CPU, memory, and storage resources. A key component in client-side virtualization is the hypervisor, also known as the Virtual Machine Manager (VMM).…
-

The central processing unit (CPU) serves as the brain of a computer, executing instructions and processing data essential for system operations. A CPU’s architecture encompasses various components and functionalities that determine its performance and capabilities. Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) The ISA defines the set of instructions a CPU can execute, including operations like arithmetic, data…







