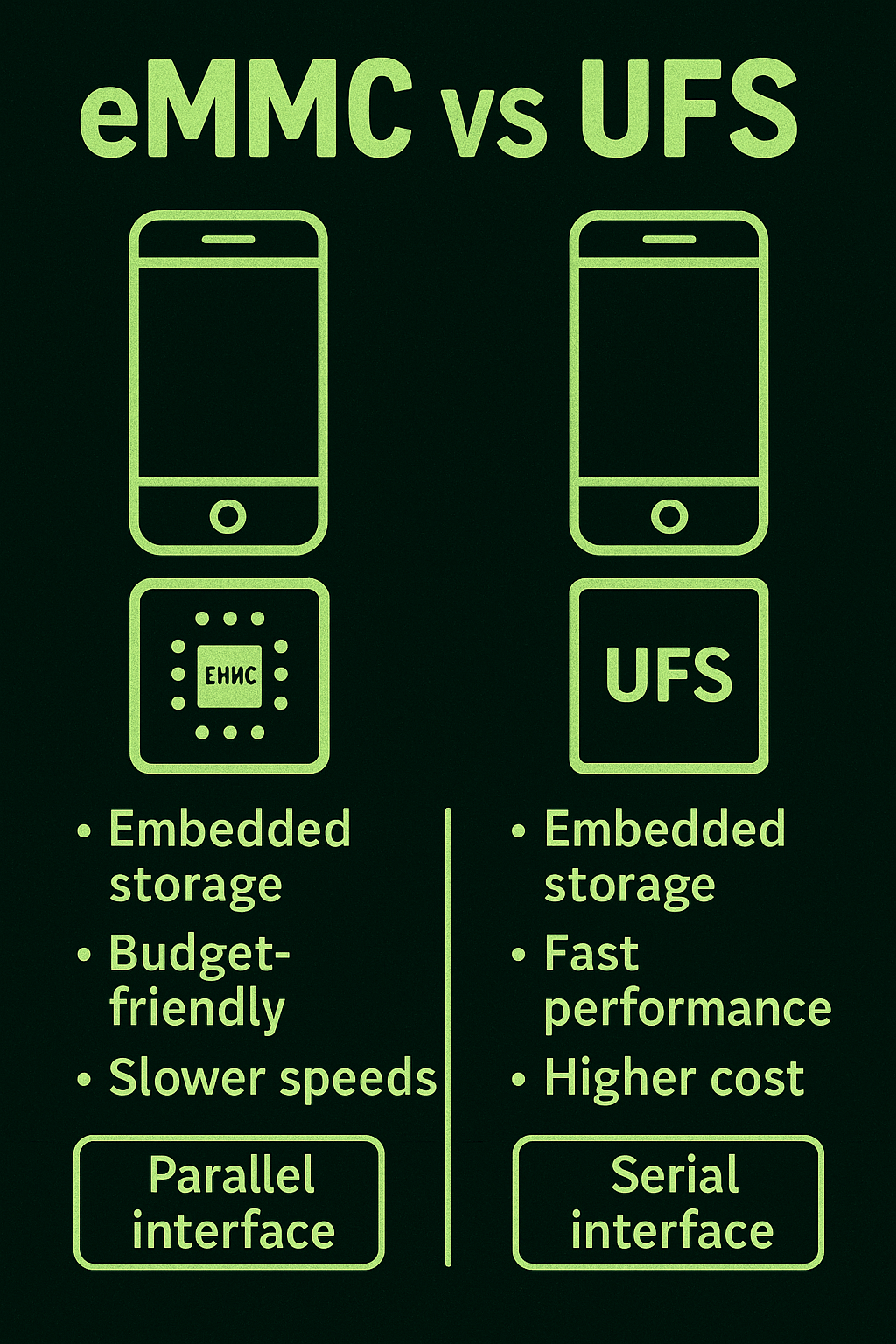
Information Technology
-
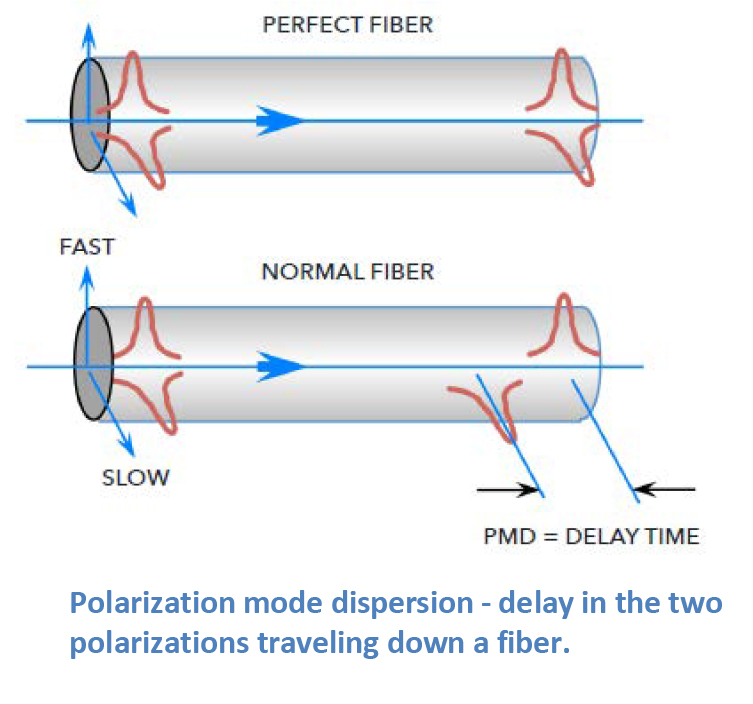
Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) refers to the distortion of optical signals caused by slight differences in the propagation speed of light’s polarization modes as they travel through fiber. In an ideal optical fiber, light of all polarization states should move uniformly. However, imperfections, asymmetries, and environmental stress within the fiber cause birefringence—splitting the light into…
-
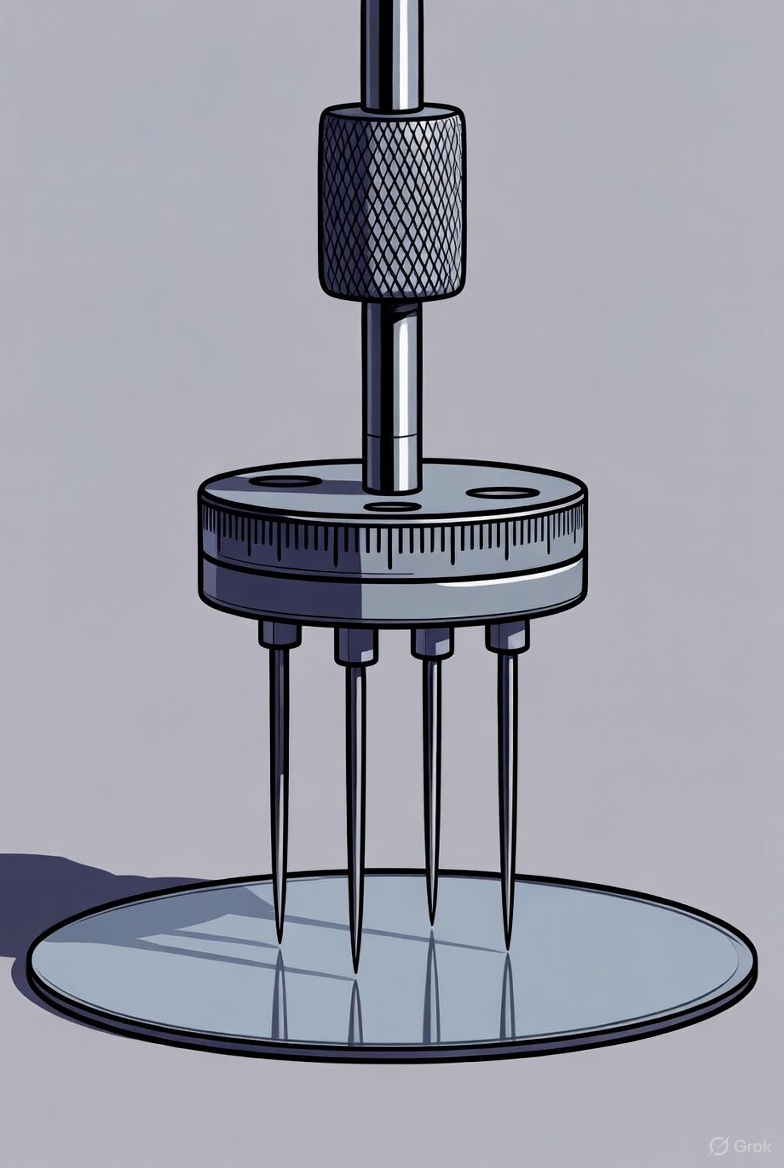
The Four-Point Probe (4PP) method is a standard, non-destructive technique used in semiconductor manufacturing and research to accurately measure the sheet resistance and subsequent resistivity of thin films, wafers, and other semiconductor materials. This technique uses a linear array of four closely spaced, collinear probes typically made of tungsten or beryllium copper, each mounted on…
-
Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) occurs when light traveling through a single-mode optical fiber splits into two orthogonal polarization components that propagate at slightly different velocities. This phenomenon is caused by random imperfections, asymmetries, and external stresses in the fiber, such as core ellipticity, bending, or temperature fluctuations. In an ideal fiber, both polarization modes would…
-

Polishing fiber is the final stage in preparing an optical fiber connector, ensuring a smooth, scratch-free end face that allows for minimal signal loss and optimal light transmission. The procedure begins after the fiber has been cleaved and secured in a connector ferrule using epoxy or a mechanical fit. Once the adhesive cures, the protruding…
-

WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a method of combining multiple optical signals onto one fiber strand by assigning each signal a unique wavelength. These wavelengths act like separate channels, allowing parallel transmission of data without interference. This dramatically increases the capacity of fiber networks without laying additional fiber. Each signal is generated by a laser…
-
Fire safety in cable installations is a critical aspect of both data center and field operations, ensuring the protection of personnel, equipment, and infrastructure. The first step toward minimizing fire risk begins with selecting the correct cable type for the environment. Plenum-rated cables, labeled CMP, are designed for air-handling spaces such as ceiling voids or…
-

MoCA, or Multimedia over Coax Alliance, is a technology that allows for networking over existing coaxial cable systems in homes. It enables the use of coaxial cables to create a high-speed Ethernet connection, providing a reliable and efficient way to distribute internet access throughout a home without the need for new wiring. MoCA networks can…
-
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a networking standard that delivers DC electrical power along with data signals through standard twisted-pair Ethernet cabling (typically Cat5e, Cat6, or higher). This innovation eliminates the need for separate power cords or outlets near devices, simplifying installation and reducing infrastructure costs. PoE works by injecting power into the Ethernet cable…
-
-

Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT) is a type of signal interference that occurs when a transmitted signal on one wire pair induces unwanted noise onto an adjacent pair at the same end of the cable where the signal originated. NEXT is most commonly encountered in twisted-pair cabling systems, such as those used in Ethernet networks. It happens…
-
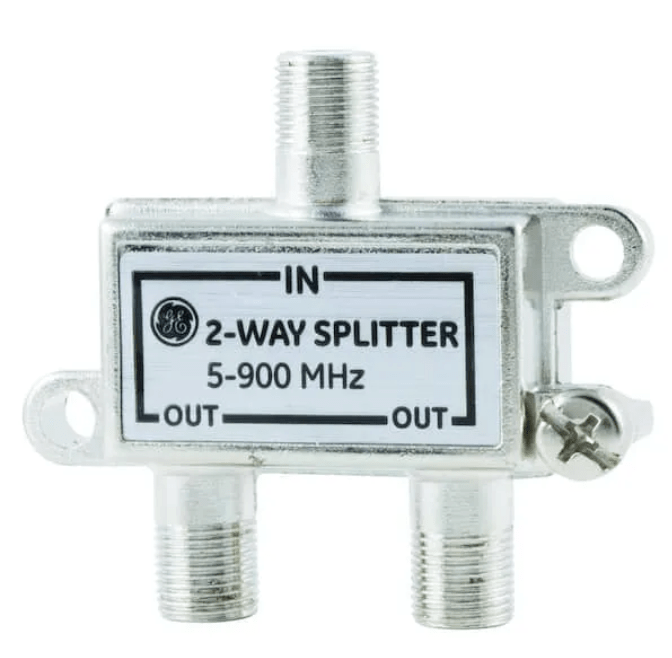
A splitter in terms of coaxial cable is a passive device that divides a single incoming radio frequency signal into multiple outputs, allowing several devices such as televisions, modems, or receivers to share the same signal source. It maintains a standard impedance of 75 ohms to prevent signal reflection and distortion, ensuring stable performance across…
-
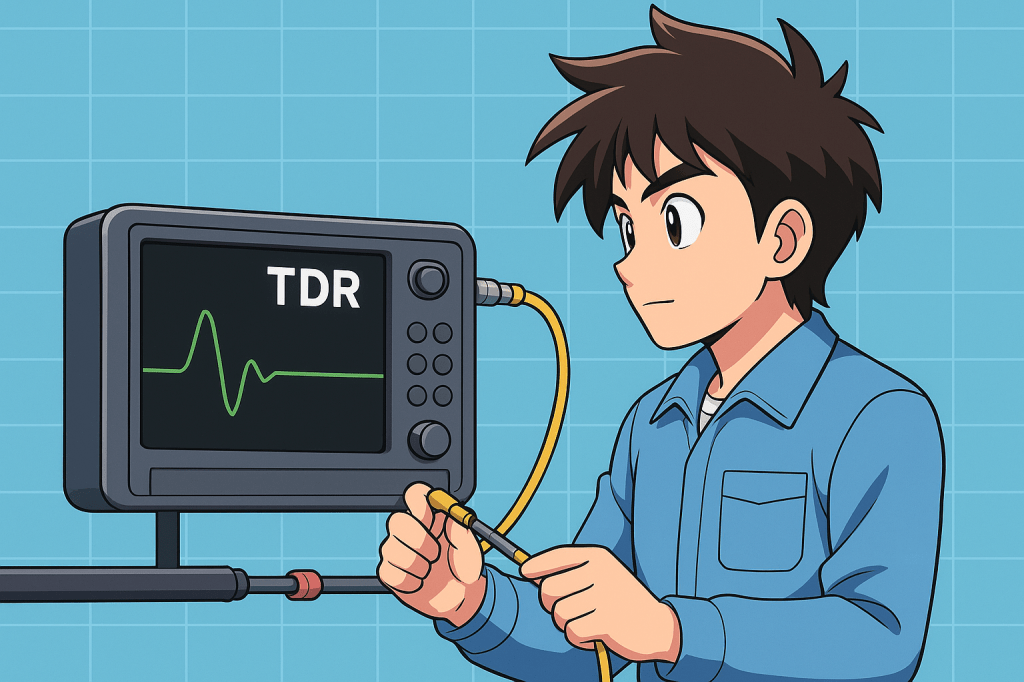
A Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR) is a diagnostic instrument used to detect faults, breaks, and impedance mismatches in coaxial cables by sending a signal pulse down the line and analyzing the reflections that return. When the pulse encounters a change in impedance—such as a splice, open, short, or damaged section—it reflects back to the TDR,…
-
A coaxial cable is a specialized electrical cable designed to carry high-frequency signals with minimal interference. Its name comes from its concentric structure—each layer shares the same axis, which helps preserve signal integrity. Coaxial cables are widely used in applications like cable television, internet service, radio transmission, and closed-circuit video systems. At the center of…
-

In telecom infrastructure, MXC is a synonym for MDF—both refer to the Main Cross-Connect, the central point where external carrier circuits interface with a building’s internal network. The Main Cross-Connect (MXC), also known as the Main Distribution Frame (MDF), is the primary physical interconnection point in a facility’s telecommunications system. It serves as the demarcation…
-

A patch cord is a short, pre-terminated cable with connectors on both ends, used to connect network devices for signal or data transmission. Patch cords are essential components in structured cabling systems, enabling flexible and efficient interconnections between equipment such as switches, routers, servers, and patch panels. They are typically used in environments like data…
-

The Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) was originally formed in 1924 as the Radio Manufacturers Association. It evolved into a major standards body for electronic components and systems in the United States. EIA was responsible for developing specifications that ensured interoperability and quality across manufacturers, particularly in consumer electronics and telecommunications. In 1988, EIA’s telecommunications division…
-

A premise cable technician specializes in installing and maintaining cabling systems within buildings or campuses. Their work typically involves running Ethernet, coaxial, and fiber optic cables through walls, ceilings, and conduits to support voice, data, and video services. These technicians are responsible for terminating cables at patch panels and jacks, testing and certifying cable runs…
-

A Visual Fault Locator (VFL) is a handheld optical testing device used in fiber optic networks to identify faults, breaks, or discontinuities in optical fibers. It emits a highly visible red laser light (usually around 650 nm) into the fiber, which allows technicians to visually trace the fiber path. Any break, bend, or poor connection…
-
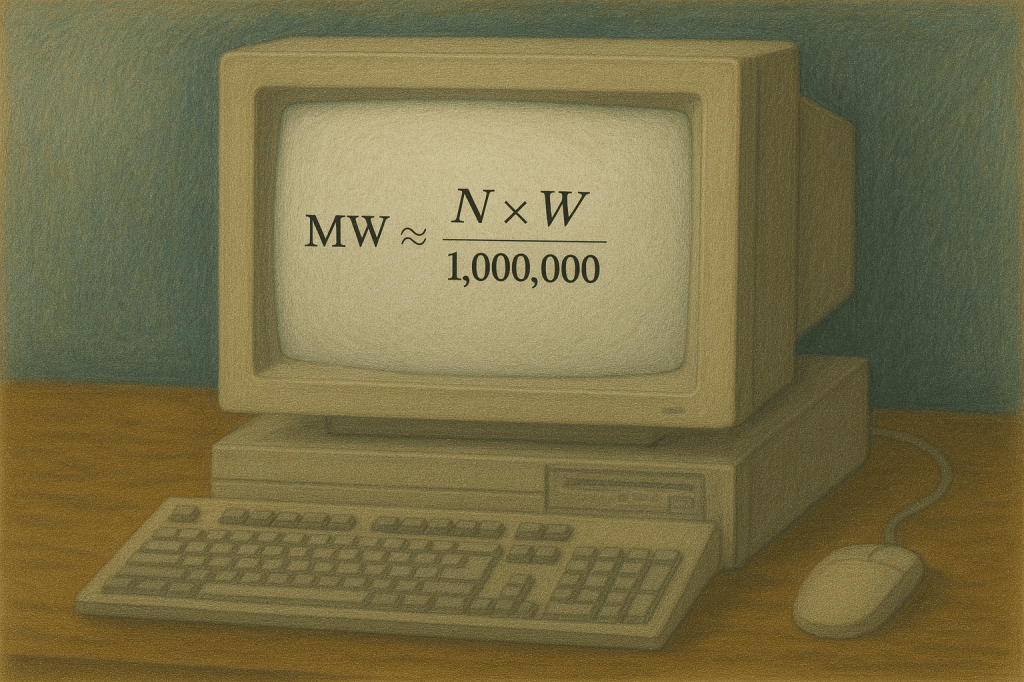
The Bitcoin Mining Air Coolant Energy Operation Equation offers a simple way for bitcoin mining engineers to translate machine count into megawatts in a language that utility operators and engineers understand. The core idea is that modern air cooled ASIC miners usually draw around 3,000 to 3,500 watts per machine, so a fleet’s IT load…
-

Direct burial in fiber optics refers to the installation of specially designed fiber optic cables directly into the ground without the need for protective conduits or ducts. These cables are engineered to withstand harsh underground conditions for long-term, maintenance-free operation. Direct burial fiber optic cables are constructed with multiple protective layers to endure soil pressure,…
-

A coupler functions by redistributing light from one or more input fibers into one or more output fibers. It does this without requiring external power, relying instead on physical principles like evanescent field coupling or fused biconical taper (FBT) technology. In FBT couplers, two or more fibers are precisely fused and tapered together, allowing light…
-

CoreThe core is the central strand of a fiber optic cable, composed of ultra-pure glass or plastic. It serves as the transmission medium for light signals. The diameter of the core depends on the fiber type—typically 9 microns for single-mode fibers and 50 or 62.5 microns for multimode. Its refractive index is slightly higher than…
-
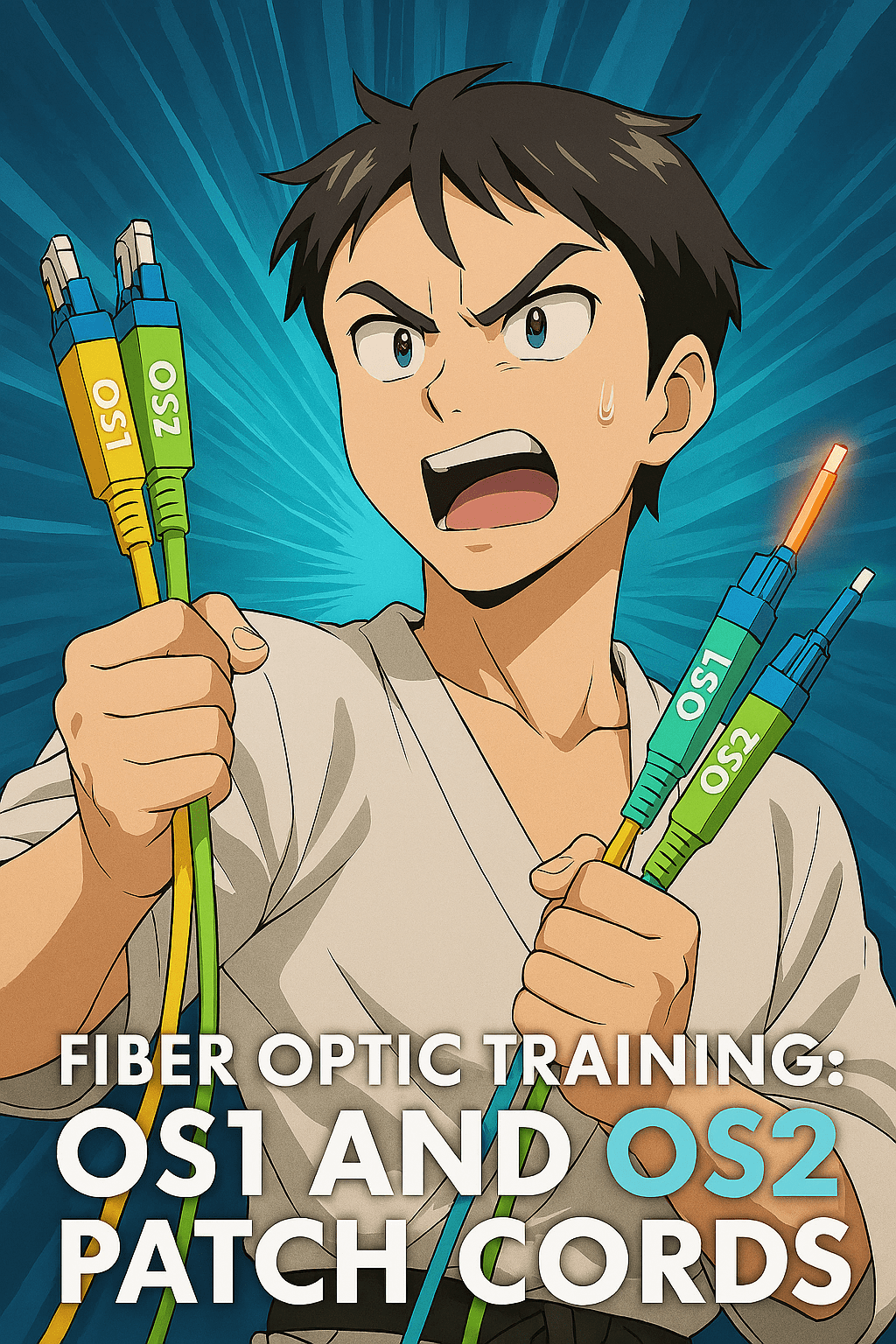
OS1 and OS2 are classifications of singlemode fiber optic cable defined by their construction and performance characteristics. OS stands for “Optical Singlemode.” OS1 is typically used for indoor applications and features tight-buffered construction, supporting up to 10 km at 1310 nm and 40 km at 1550 nm. OS2 is optimized for outdoor and long-haul deployments,…
-
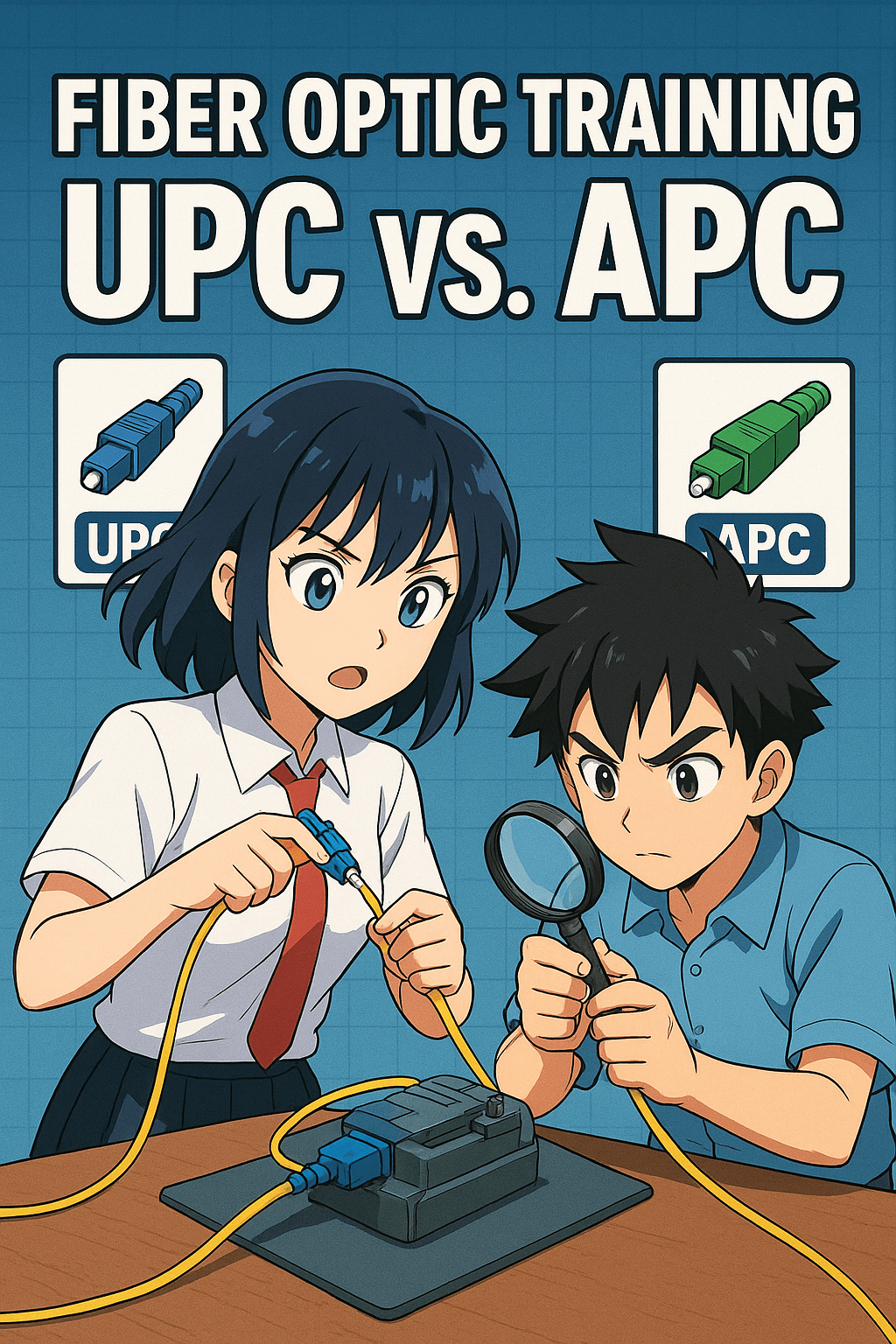
UPC and APC refer to two types of fiber optic connector polish styles: Ultra Physical Contact (UPC) and Angled Physical Contact (APC). UPC connectors have a flat, slightly domed end-face that provides low insertion loss and are commonly used in digital systems like Ethernet and CATV. APC connectors feature an 8-degree angled end-face that minimizes…
-
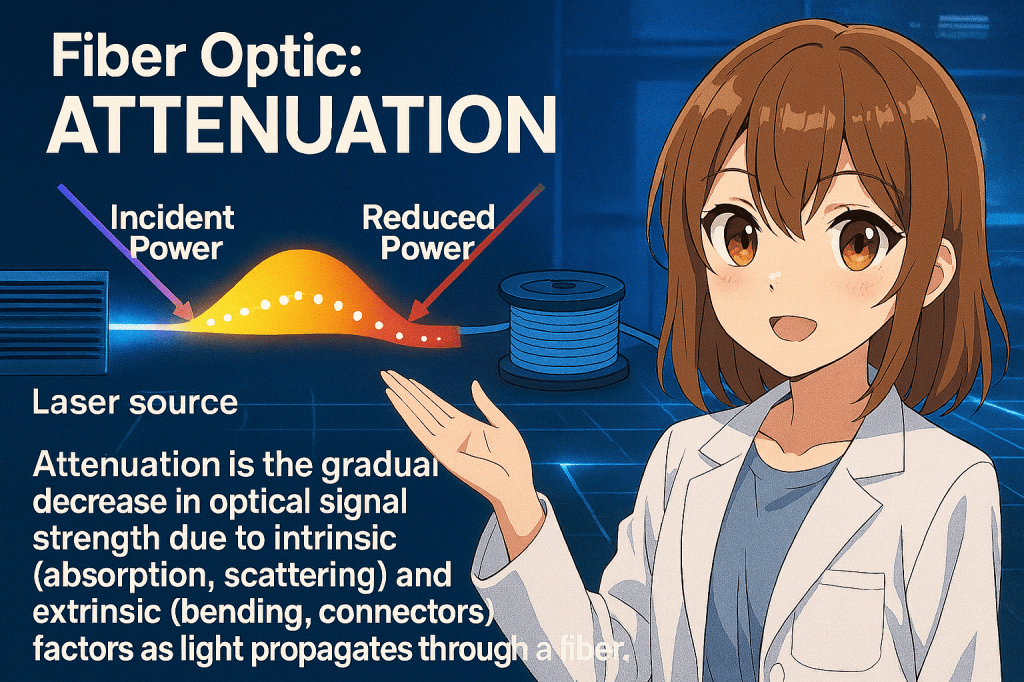
Attenuation in fiber optics refers to the gradual weakening of an optical signal as it travels through the fiber. This loss happens because some of the light energy is absorbed by the glass material or scattered due to microscopic irregularities. It’s measured in decibels per kilometer (dB/km), and the lower the number, the better the…
-

Proper network termination matters. Every ethernet cable you build connects people, ideas, and organizations, enabling communication that strengthens relationships and drives opportunity. By following standards like T568B, we can create networks that are reliable and impactful. This 8-minute instructional video demonstrates those techniques, showing how network termination helps connect lives and build communities. T568B Ethernet…
-

Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a fundamental component of IPv4 networking that enables devices within a local area network (LAN) to discover the physical hardware address (MAC address) associated with a given IP address. Operating at the intersection of the OSI model’s Data Link (Layer 2) and Network (Layer 3) layers, ARP facilitates the translation…
-
Secure Shell, commonly known as SSH, is a cryptographic network protocol used to establish secure and encrypted communication between two systems over an unsecured network. It allows users to remotely access and control another computer, typically through a command-line interface. SSH ensures that all data, including login credentials and command outputs, are encrypted to prevent…
-

The /sbin directory in Linux holds system administration commands, which are mostly used by the root user or users with administrative privileges. Commands in /sbin help control and manage core parts of the system such as filesystems, networking, and startup processes. Tools like fsck (file system check), ifconfig (network configuration), and reboot are typically located…
-

Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated chip embedded on a computer’s motherboard, designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. It stores sensitive information such as encryption keys, digital certificates, and passwords in a tamper-resistant environment. TPM is commonly used for: The current standard is TPM 2.0, which is required by modern operating systems…
-

What Is an SSD? A Solid-State Drive (SSD) uses flash memory chips to store data. There are no moving parts, making it faster, quieter, and more durable than traditional hard drives. SSDs have extremely fast read/write speeds, especially in NVMe (PCIe) form, which are ideal for boot drives, gaming systems, and business apps. SSDs come…
-
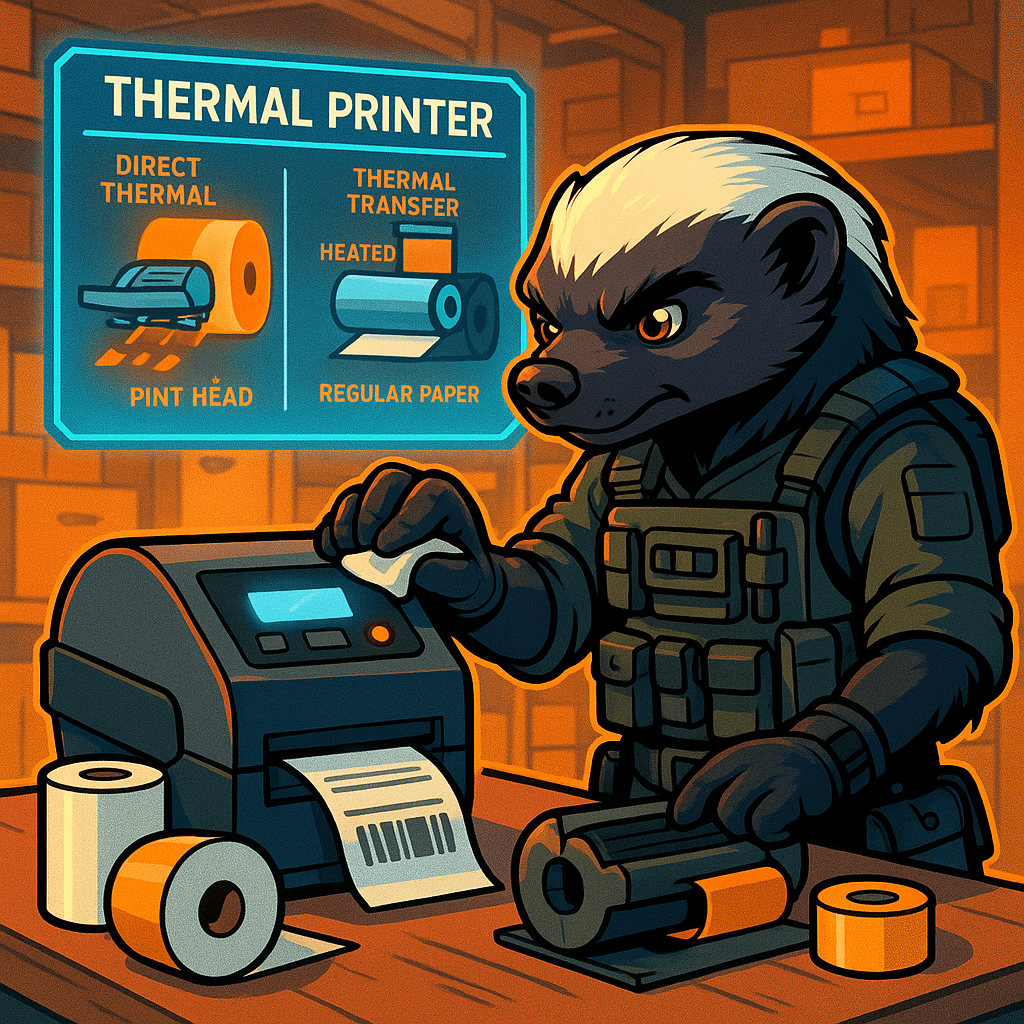

A thermal printer uses heat to transfer images onto paper. It comes in two types: Consumables and Maintenance Direct thermal printers require only thermal paper, while thermal transfer printers need both ribbon and label stock.Maintenance includes: Technicians must also check for signs of printhead wear, incorrect temperatures, or paper with poor heat response when troubleshooting…
-

Two of the most recognized and widely used printer languages in the industry are PCL (Printer Command Language) and PostScript. Each one comes with unique advantages and is suited for different types of environments and workloads. PCL, developed by Hewlett-Packard, is a standard language found in many office printers. It’s built for speed and efficiency—great…
-

Every desktop computer relies on a Power Supply Unit (PSU) to convert wall electricity into usable voltage levels that safely power internal components. The PSU takes in AC (Alternating Current) and outputs DC (Direct Current) in multiple voltages—typically +12V, +5V, and +3.3V—distributed to the motherboard, CPU, storage devices, and GPU. Without proper power regulation, even…
-

Secure Shell, commonly known as SSH, is a cryptographic network protocol used to establish secure and encrypted communication between two systems over an unsecured network. It allows users to remotely access and control another computer, typically through a command-line interface. SSH ensures that all data, including login credentials and command outputs, are encrypted to prevent…
-

The taskkill command is a powerful Windows OS CLI tool that allows users to forcefully terminate running processes directly from the terminal. Unlike the Task Manager’s graphical interface, taskkill gives users precise control over which processes to end, either by using the process name (also called the image name) or its unique process ID (PID).…
-

Modern systems now rely heavily on Solid-State Drives (SSDs) for fast data access, but not all SSDs are built the same. Two common types—NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) and SATA (Serial ATA)—differ dramatically in speed, interface, and performance. SATA SSDs use the older SATA interface, originally designed for hard drives. They’re limited to a theoretical maximum…
-
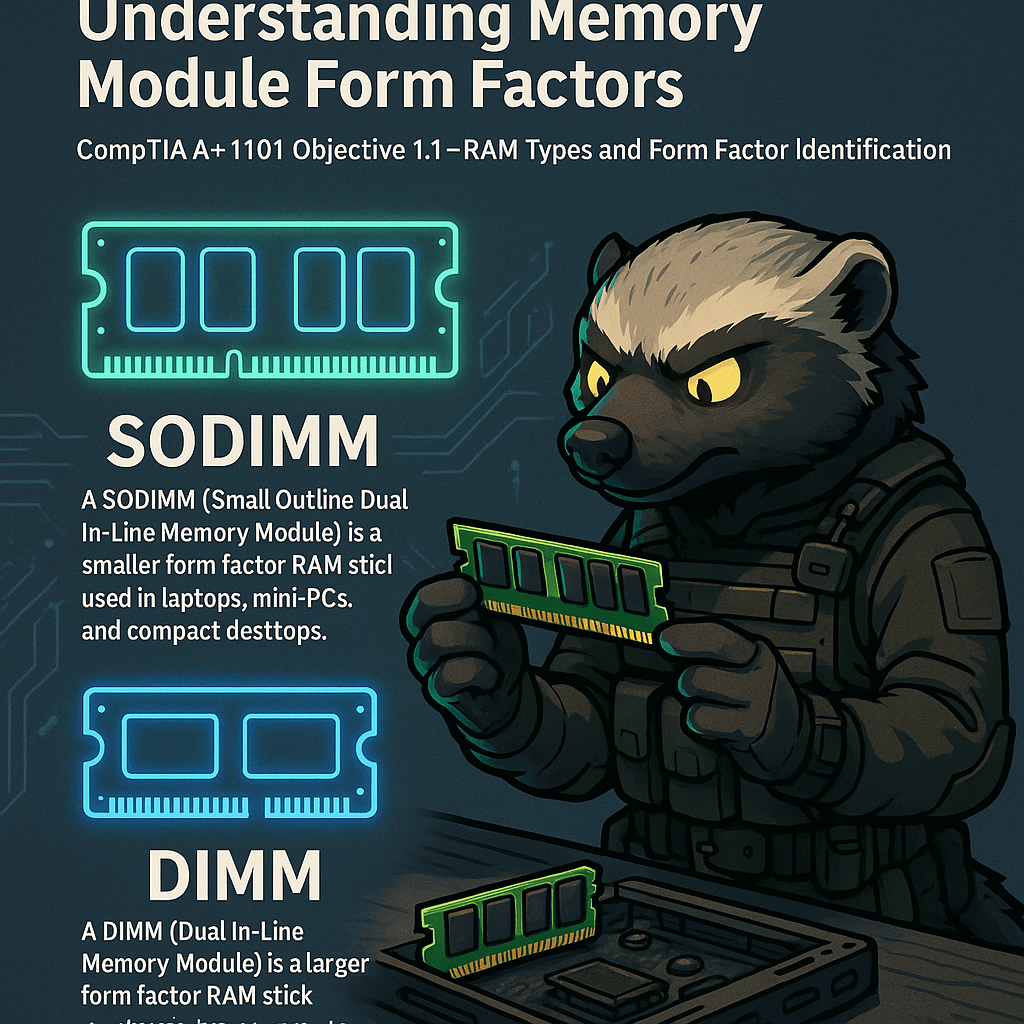
Memory modules come in different physical sizes depending on the device they’re intended for. DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module) is the standard memory format used in desktop computers, while SODIMM (Small Outline DIMM) is the compact version used in laptops, mini-PCs, and some all-in-one systems. Both types serve the same function—providing volatile memory that supports…
-

Liquid cooling is an advanced thermal management solution used in desktops to dissipate heat more effectively than traditional air cooling. It involves circulating a coolant—usually distilled water or a specialized liquid—through tubes connected to a water block mounted on the CPU or GPU. Heat is transferred from the component to the coolant, then pushed through…
-
OLED stands for Organic Light-Emitting Diode. Unlike traditional LCDs, OLEDs emit light directly from each pixel without requiring a separate backlight. This allows for ultra-thin screens, true blacks, and higher contrast ratios. Each pixel in an OLED screen is made from organic compounds that emit light when current passes through them. This direct emission is…
-

ATA, or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, is a computer bus interface used to connect hard drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and optical drives to the motherboard. It replaced older parallel ATA (PATA) standards by using a 7-pin data cable and a 15-pin power connector, simplifying cabling and improving airflow. SATA supports hot-swapping (with the correct…
-

Impact printers, such as dot matrix printers, use a physical print head that strikes an ink-soaked ribbon against the paper—similar to a typewriter. These devices are primarily used in environments where multi-part forms, carbon copies, or durability in dusty conditions are required, such as warehouses, industrial settings, and point-of-sale systems. A key feature of impact…
-
An IP address is a unique identifier assigned to devices on a network to enable communication. There are two main versions: IPv4, a 32-bit address format (e.g., 192.168.1.1), and IPv6, a 128-bit format (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334), created to handle the growing number of connected devices. IPv4 supports around 4.3 billion addresses and uses dot-decimal notation. It’s…
-
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System. It is firmware stored on a chip on the motherboard that initializes hardware components and loads the operating system. BIOS interfaces are text-based, and users access them by pressing keys like DEL, F2, or ESC during system startup. BIOS uses Legacy Boot, has limited drive support (up to 2.2…
-
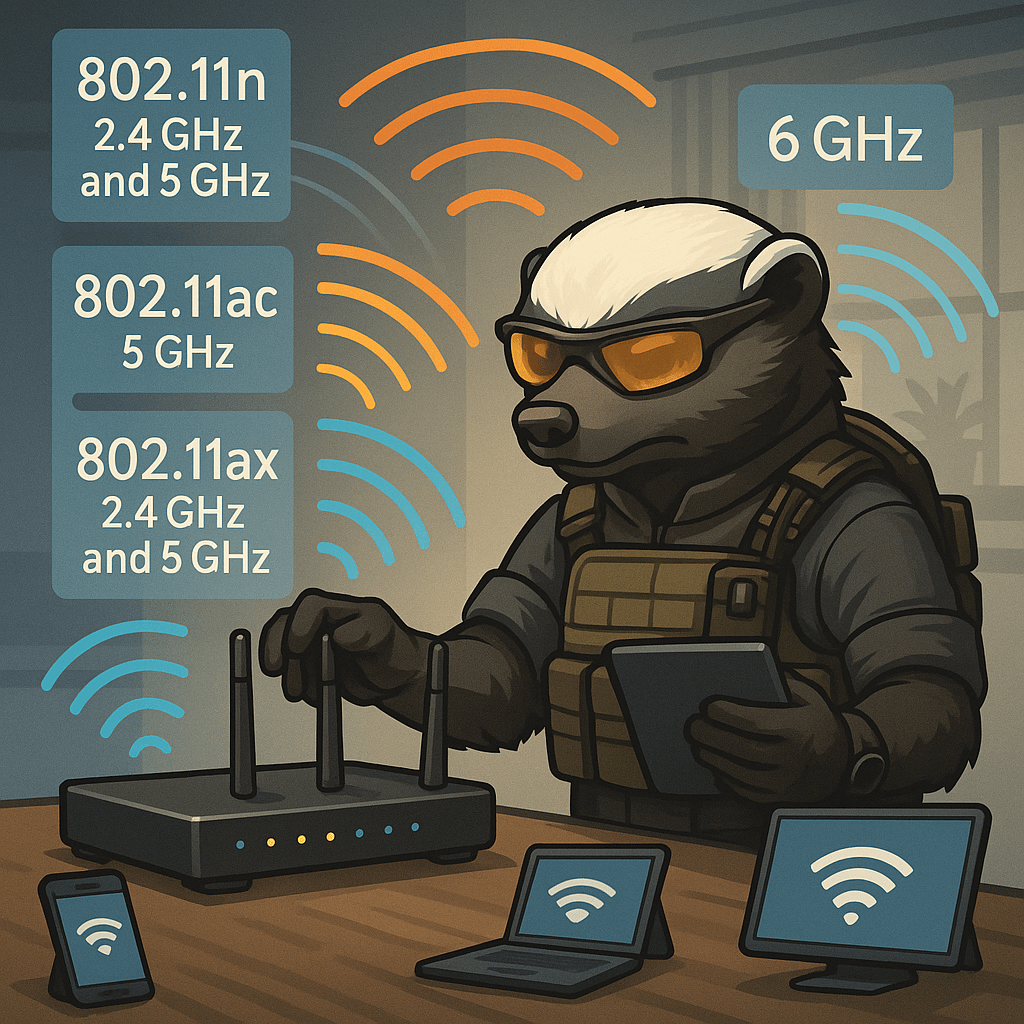
Modern wireless networks operate using evolving Wi-Fi standards, each offering different speed, range, and frequency capabilities. These standards, managed by the IEEE under the 802.11 umbrella, are critical to understand for any technician tasked with configuring or troubleshooting wireless networks. 802.11n, released in 2009, was the first to support dual-band operation—using both 2.4 GHz and…
-

The duplexing assembly is a specialized component in many modern printers that enables automatic double-sided printing—also known as duplex printing. Rather than requiring the user to manually flip pages to print on the other side, the duplexer takes over that function, flipping the sheet internally and refeeding it through the print path for the second…
-

Older laptop models that use CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) backlighting rely on a display inverter to power the screen’s illumination. The inverter’s job is to convert the laptop’s DC power into AC voltage needed by the CCFL tube inside the display panel. Without a functioning inverter, the screen may be technically on but will…
-

The /sbin directory in Linux holds system administration commands, which are mostly used by the root user or users with administrative privileges. Commands in /sbin help control and manage core parts of the system such as filesystems, networking, and startup processes. Tools like fsck (file system check), ifconfig (network configuration), and reboot are typically located…
-

Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated chip embedded on a computer’s motherboard, designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. It stores sensitive information such as encryption keys, digital certificates, and passwords in a tamper-resistant environment. TPM is commonly used for: The current standard is TPM 2.0, which is required by modern operating systems…
-
Using FTP, File Transfers are fun; I can use tcp/20 or /21! With port 22, I’m feeling well; Secure communication in my little Shell. Telnet’s the same, but more easy to see; nobody likes you when you’re port 23. SMTP is where Simple Mail thrives; it’s Transferred to servers with port 25. With DNS, I…
-

What Is an SSD? A Solid-State Drive (SSD) uses flash memory chips to store data. There are no moving parts, making it faster, quieter, and more durable than traditional hard drives. SSDs have extremely fast read/write speeds, especially in NVMe (PCIe) form, which are ideal for boot drives, gaming systems, and business apps. SSDs come…
-

A thermal printer uses heat to transfer images onto paper. It comes in two types: Consumables and Maintenance Direct thermal printers require only thermal paper, while thermal transfer printers need both ribbon and label stock.Maintenance includes: Technicians must also check for signs of printhead wear, incorrect temperatures, or paper with poor heat response when troubleshooting…
-

Two of the most recognized and widely used printer languages in the industry are PCL (Printer Command Language) and PostScript. Each one comes with unique advantages and is suited for different types of environments and workloads. PCL, developed by Hewlett-Packard, is a standard language found in many office printers. It’s built for speed and efficiency—great…
-

Every desktop computer relies on a Power Supply Unit (PSU) to convert wall electricity into usable voltage levels that safely power internal components. The PSU takes in AC (Alternating Current) and outputs DC (Direct Current) in multiple voltages—typically +12V, +5V, and +3.3V—distributed to the motherboard, CPU, storage devices, and GPU. Without proper power regulation, even…
-
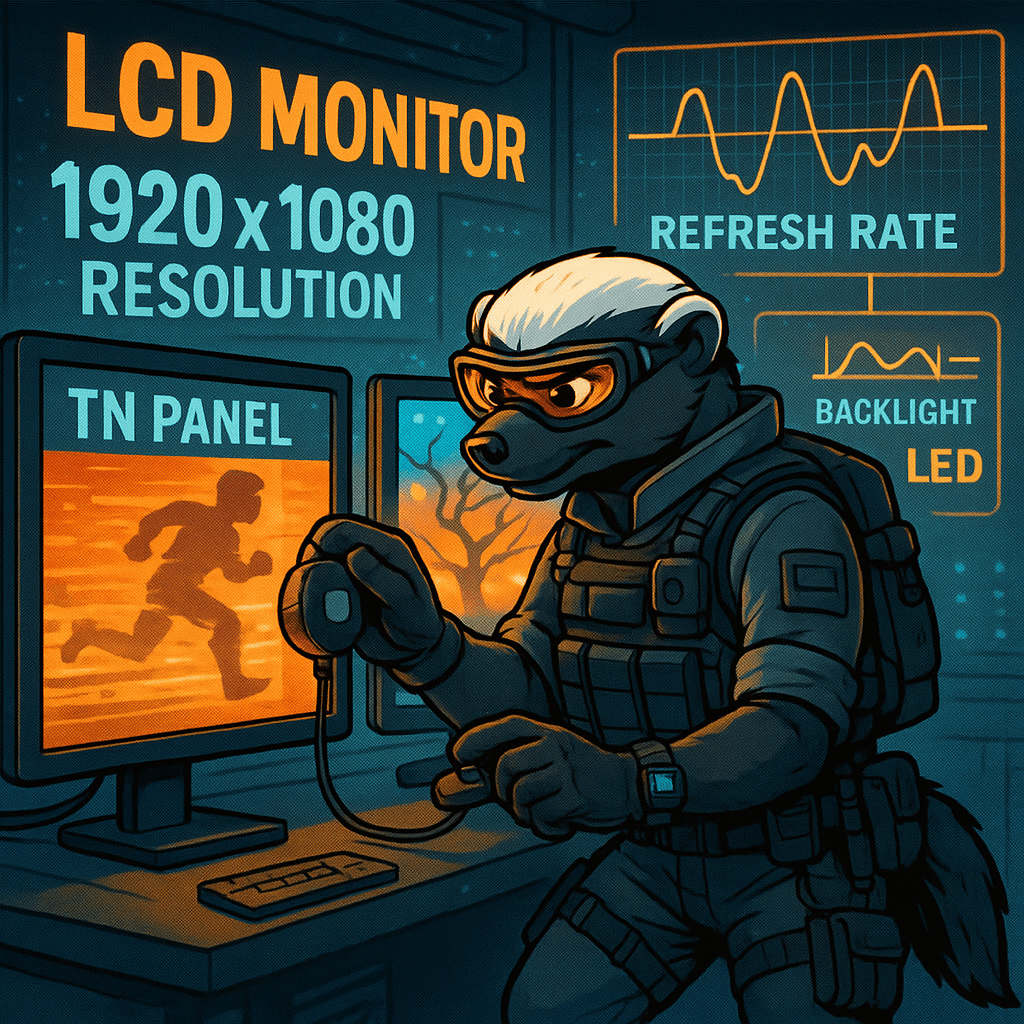
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) monitors use liquid crystals and a backlight to create images on screen. Each pixel is composed of subpixels (red, green, and blue) controlled by liquid crystal alignment, which either blocks or passes light from the backlight. There are two key types of LCD panel technologies: All LCDs require a backlight, either…
-
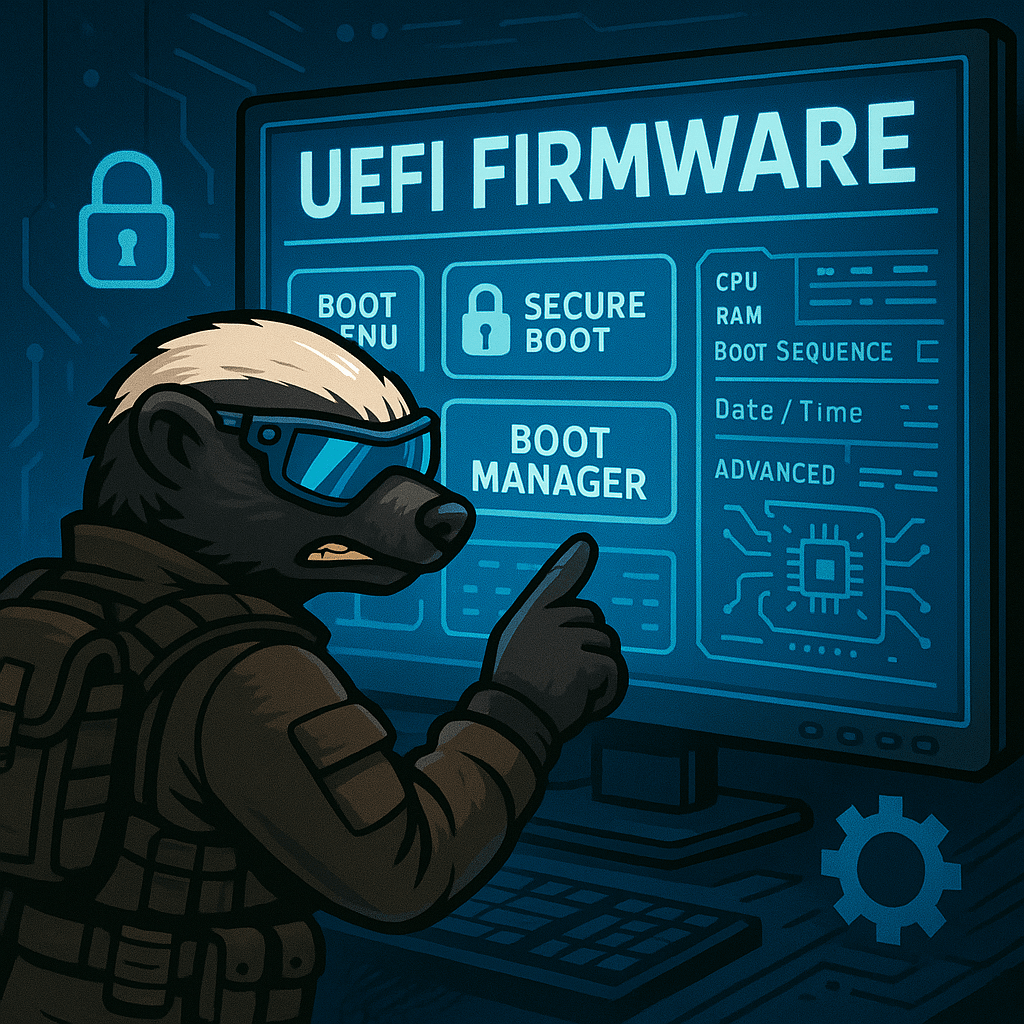
UEFI, or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, is the modern replacement for traditional BIOS in today’s computers. It is the firmware layer that initializes hardware components and passes control to the operating system during the boot process. UEFI offers several advantages over BIOS, including support for larger drives (over 2 TB), faster boot times, a graphical…
-

Inkjet printers are among the most common types of consumer and small office printers, known for their ability to produce detailed color images and sharp text on a variety of media. They function by spraying tiny droplets of ink directly onto paper through nozzles in the printhead. These droplets are controlled with extreme precision, often…
-

RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a method of combining multiple physical drives into a single logical unit to improve performance, redundancy, or both. It’s commonly used in servers, NAS devices, and business-class desktops to ensure data reliability and uptime. Different RAID levels offer different trade-offs between speed, fault tolerance, and capacity. RAID…
-
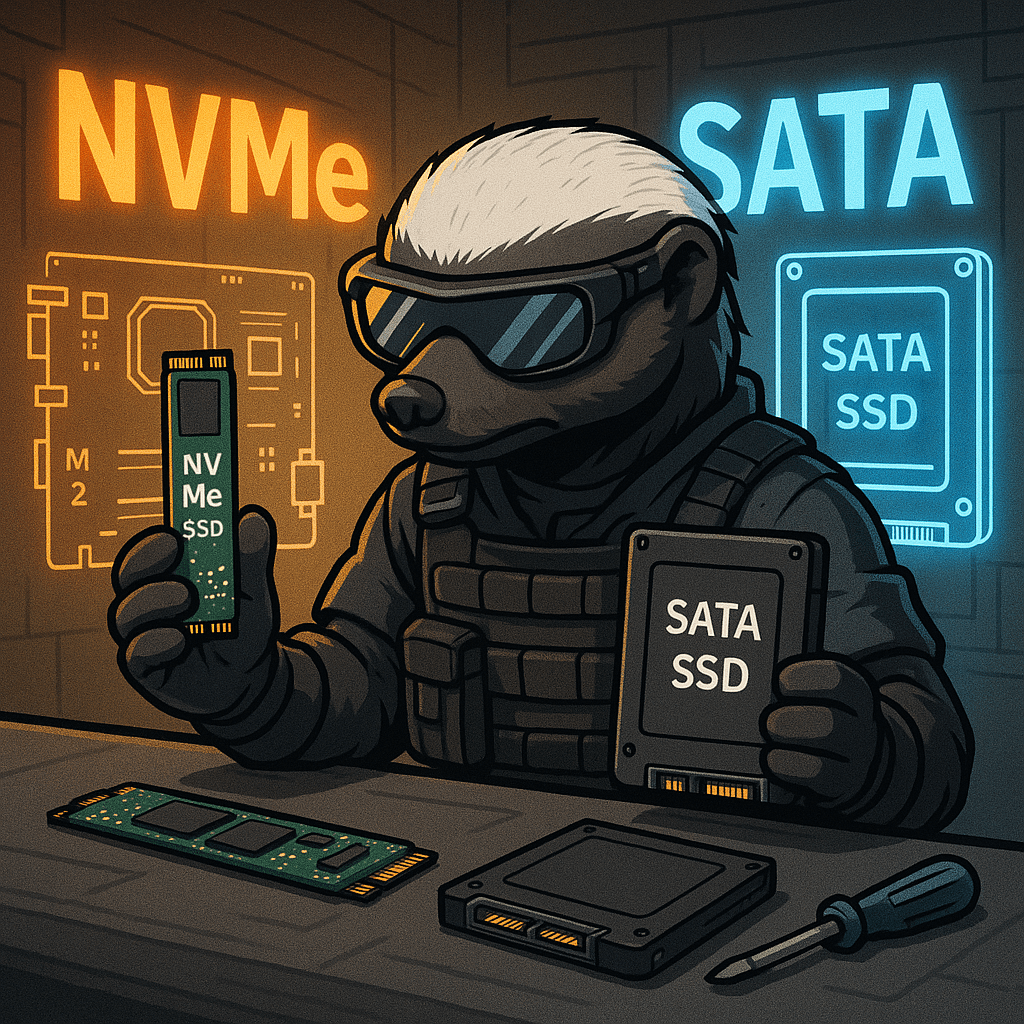
In modern computing, Solid State Drives (SSDs) have largely replaced traditional spinning hard drives due to their superior speed and reliability. Among SSD types, two interfaces dominate: SATA SSDs and NVMe SSDs. Both offer fast performance compared to HDDs, but the underlying technology and connection methods set them apart significantly. SATA SSDs use the Serial…
-
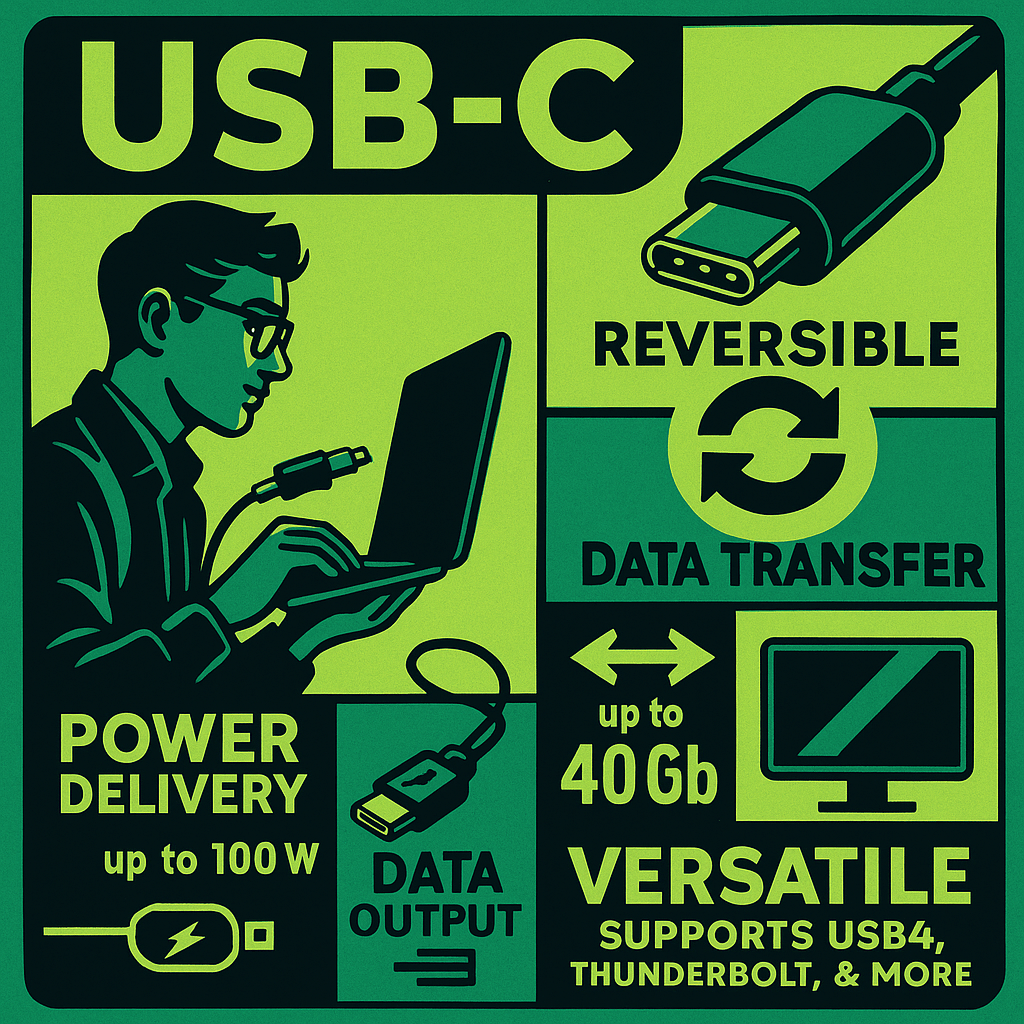
USB-C (Universal Serial Bus Type-C) is a modern, reversible 24-pin connector designed to replace earlier USB types (USB-A, USB-B, Micro-USB) with a more compact, versatile, and powerful solution. Unlike previous versions, USB-C can transmit data, video, and power through a single cable, making it ideal for charging laptops, connecting external displays, and transferring high-speed data.…
-
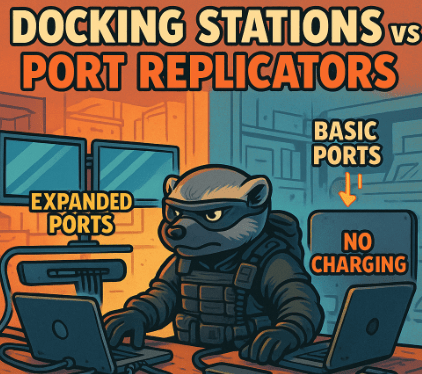
What Is a Docking Station? A docking station is a physical expansion unit that connects to a laptop and transforms it into a full desktop workstation. It adds additional ports such as USB, Ethernet, HDMI, DisplayPort, audio jacks, and charging capabilities, often through a single USB-C or proprietary connector. Docking stations typically: Used in corporate…
-

The IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) is a unique 15-digit number assigned to every mobile device that connects to a cellular network. Unlike a SIM card, which identifies the user, the IMEI identifies the device itself. It is used by carriers to track stolen devices, block lost phones from network access, and enforce blacklists. IMEI…
-
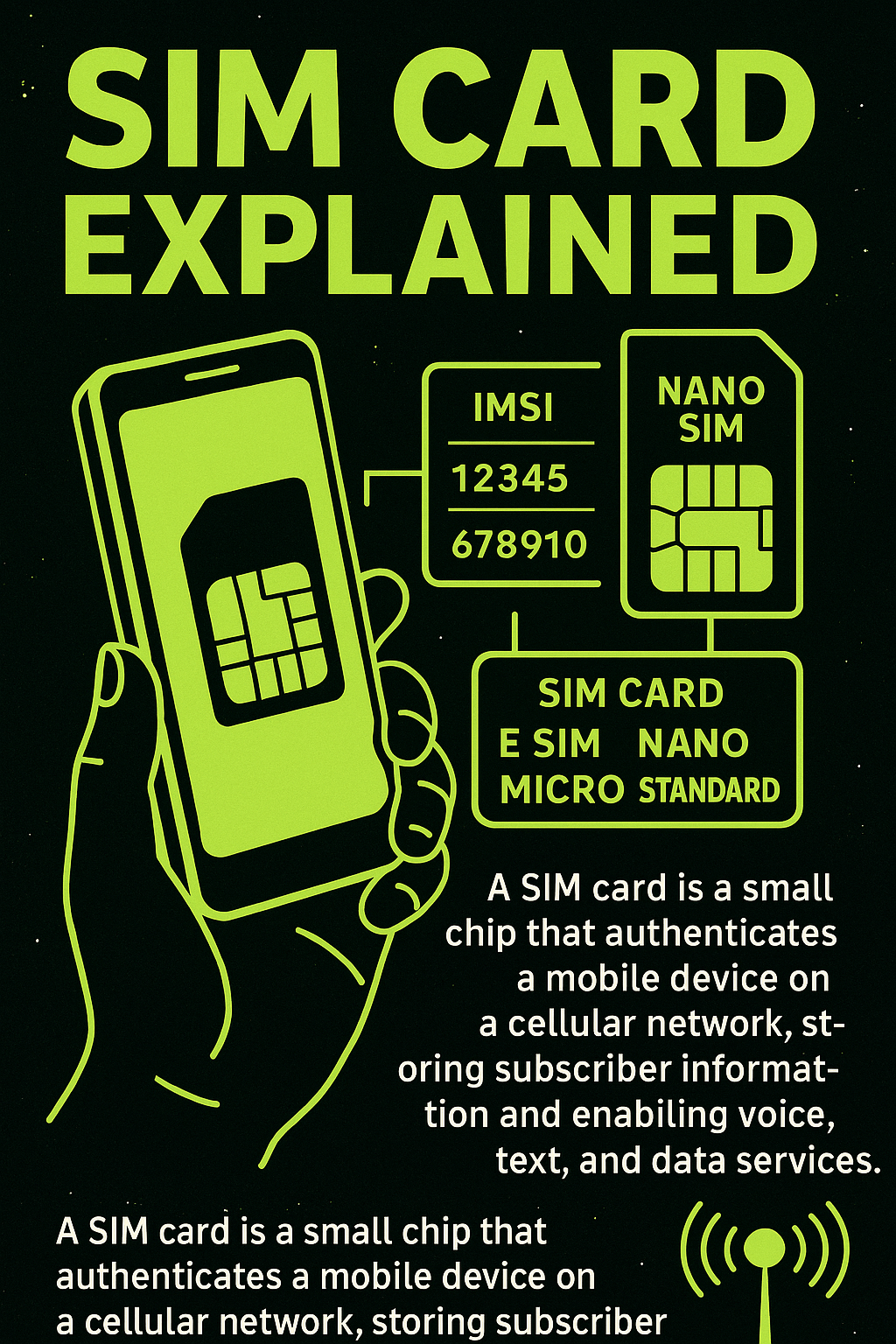
A SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module) is a small, removable smart card used in mobile devices to securely store information that authenticates a user to a mobile carrier’s network. It contains the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) and a secret authentication key, which allows the mobile device to connect to the carrier’s GSM, LTE, or…
-
The file command in Linux is used to determine the true type of a file by inspecting its contents, not just its name or extension. Unlike many operating systems that rely on file extensions (like .jpg, .txt, or .mp3), Linux doesn’t depend on naming alone. The file command reads the internal binary signatures of the…
-
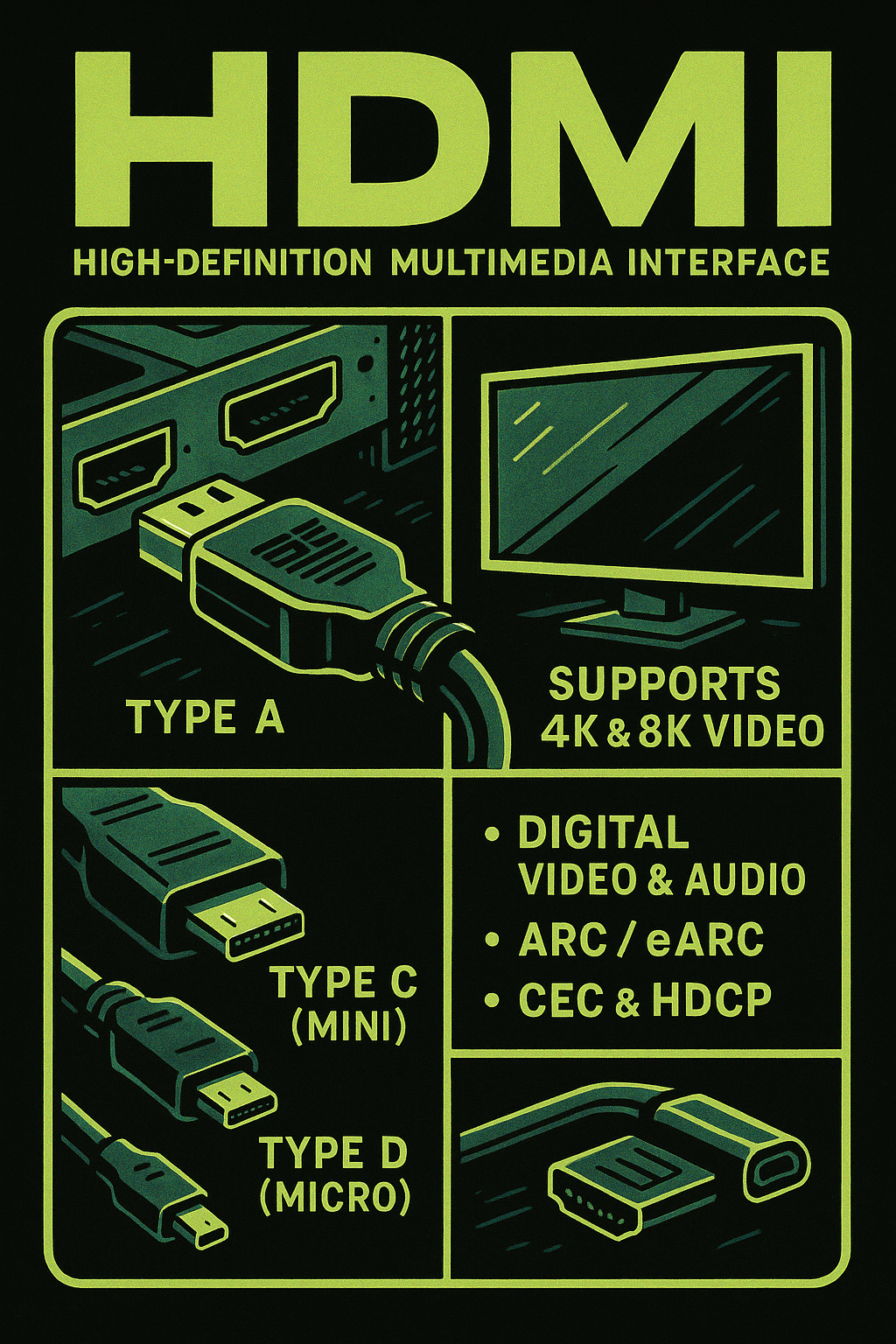
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a proprietary audio/video interface designed to transmit uncompressed digital video and audio from a source device to a display or audio receiver. It supports a wide range of high-resolution formats, including 1080p, 4K, and even 8K video, along with multi-channel digital audio—all through a single cable. HDMI connectors come in…
-
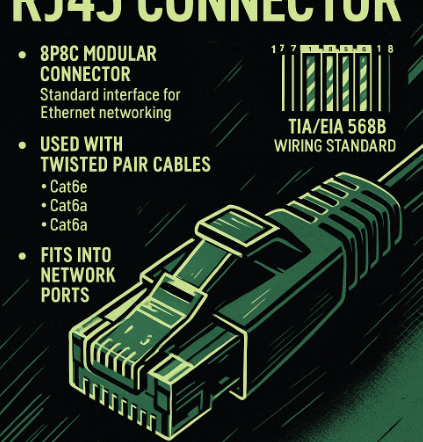
The RJ45 connector is the industry-standard interface used to terminate twisted-pair Ethernet cables for wired networking. Formally known as an 8P8C (eight positions, eight contacts) modular connector, RJ45 is used to connect devices such as computers, routers, switches, and patch panels in both residential and enterprise environments. It supports network standards like 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T,…
-

HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) is the foundation of data communication on the World Wide Web, enabling browsers and servers to exchange information like webpages, images, and files. HTTP operates on TCP port 80 and transmits data in plaintext, making it vulnerable to interception, eavesdropping, and man-in-the-middle attacks. While still used in some internal or legacy…
-
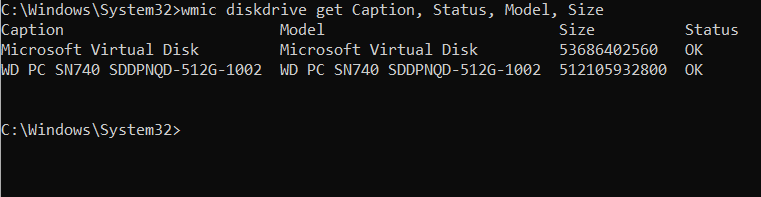
The Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC) tool is a command-line utility that enables users to interact with the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) system. WMI provides access to detailed system information, hardware diagnostics, and management capabilities without requiring a graphical interface. WMIC simplifies querying system properties, retrieving hardware data, and monitoring system health using predefined aliases.…
-
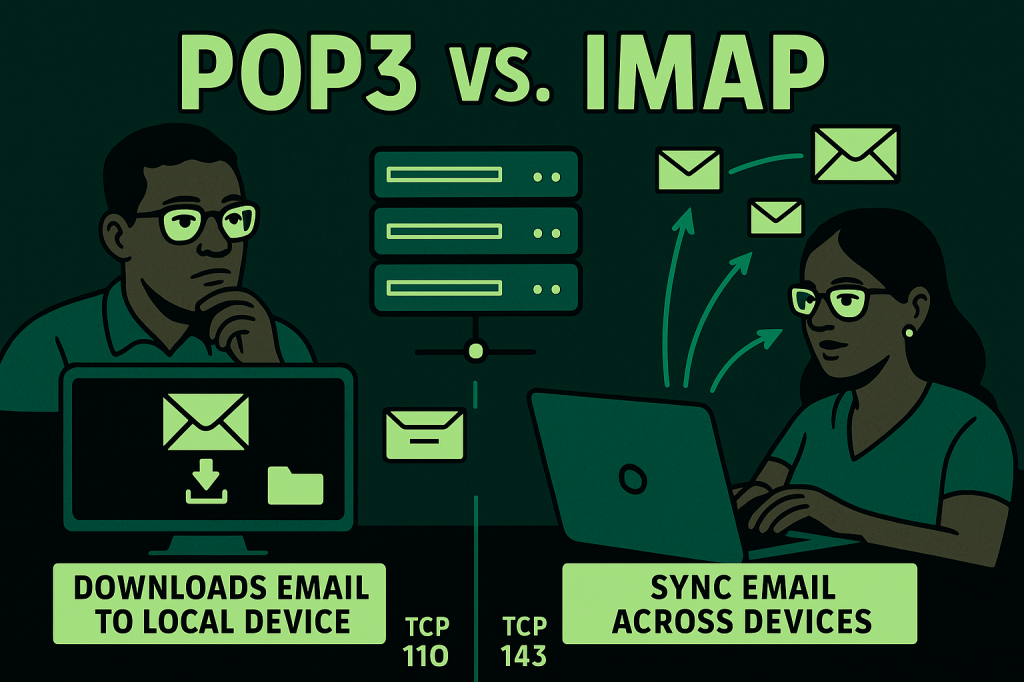
POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) is an email retrieval protocol that allows a client to download messages from a mail server to a local device. Operating over TCP port 110 (or 995 with SSL/TLS), POP3 typically downloads and then deletes messages from the server unless configured otherwise. It is ideal for users who want…
-
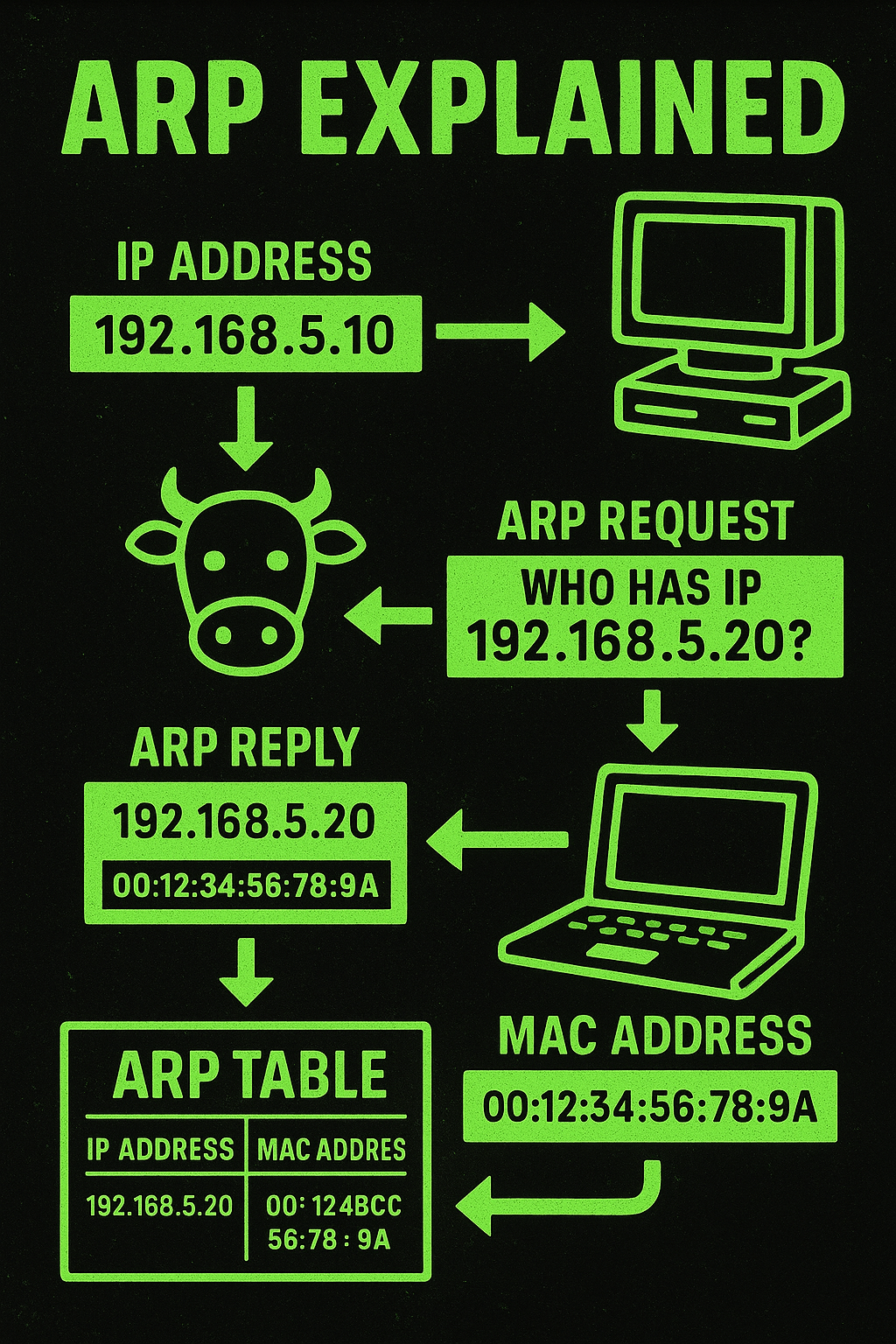
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a Layer 2 protocol used to map a known IPv4 address to its corresponding MAC address on a local network segment. When a device wants to communicate with another IP on the same subnet, it broadcasts an ARP Request to ask, “Who has this IP?” The device with the matching…
-
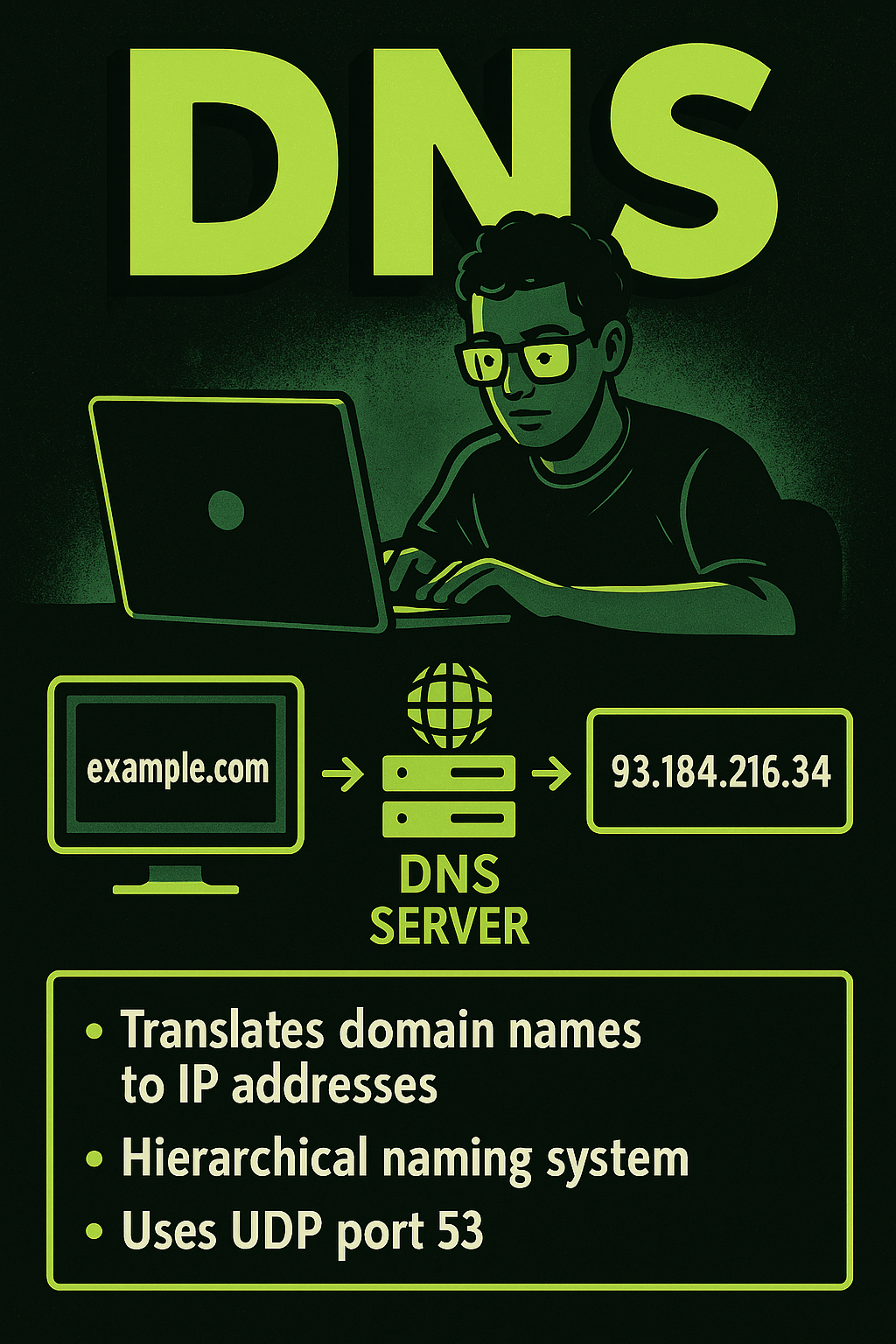
DNS (Domain Name System) is a foundational internet service that translates human-friendly domain names like example.com into IP addresses that computers use to communicate, such as 93.184.216.34. This system works in a hierarchical manner, involving root servers, top-level domains (TLDs), and authoritative name servers. When a user enters a URL into a browser, a DNS…
-
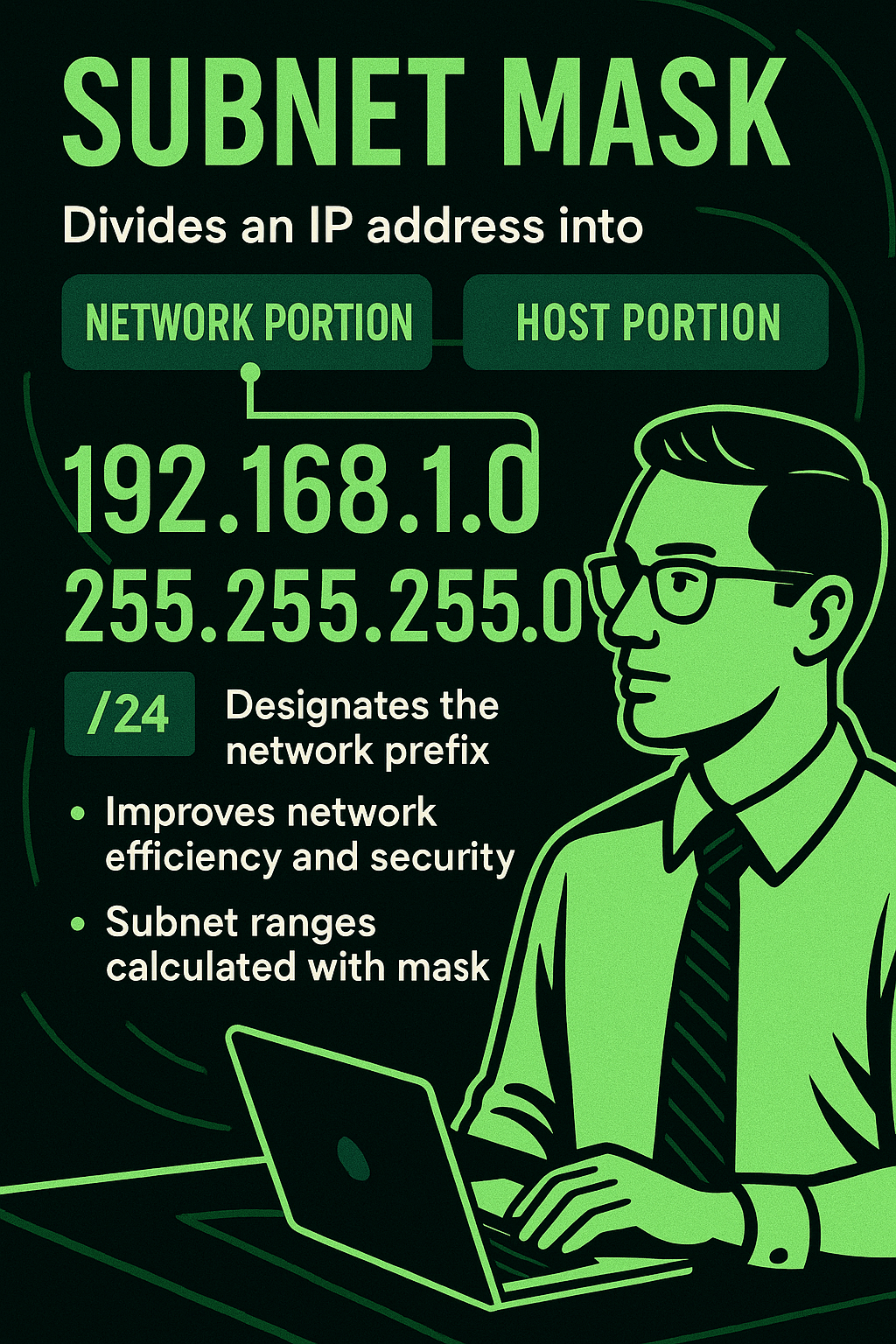
A subnet mask is used in IP networking to divide an IP address into network and host portions, allowing efficient IP address allocation and enhancing routing performance. For example, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (or /24 in CIDR notation) designates the first 24 bits of the IP address as the network portion, leaving the remaining…
-
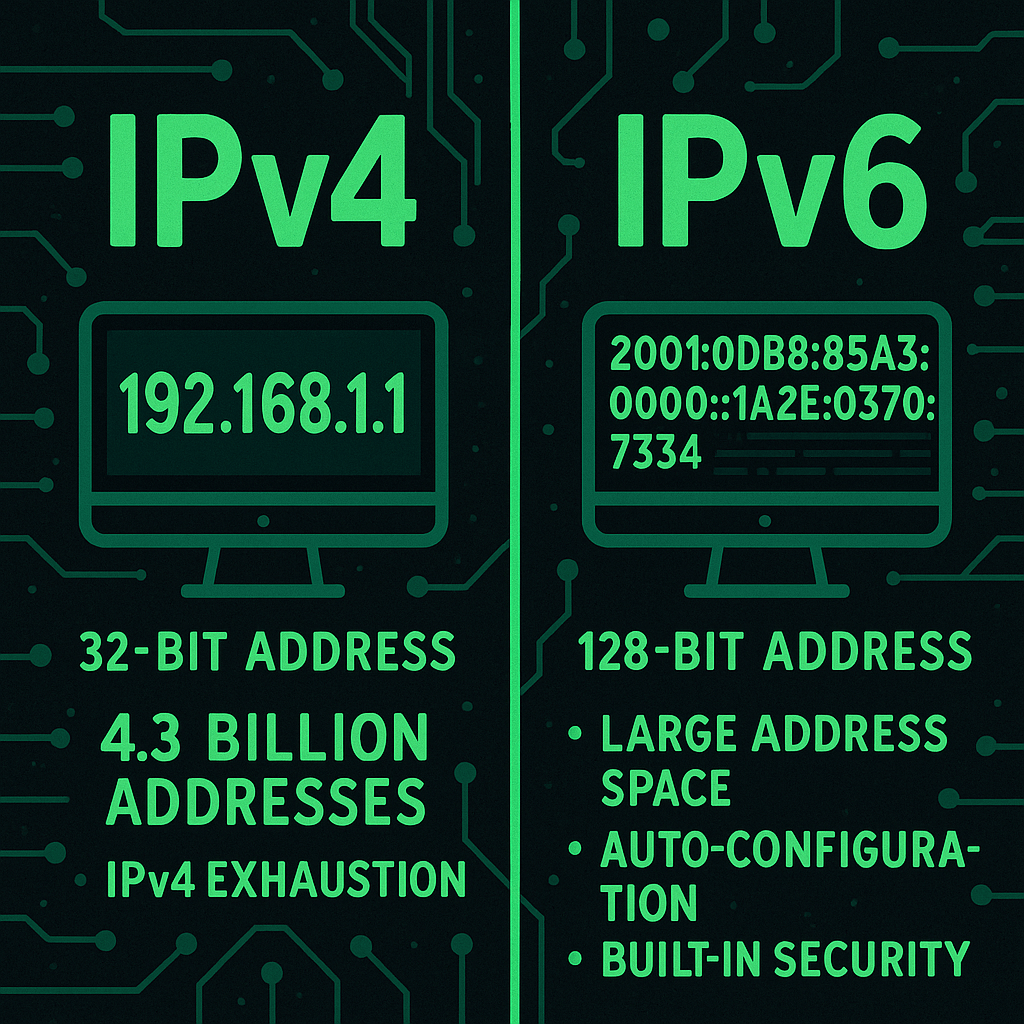
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) is the fourth version of the IP protocol and remains the most widely used standard for assigning IP addresses on the internet and private networks. It uses a 32-bit addressing scheme, represented in dotted decimal format (e.g., 192.168.1.1), which provides approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses. Due to the limited pool…
-
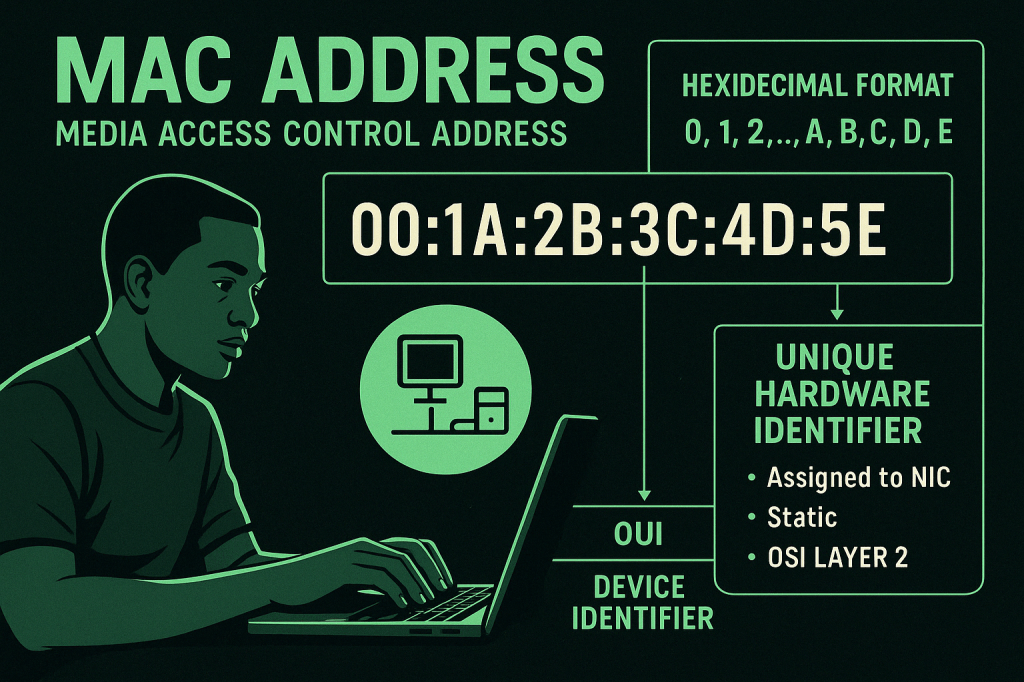
A MAC address (Media Access Control address) is a globally unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) by the manufacturer. It operates at OSI Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) and is typically written in hexadecimal format, such as 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E. The MAC address consists of two parts: the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), which identifies…
-
RJ45 Ethernet cabling and fiber optic cabling are two dominant physical media used in networking, each with unique characteristics suited for different scenarios. RJ45 uses twisted-pair copper wires terminated with an 8P8C modular connector (commonly referred to as RJ45) and is typically deployed in LAN environments. Ethernet standards like Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a support speeds…
-
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) and DisplayPort are two widely adopted digital display interfaces, but they are optimized for different environments. HDMI is the standard for consumer electronics, including TVs, projectors, game consoles, and media players. It supports both audio and video in a single cable and includes features like CEC (Consumer Electronics Control) and ARC…
-

BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) are closely related components in PC architecture, but they serve distinct functions. BIOS is firmware stored on a chip on the motherboard, responsible for initializing hardware during boot-up, performing POST (Power-On Self-Test), and launching the operating system. It also provides a configuration interface where users can…
-

Peripherals are external devices that connect to a computer to extend its input, output, or storage capabilities. They fall into three main categories: input devices, output devices, and input/output (I/O) devices. Common input peripherals include keyboards, mice, trackpads, scanners, microphones, and webcams. These devices allow users to enter data, control the system, and capture images…
-
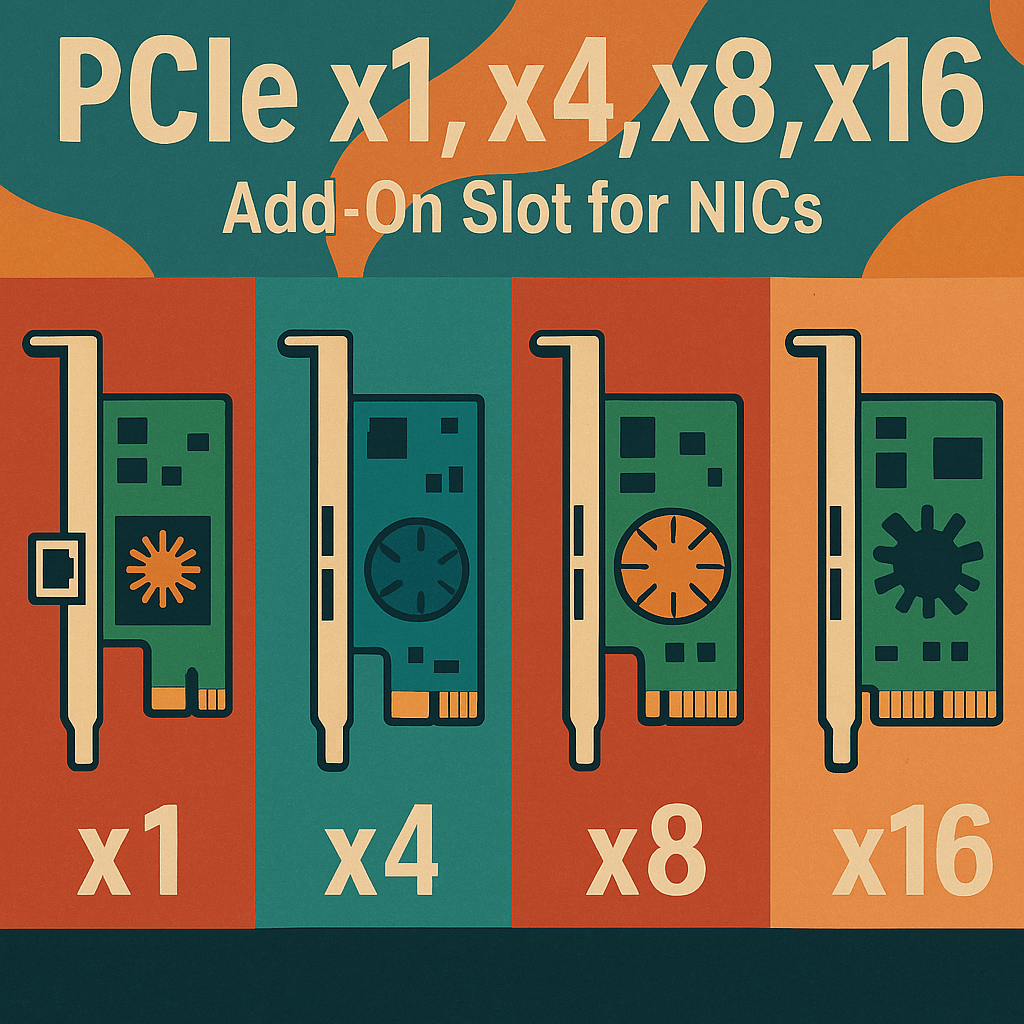
PCI Express (PCIe) is the industry-standard high-speed interface used to connect add-on components—like network interface cards (NICs)—to a computer’s motherboard. For NICs, PCIe offers dedicated data lanes to the CPU or chipset, ensuring low-latency, high-throughput, and scalable bandwidth. PCIe slots are designated by their lane count: x1, x4, x8, and x16. Each lane consists of…
-
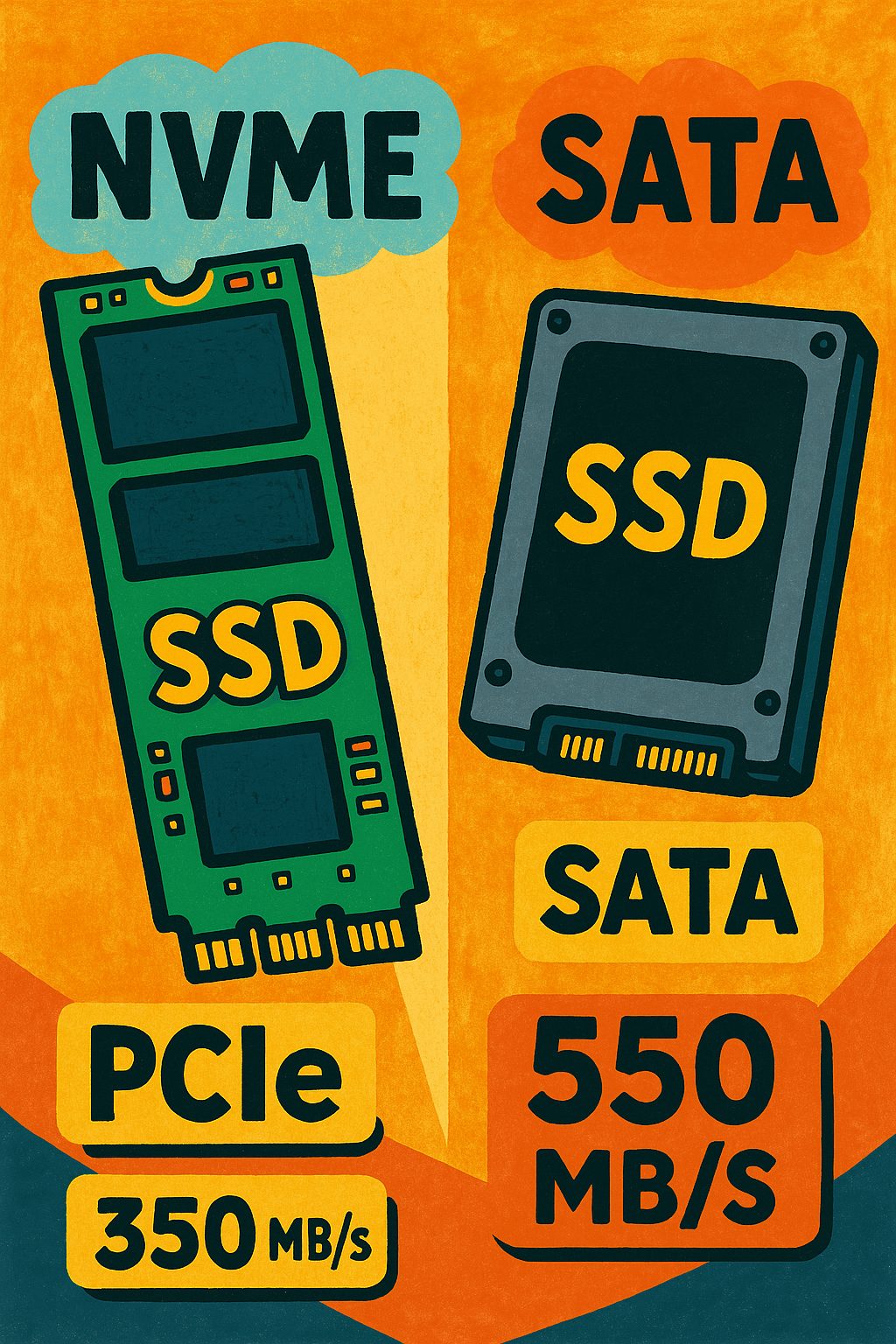
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) and SATA (Serial ATA) are two types of interfaces used to connect SSDs to a system, and while both offer significant advantages over traditional HDDs, their performance differences are critical. SATA SSDs, which use the older AHCI protocol and connect via the SATA III interface, typically max out at 550 MB/s…
-

Storage drive problems can cause system crashes, data loss, and performance degradation. Symptoms may include the system failing to boot, slow file access, corrupted files, or frequent read/write errors. Initial troubleshooting begins by checking physical connections such as SATA, NVMe, or power cables, and confirming that the drive is detected in BIOS or UEFI. For…
-

Installing and configuring common devices is a foundational task for entry-level IT technicians and often the first step in setting up functional workstations for users. Devices in this category include monitors, printers, external drives, input devices like mice and keyboards, and audio peripherals such as speakers and headsets. Installation begins with identifying the correct interface—typically…
-

The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network service used to automatically assign IP addresses and other configuration information—such as the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers—to client devices on a network. This removes the need for manual IP configuration and helps avoid conflicts caused by duplicate IPs. DHCP is essential for managing…
-
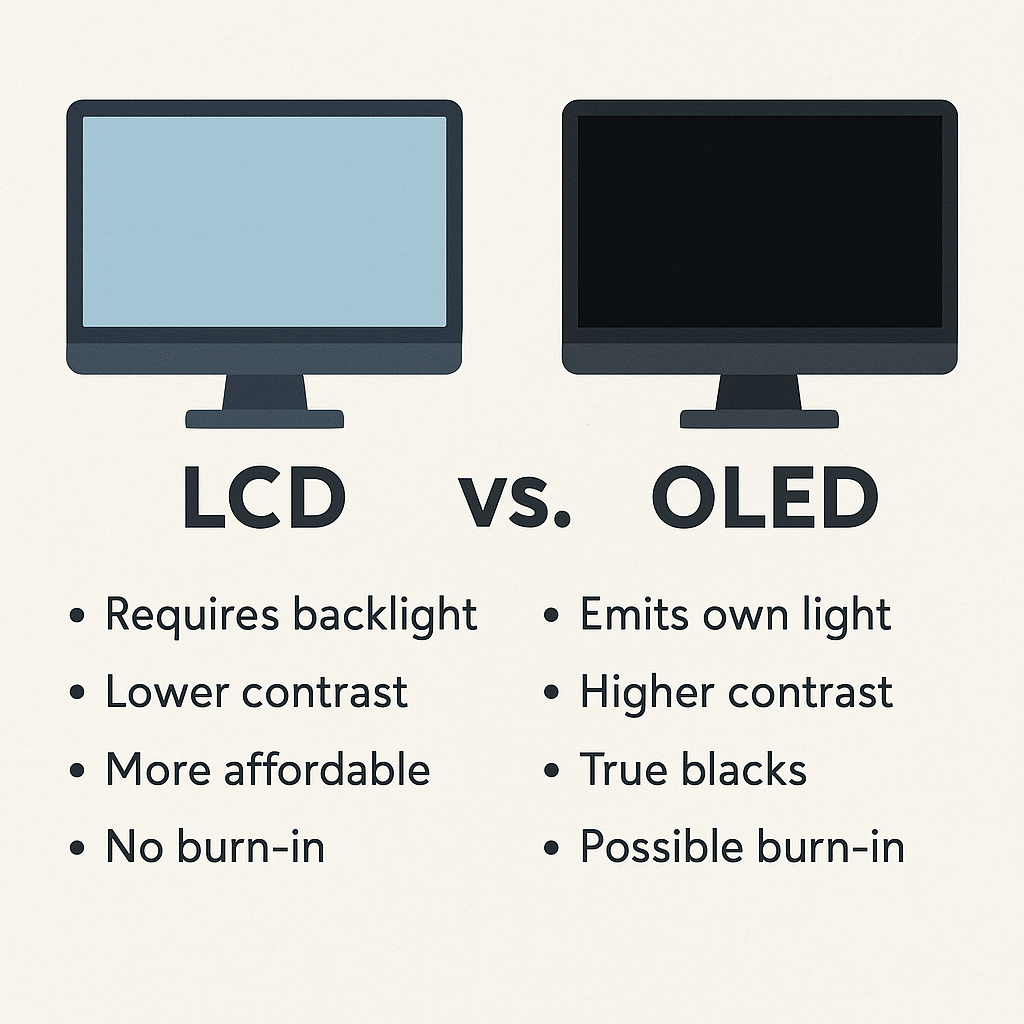
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) technologies are two widely used screen types in modern devices, each with distinct characteristics. LCDs require a backlight to illuminate pixels, which means blacks can appear grayish, but they offer consistent brightness and are generally more affordable. OLED displays, on the other hand, emit their…
-
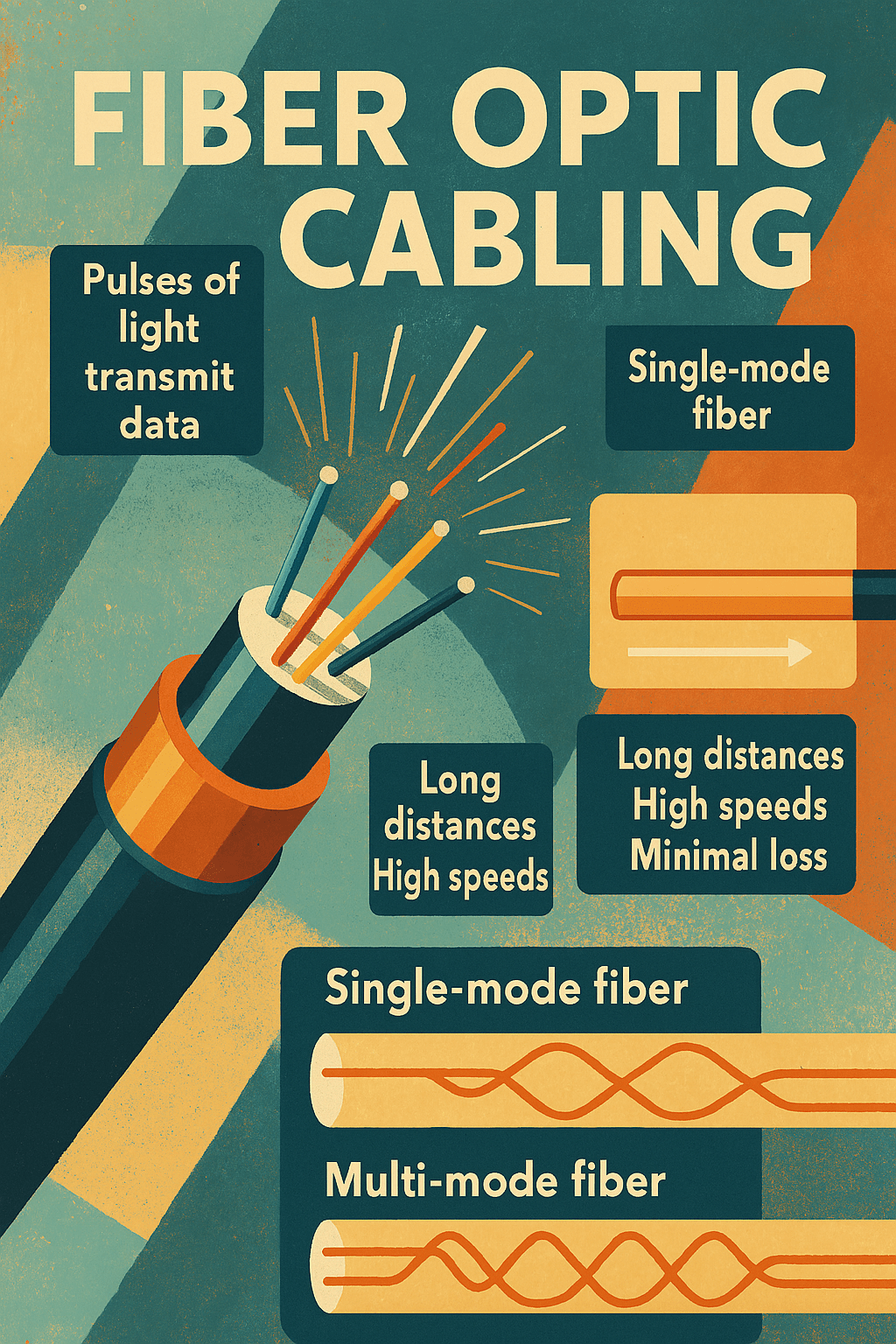
Fiber optic cabling is a high-speed transmission medium that uses pulses of light instead of electrical signals to carry data over glass or plastic strands. It supports far greater bandwidth and significantly longer transmission distances than copper cabling, making it essential for enterprise backbones, internet service providers, data centers, and long-haul telecommunications. Two core types…
-
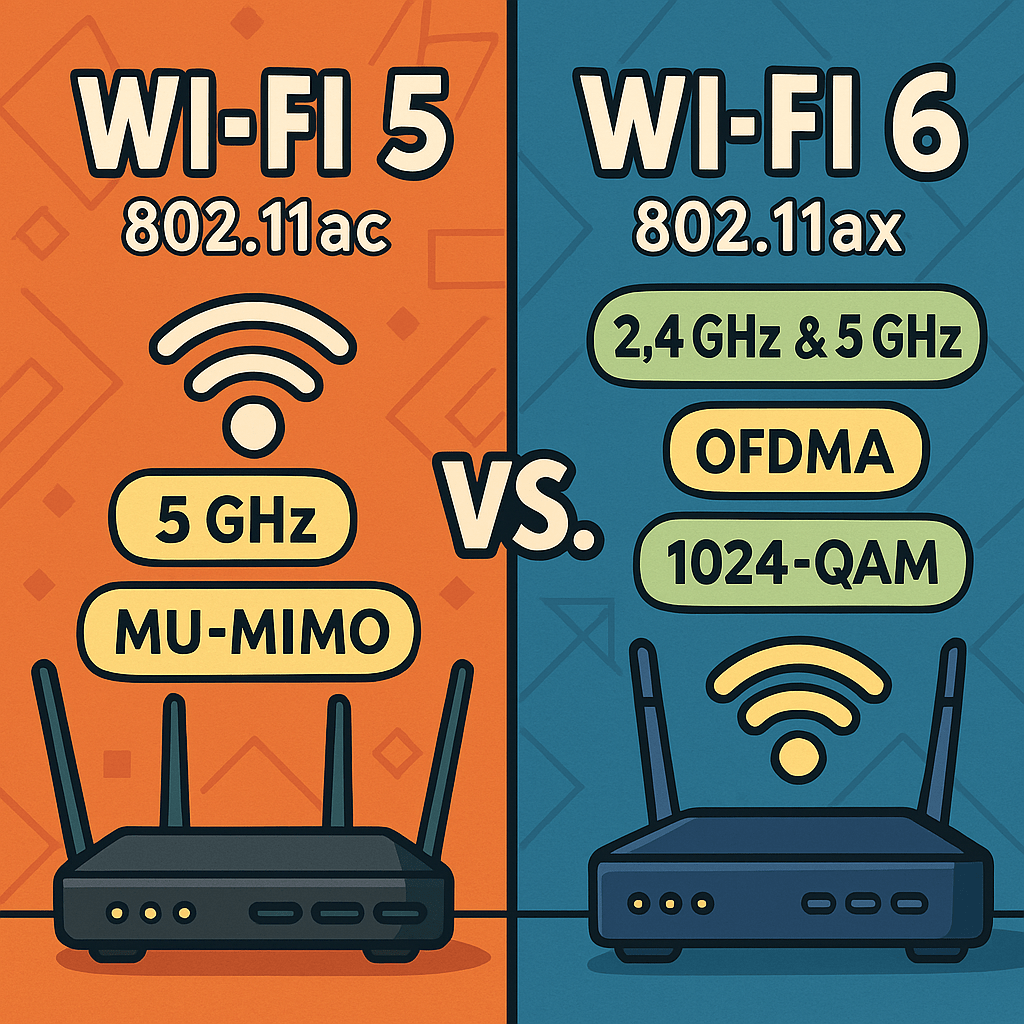
Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) and Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) are two prevalent standards that IT professionals should be familiar with. Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac): Wi-Fi 5, introduced in 2013, operates exclusively on the 5 GHz frequency band. It brought significant improvements over its predecessor, 802.11n, by offering higher data rates and enhanced performance. The standard supports channel widths…
-
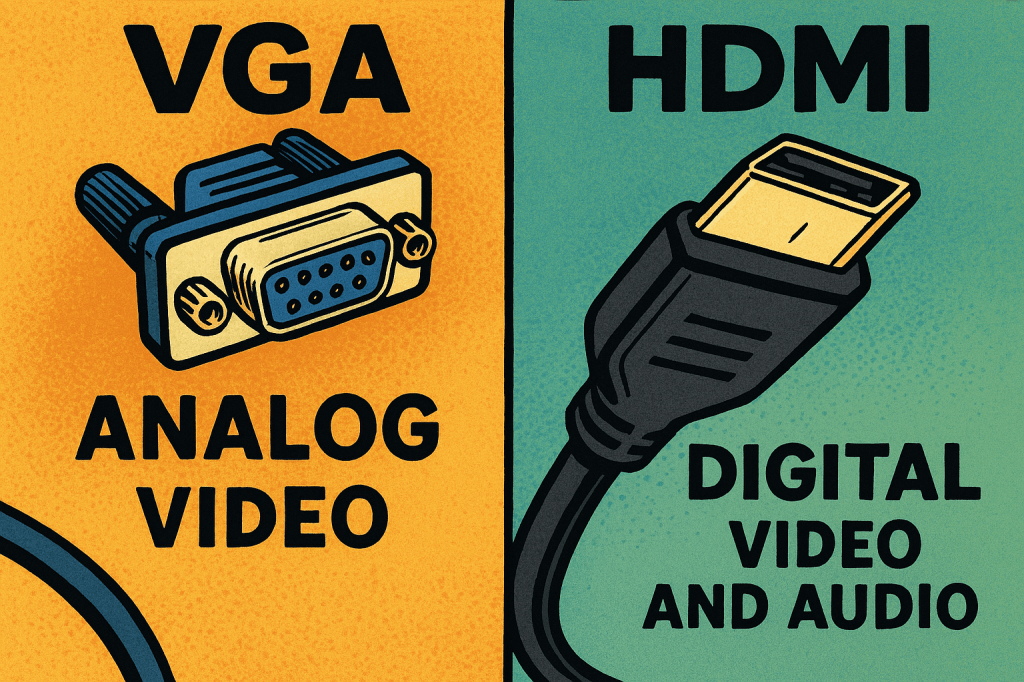
VGA (Video Graphics Array) and HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) are both used to connect displays to computers, but they differ in signal type, quality, and capabilities. VGA is an older analog interface introduced in the late 1980s that transmits video only. It uses a 15-pin D-sub connector and is prone to signal degradation over long…
-
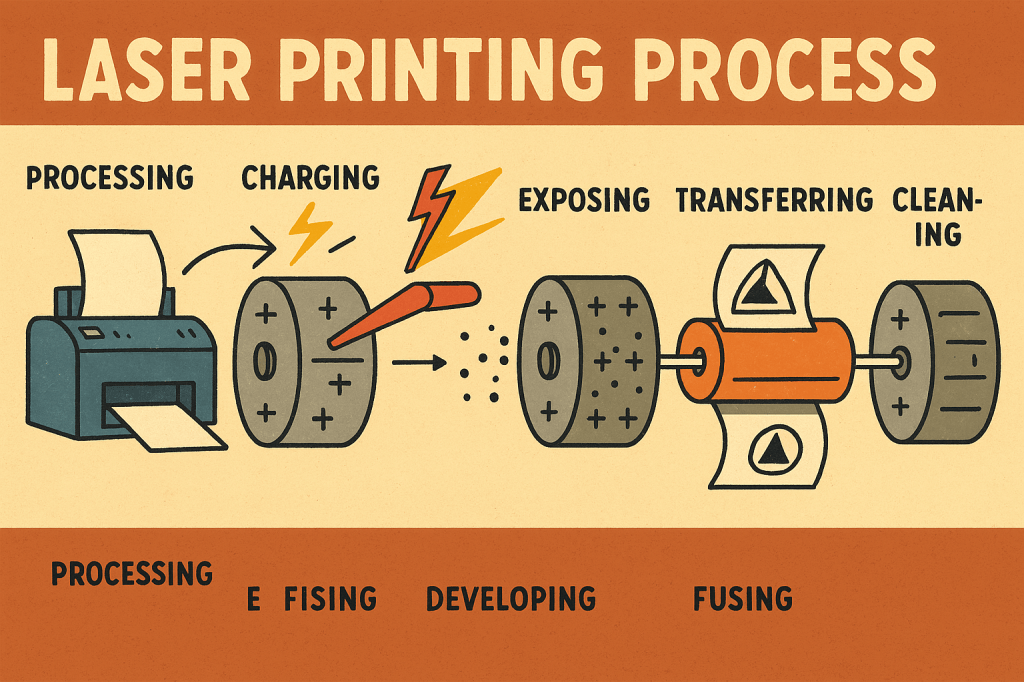
The laser printing process is a precise, multi-step method that relies on electrostatics, heat, and toner to produce high-quality prints quickly and efficiently. It begins with the processing stage, where the printer receives the data from the computer and organizes it into printable instructions. In the charging phase, a primary corona wire or roller applies…
-

External storage devices, like USB flash drives, external hard drives (HDDs), and portable solid-state drives (SSDs), are essential tools for storing and transferring data. USB flash drives are compact, portable, and often used for quick file sharing between devices, with capacities ranging from 4GB to 2TB. External HDDs, such as the WD My Passport, offer…
-

Mobile device issues are diverse and may involve power problems, unresponsive screens, charging failures, or connectivity issues. The first step is verifying the basics—does the device power on, is the battery charged, and is the power adapter functioning correctly? A common issue is a dead battery or a faulty charging cable, which can easily be…
-

Wi-Fi 5, also known by its IEEE standard 802.11ac, was introduced in 2013 and became the dominant wireless standard for high-speed consumer and enterprise networking. Operating exclusively on the 5 GHz frequency band, Wi-Fi 5 offered major improvements over its predecessor, 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4), by introducing wider channels (up to 160 MHz), MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple…
-
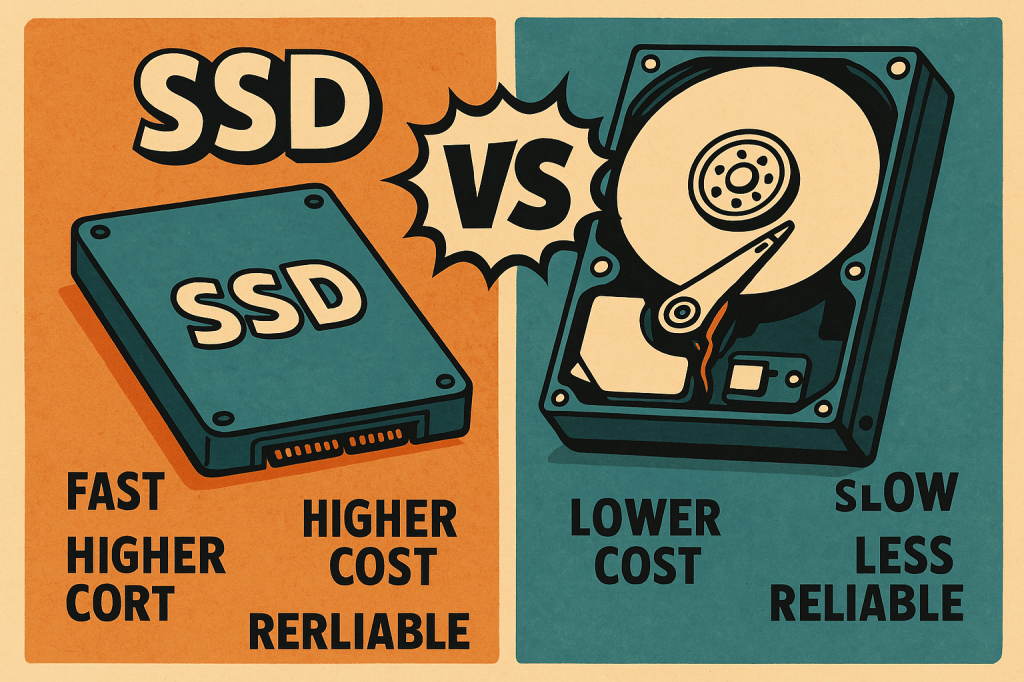
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are two primary forms of internal and external storage used in desktops, laptops, and servers, each with distinct characteristics. SSDs store data on flash memory chips, offering lightning-fast read/write speeds, lower latency, and greater durability due to the absence of moving parts. They’re ideal for operating systems,…
-

The 802.11 wireless standards represent a series of specifications developed by the IEEE for wireless local area networking (WLAN). The original 802.11 standard, established in 1997, supported data rates up to 2 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz frequency band but quickly became obsolete. The 802.11a standard, released in 1999, introduced operation in the 5 GHz…
-
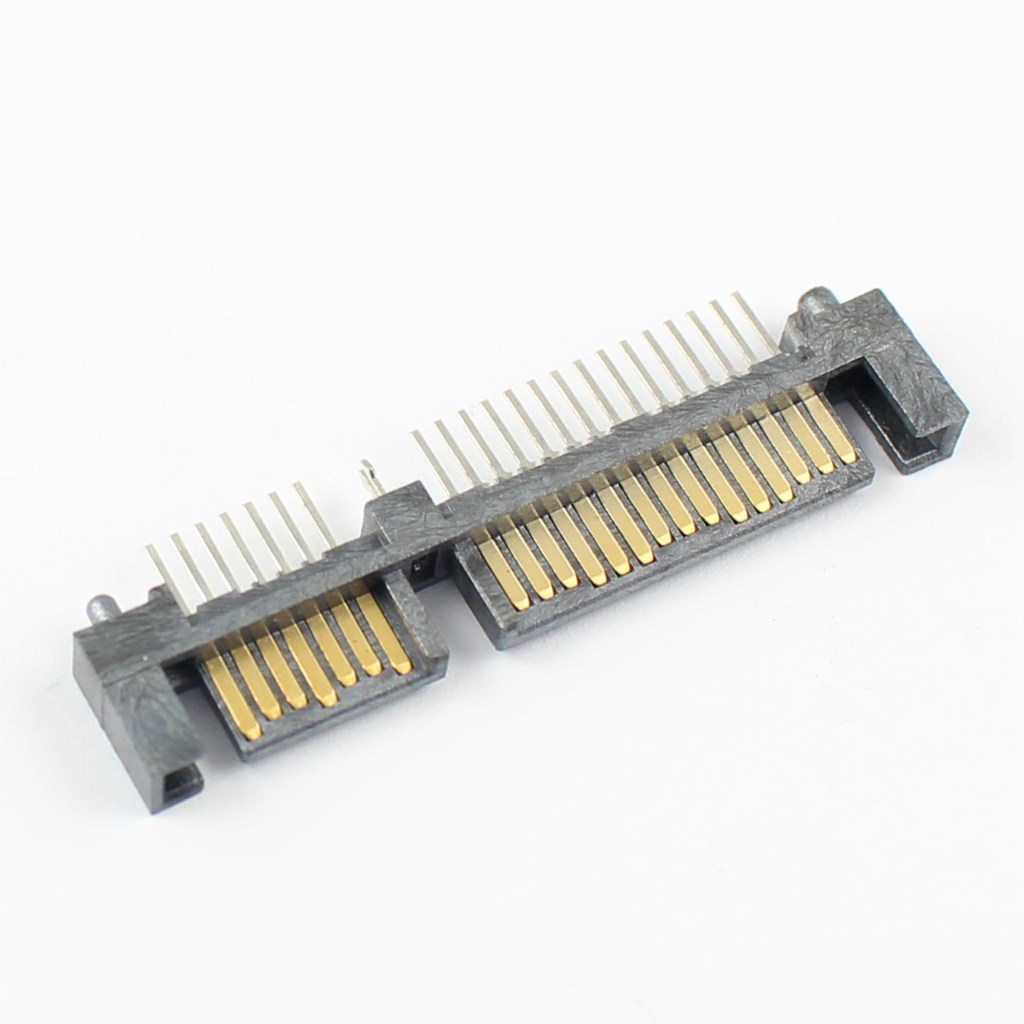

SATA (Serial ATA) hard drives are widely used for internal storage in desktops and laptops, offering a balance of performance and cost for general computing tasks. Introduced as a replacement for older PATA (Parallel ATA) drives, SATA provides faster data transfer speeds and thinner cables for improved airflow within the system chassis. The most common…