Tech Docs
-
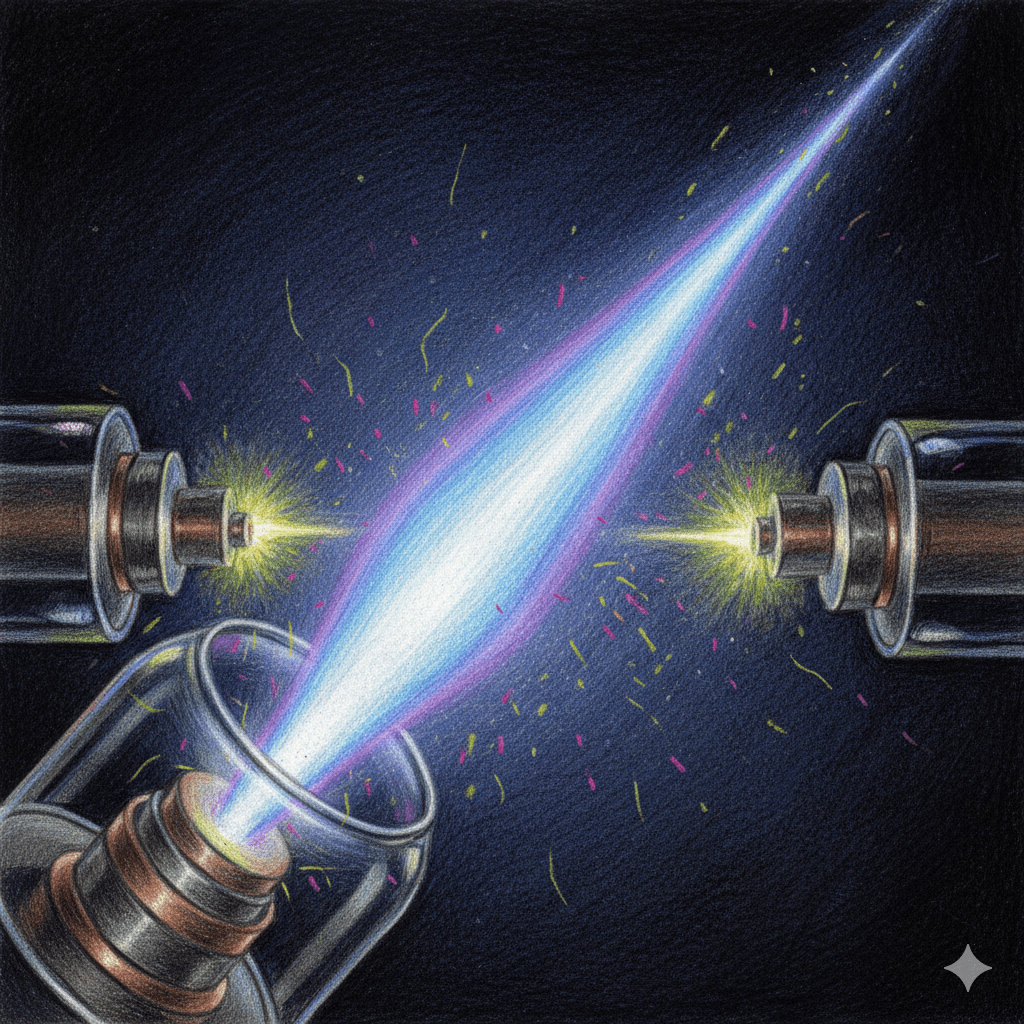
SIMS (Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry) instrumentation is designed to analyze the surface composition of materials by detecting ions ejected from the surface. The system includes a primary ion source that fires a focused beam of ions (like gallium or cesium) onto the sample. This bombardment knocks atoms and molecules off the surface, some of which…
-
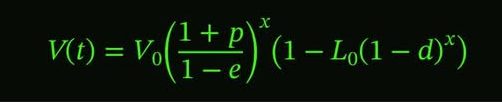
Let me be very clear. Power Efficiency Theory seeks to measure verifiable energy metrics directly related to the bitcoin protocol. I contend that the individual system (the ASIC machine) is the most reliable way to measure the anticipated value of bitcoin. You can collect metrics using the Individual systems or the entire system, but there…
-
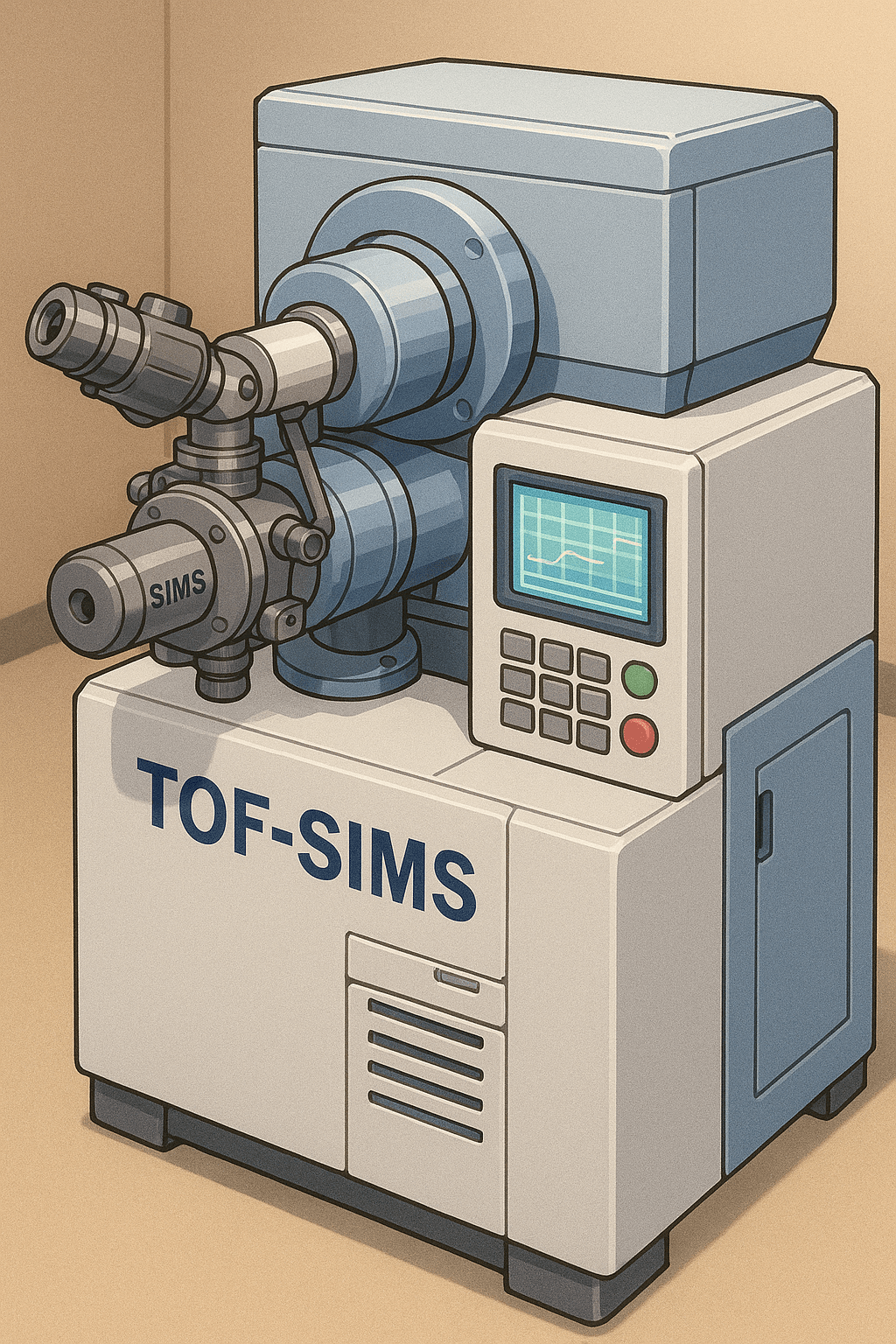
Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (TOF-SIMS) is a powerful technique used to analyze the surface of materials by detecting the chemical composition of just the outermost layers. The technique allows for analysis of a chemical structure in 3D with nanoscale resolution. In this method, a sample is bombarded with a focused beam of primary ions.…
-
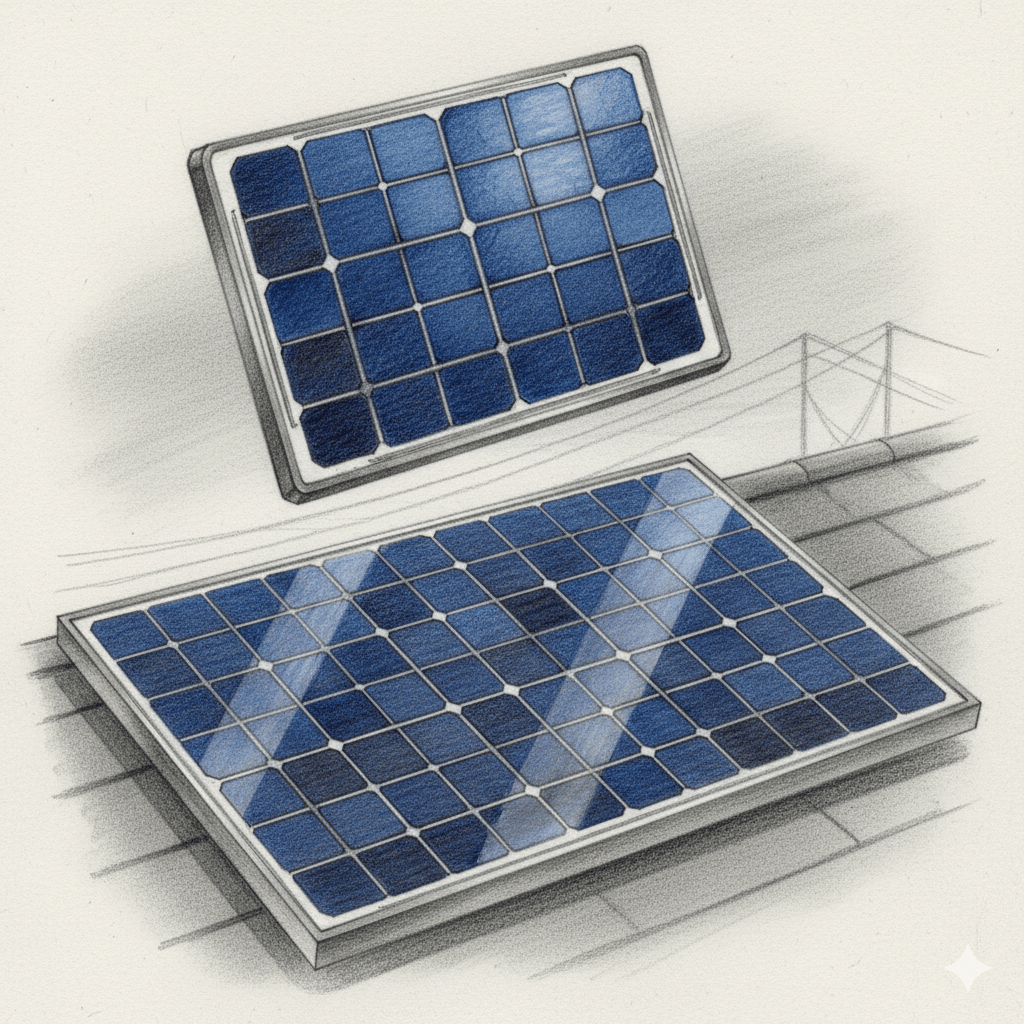
The solar energy industry traces its roots to nineteenth century scientific discoveries, beginning with the photovoltaic effect identified by Edmond Becquerel in 1839 and early selenium based cells in the late 1800s. It did not become a modern commercial sector until Bell Labs created the first practical silicon solar cell in 1954, which initially found…
-
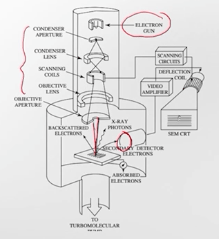
Scanning Electron Microscopy, or SEM, is a way to take very close‑up pictures of tiny things by shooting a thin beam of electrons onto a sample and moving the beam back and forth like a scanner. When the electrons hit the surface, they knock out other electrons and sometimes cause the material to emit X‑rays;…
-
A key logger (short for “key logger”) is a software or hardware tool that records the keys pressed on a keyboard, capturing the characters typed by a user. The collected data can include passwords, messages, personal information, and any other text entered on the device. Key loggers are often used covertly to monitor activity without…
-
Electron beam characterization involves using a focused beam of electrons to probe and analyze materials at very fine scales. Techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) rely on the interaction between electrons and the atoms in a sample to reveal details about surface morphology, internal structure, and even chemical composition.…
-
Solar cells, often called photovoltaic cells, are semiconductor devices that convert light from the sun directly into electrical energy. They form the basic building block of solar panels and many other solar power systems. Basic idea A solar cell takes incoming light, absorbs part of that light inside a semiconductor, and turns the absorbed energy…
-
MOSFETs, or Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors, are essential components in modern electronics, and understanding their operating characteristics is crucial for anyone interested in electronics. These devices function as switches or amplifiers, controlling the flow of electrical current. The key to their operation lies in the voltage applied to the gate terminal, which influences the conductivity between…
-
Understanding oxide charge density in semiconductors is an important concept in electronics and materials science. Semiconductors are materials that have electrical properties between those of conductors and insulators. They are essential for making electronic devices like computers and smartphones. The oxide charge density refers to the amount of electric charge that is stored in the…
-
The flatband capacitance (CFB) is defined as the total measured capacitance of a Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) structure or a similar semiconductor device when the applied gate voltage is exactly equal to the flatband voltage VFB. This flatband voltage represents the specific potential needed to establish the flatband condition, where the energy bands within the semiconductor substrate…
-
-
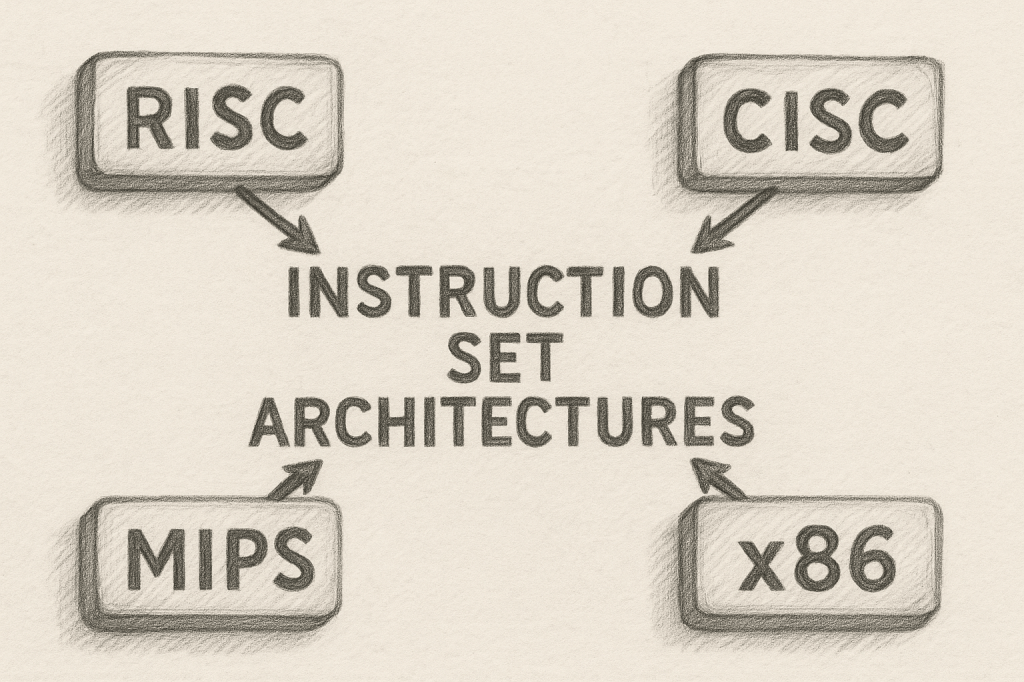
Instruction set architectures (ISAs) are crucial components of computer systems that define how software communicates with hardware. They specify the set of instructions that a processor can execute, including operations like arithmetic, data movement, and control flow. By establishing a standard interface, ISAs allow programmers to write software that can run on different hardware platforms…
-
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas, primarily methane, that has been converted into a liquid state by cooling it to approximately 260 degrees Fahrenheit (162 Degrees Celcius) a cryogenic process that dramatically reduces its volume to about 1/600th of its gaseous state. This enormous volume reduction makes it economically feasible and safe to transport…
-
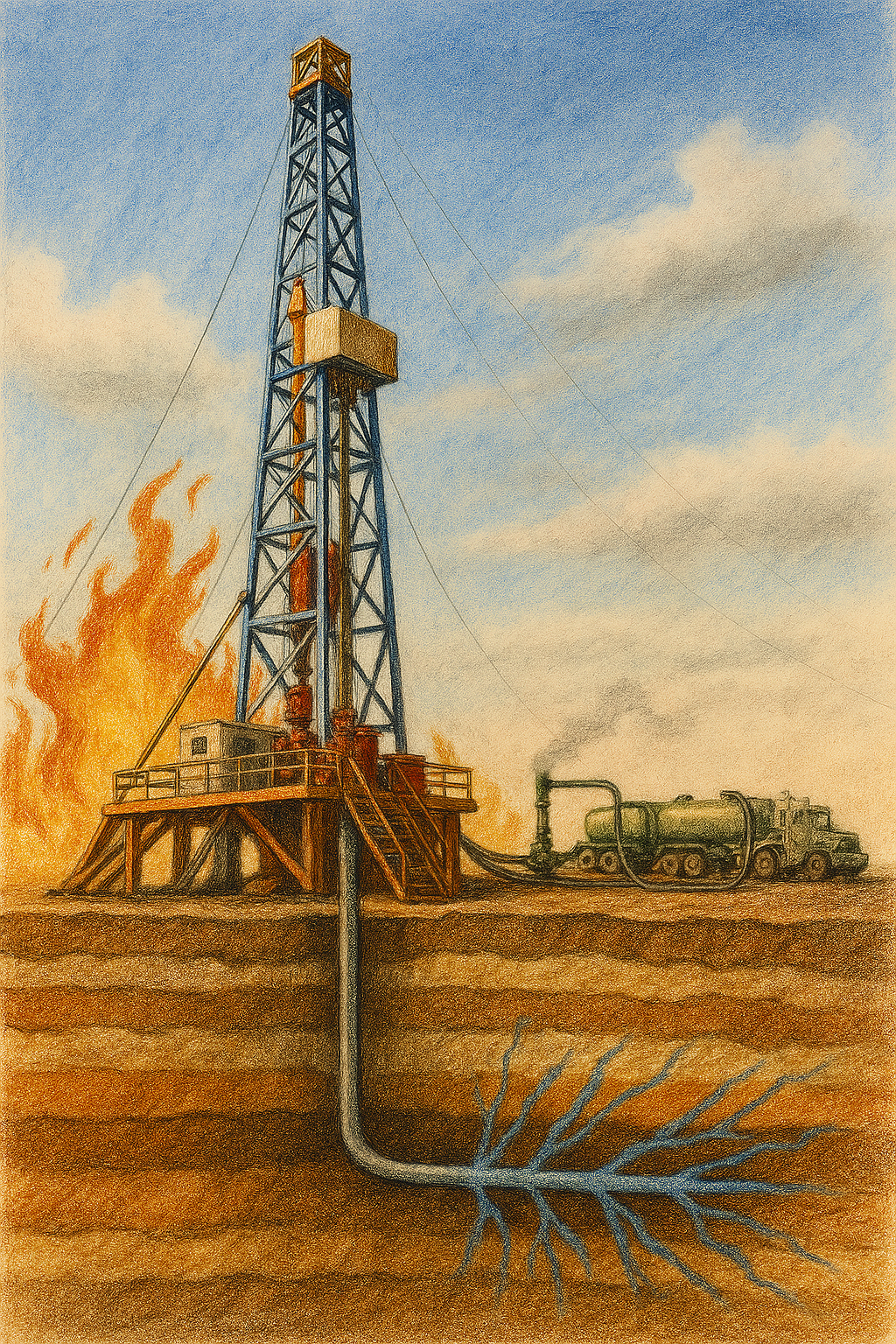

Drilling in the oil and gas industry refers to the complex, multi-stage operation of penetrating the Earth’s surface to reach underground reservoirs of hydrocarbons. It begins with site selection and permitting, followed by the deployment of a drilling rig—a towering structure equipped with rotary systems, drill bits, and support equipment. The process involves rotating a…
-
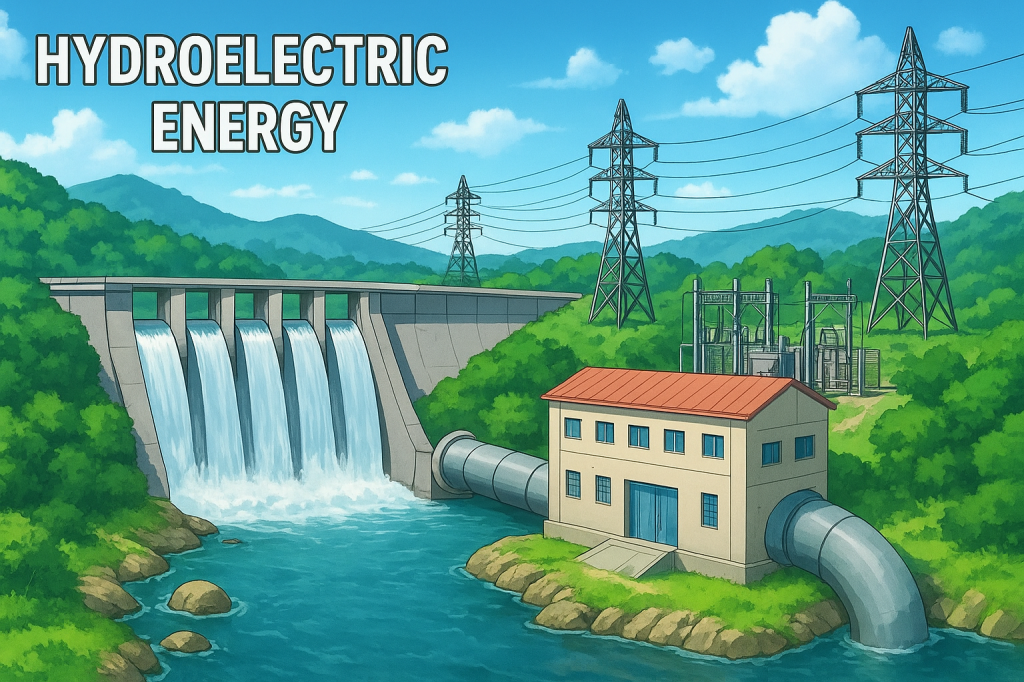
Hydroelectric energy is power produced by capturing the movement of water and converting it into electricity. Water stored in a reservoir or flowing naturally in a river passes through turbines that spin generators. This process transforms the mechanical motion of water into electrical energy through controlled and predictable operation. The system depends on gravity, flow…
-

Energy is a fundamental concept in both science and everyday life, representing the capacity to perform work or produce change. It exists in various forms, including kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion, and potential energy, which is stored energy based on an object’s position or state. For instance, a moving car possesses kinetic…
-

Solar energy is the energy that comes from the sun. It is a renewable source of energy, which means it can be used over and over again without running out. The sun produces an enormous amount of energy every day, and scientists have developed ways to capture and use this energy for various purposes. Solar…
-
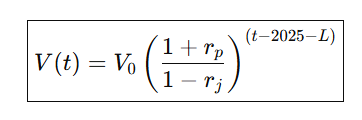
Power Efficiency Theory could also be used to measure the “physical intrinsic value” of products across different markets. When a well-off individual says something like a market asset would “fall to its utility value”, they are implying that the asset has been miscalculated due to superficial or artificial or non-physical factors that sometimes enter the…
-

Renewable energy is power that comes from sources that are constantly and naturally refilled. Imagine energy sources that never run out because they are always being replaced. This is different from fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels took millions of years to form deep underground, and when we use them up,…
-
We know that Force is equal to mass times acceleration. A home has physical mass, structural strength, and load-bearing capacity. These properties give it force capacity in the physical sense. However, a home does not move and does not perform continuous work, so its velocity is effectively zero. As a result, its power output, in…
-
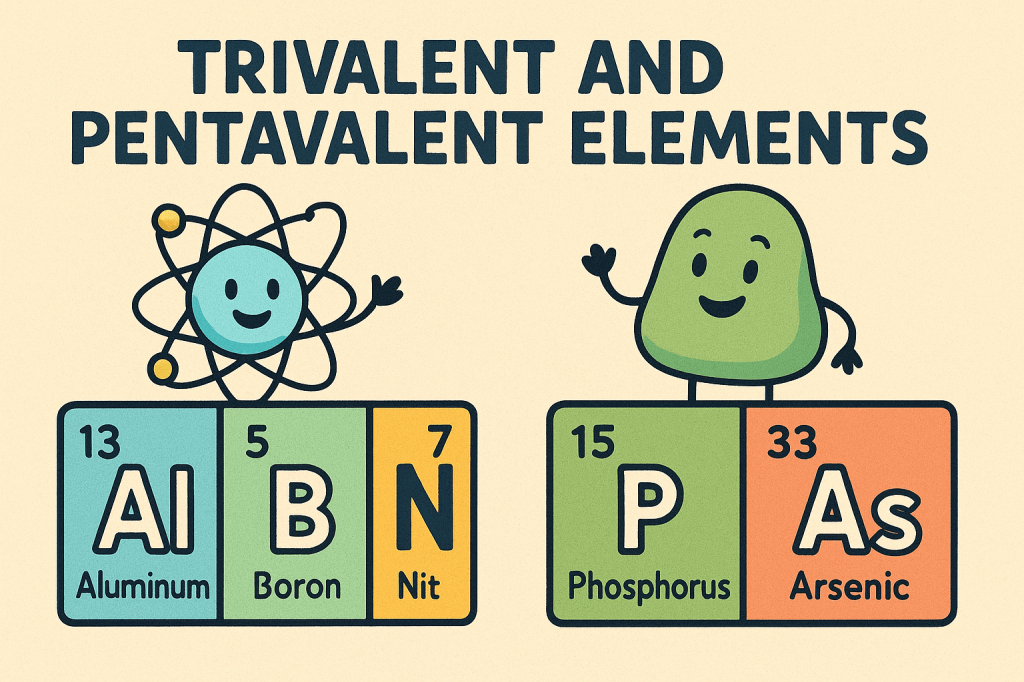
Trivalent and pentavalent elements are terms used to describe the number of valence electrons that an atom has available for bonding. Trivalent elements have three valence electrons, which means they can form three bonds with other atoms. This property is often seen in elements like aluminum and gallium. These elements typically participate in chemical reactions…
-
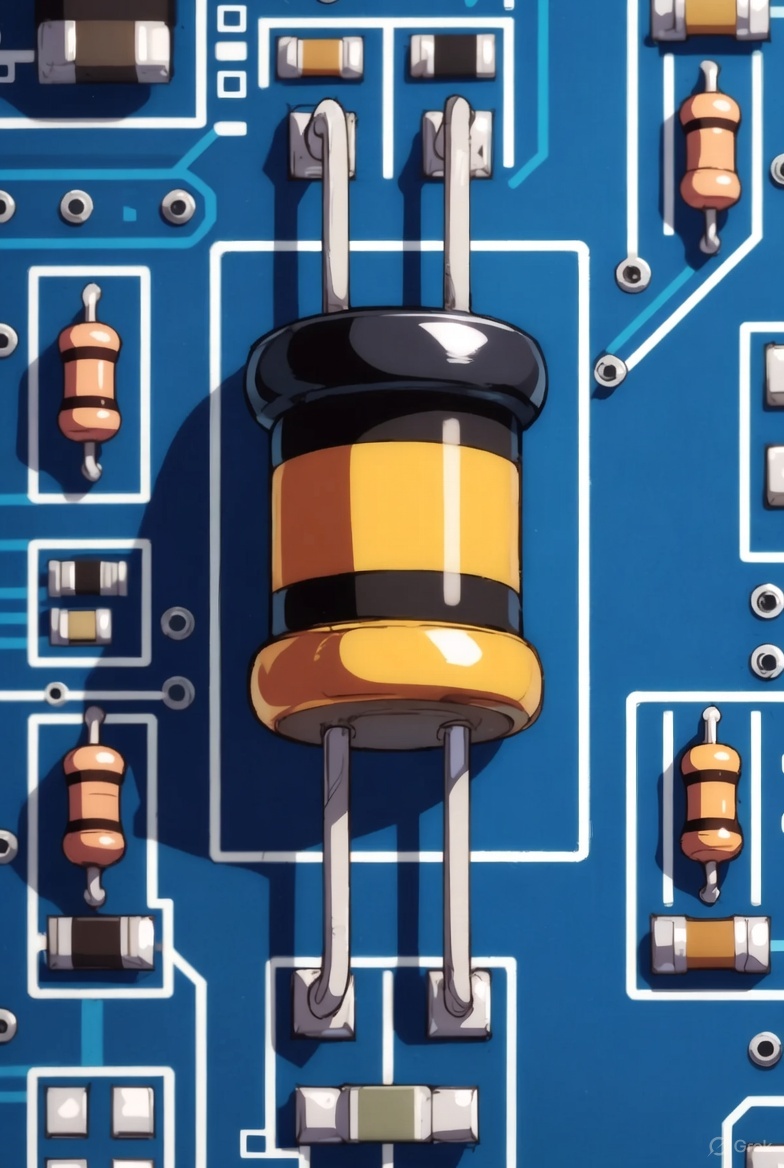
When we talk about diode series resistance, we are referring to the resistance that is present in the diode when it is conducting current. This resistance is not just a simple number; it can change based on various factors, such as the amount of current flowing through the diode and the temperature of the diode…
-
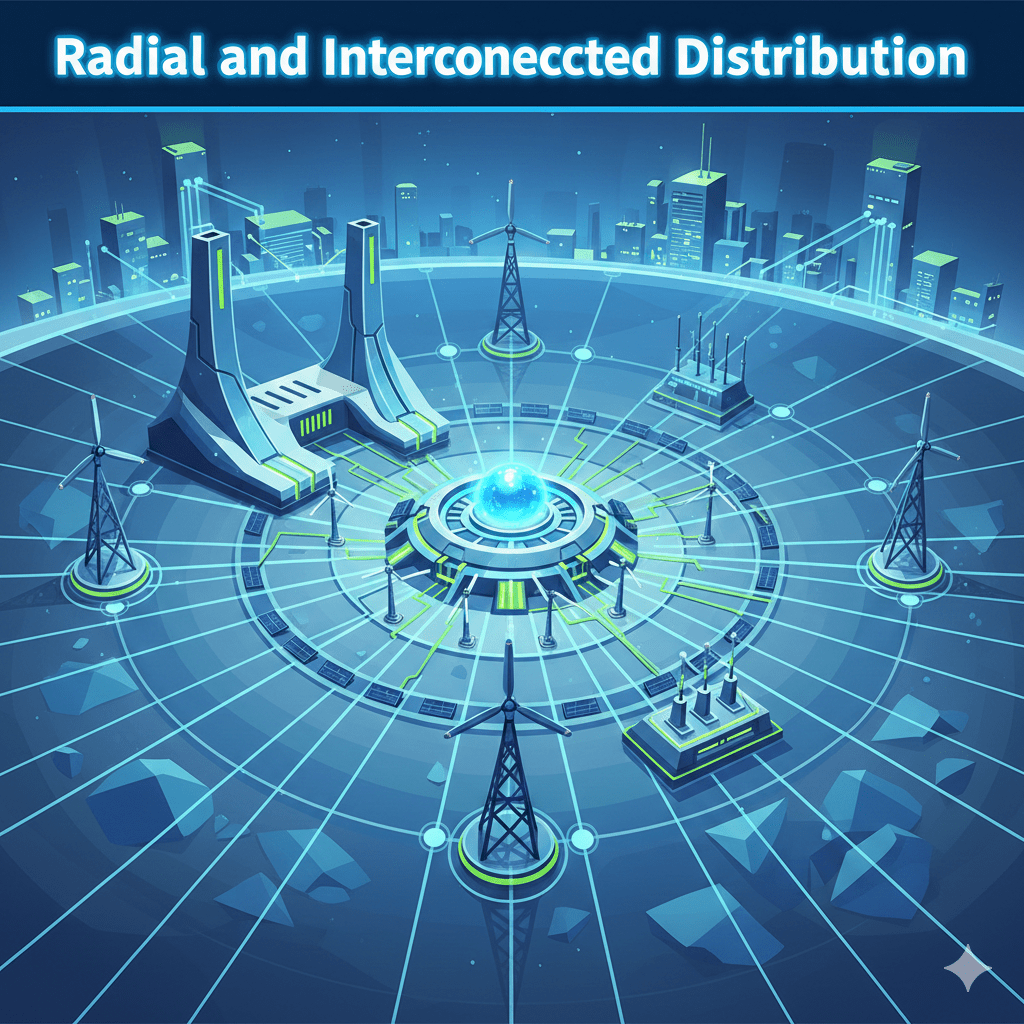
Radial and interconnected distribution networks represent two distinct approaches to the design and operation of electrical distribution systems. A radial distribution network is characterized by a tree-like structure where power flows from a single source through a series of branches to reach various consumers. This configuration is straightforward and easy to manage, but it can…
-
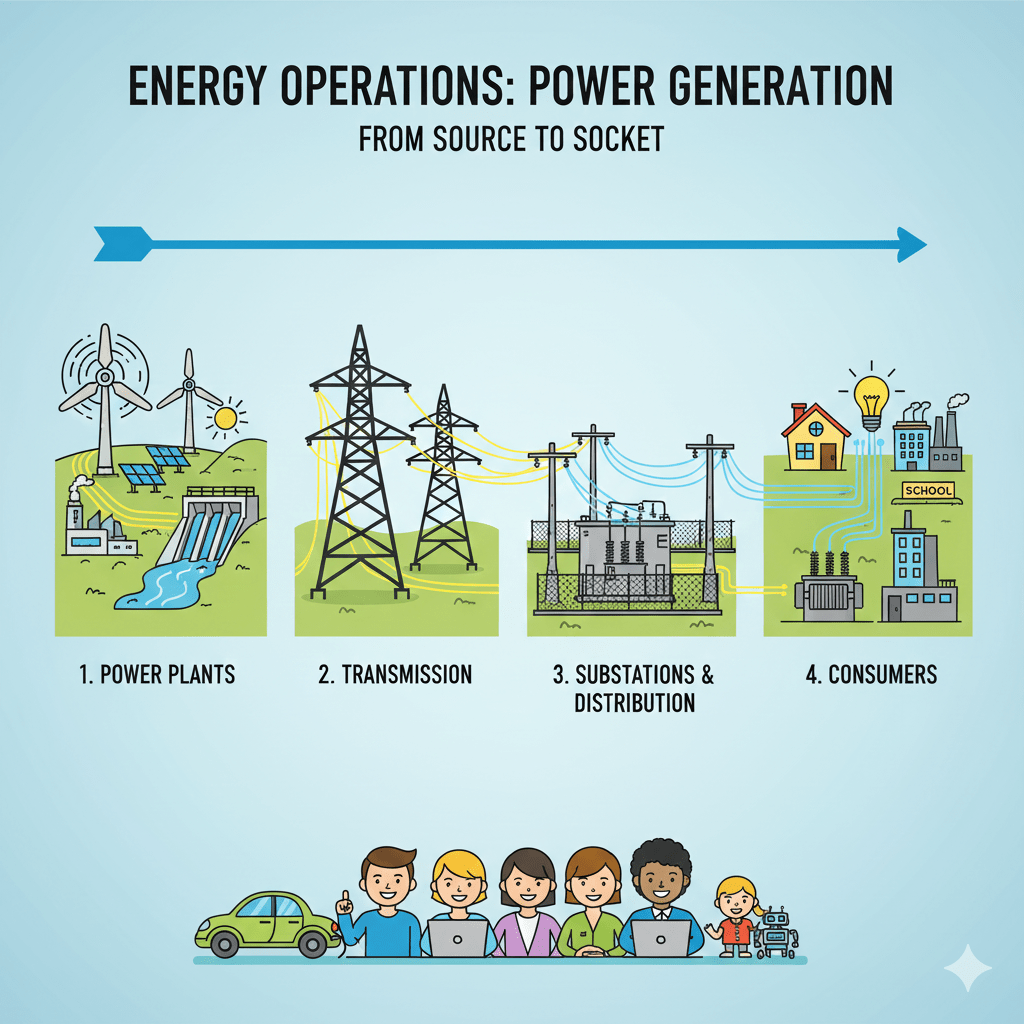
Power generation in terms of the energy grid refers to the process of producing electrical power at power stations or generation assets, which are connected to an interconnected network called the electrical grid. This grid is a complex system comprising power generation facilities, transmission lines, substations, distribution lines, and consumers. The power generated comes from…
-
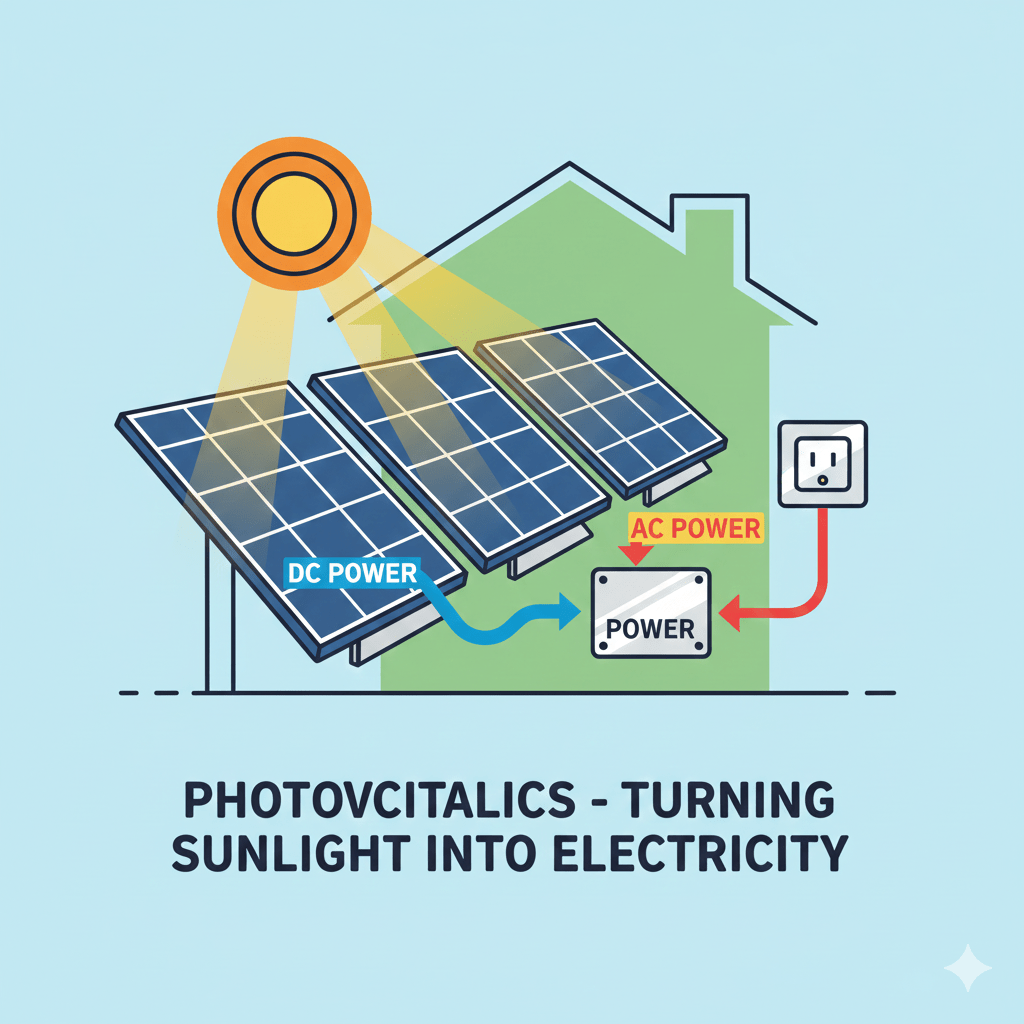
Photovoltaics is the technological principle and scientific field concerned with the direct conversion of light energy, specifically photons from sunlight, into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect, a physical and chemical process that occurs within a class of materials known as semiconductors, most commonly crystalline silicon. The fundamental unit of this conversion is the photovoltaic cell,…
-
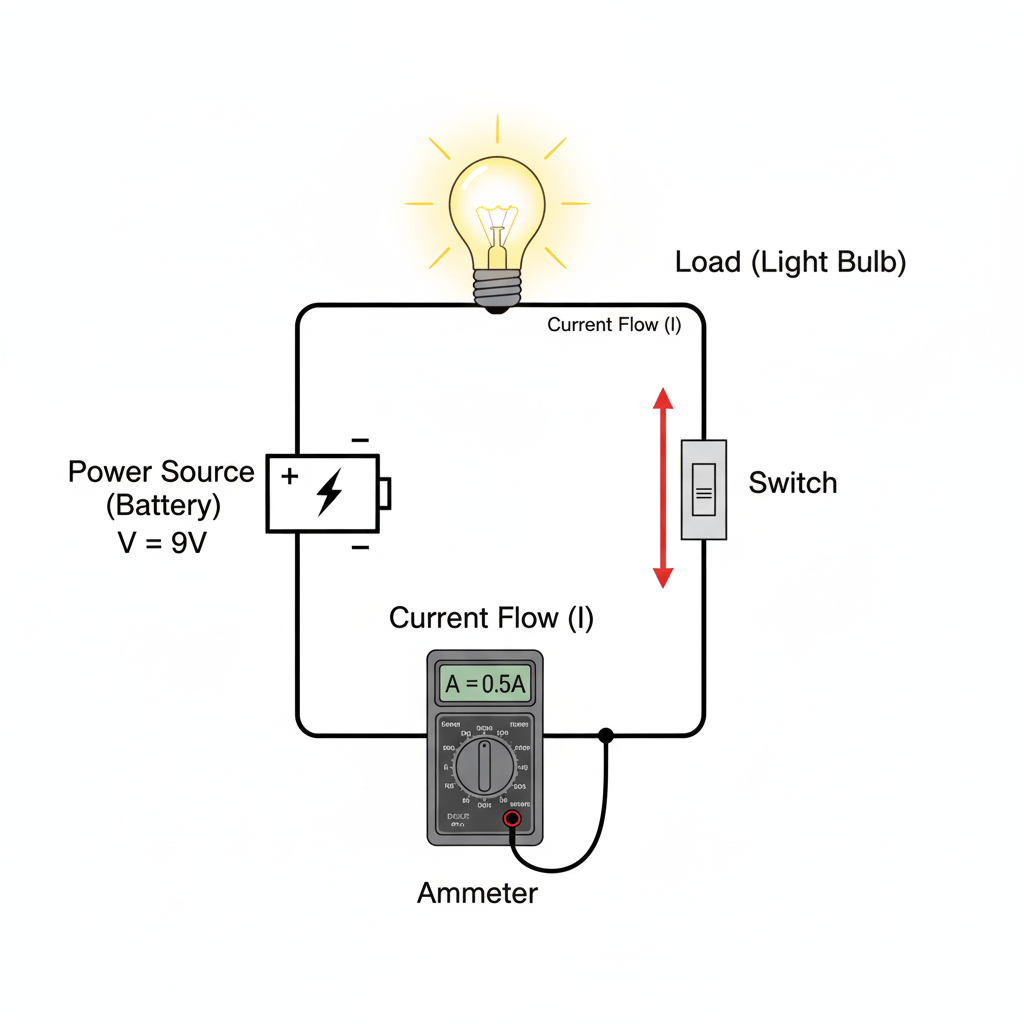
A simple circuit is an electrical circuit that consists of just a few basic components, creating a closed loop through which electric current flows. Typically, it includes a power source like a battery, a conductive path such as wires, and a load, which can be a device like a light bulb or resistor that uses…
-
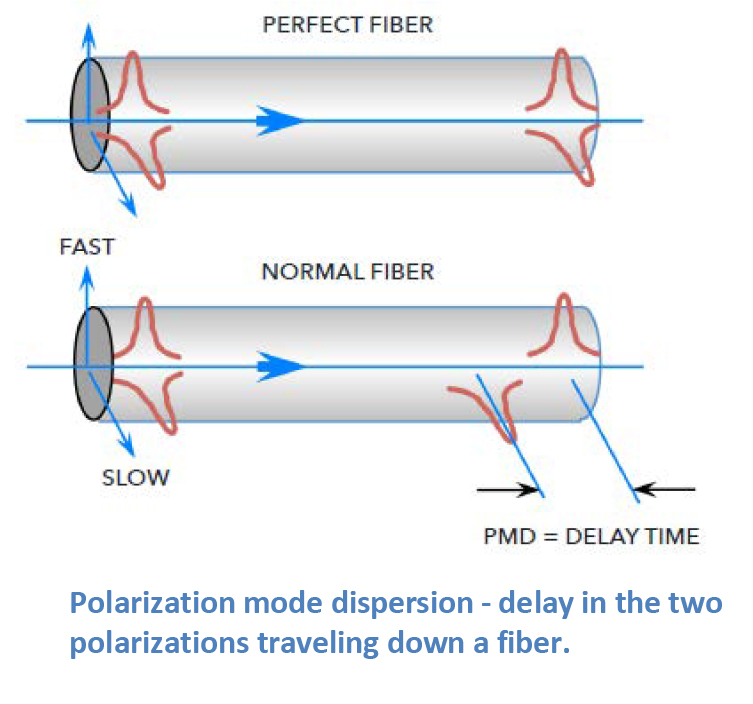
Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) refers to the distortion of optical signals caused by slight differences in the propagation speed of light’s polarization modes as they travel through fiber. In an ideal optical fiber, light of all polarization states should move uniformly. However, imperfections, asymmetries, and environmental stress within the fiber cause birefringence—splitting the light into…
-

Contact resistance in semiconductor diodes refers to the parasitic electrical resistance that arises at the interfaces between the semiconductor material and the metal contacts (electrodes) that are attached to it. These metal-semiconductor interfaces are critical for injecting current into or extracting current from the active regions of the diode. The origin of this resistance is…
-
Resistance is the measurable opposition to the flow of electric current presented by a specific, complete object, such as a wire or a resistor. It is an extrinsic property, meaning its value is not fixed but is instead dictated by the physical geometry of the object. A long and narrow component will exhibit high resistance, making…
-
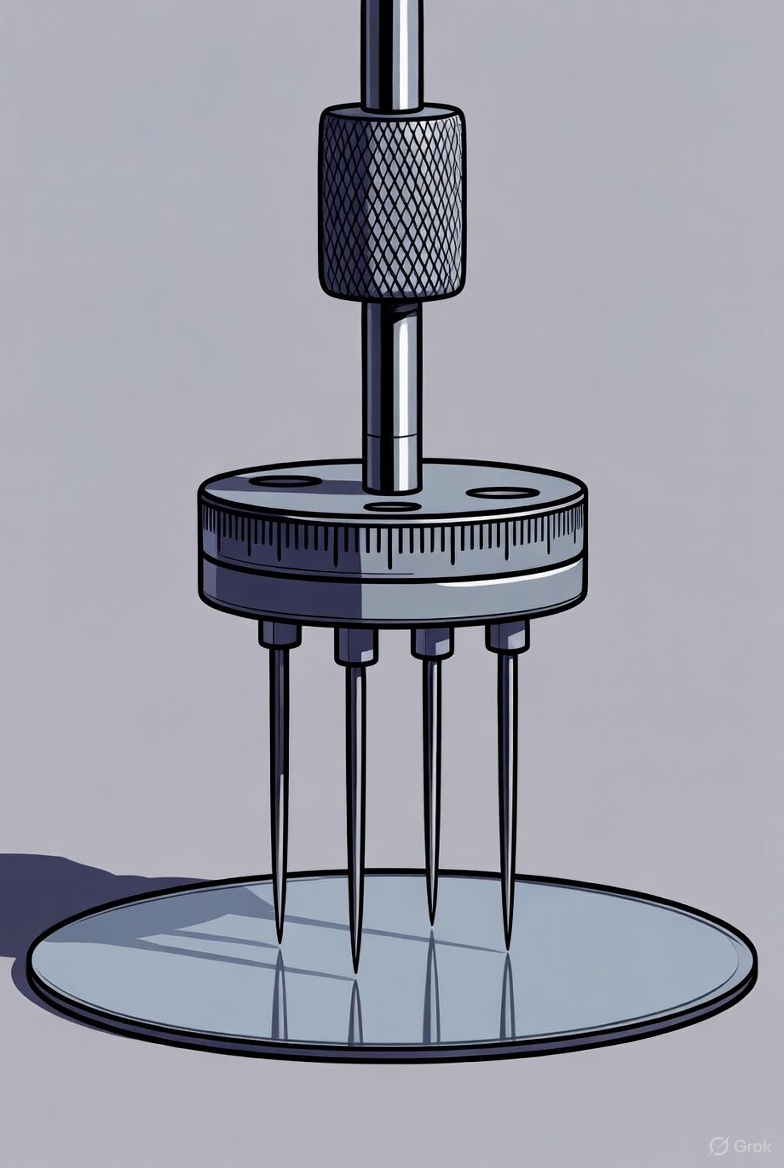
The Four-Point Probe (4PP) method is a standard, non-destructive technique used in semiconductor manufacturing and research to accurately measure the sheet resistance and subsequent resistivity of thin films, wafers, and other semiconductor materials. This technique uses a linear array of four closely spaced, collinear probes typically made of tungsten or beryllium copper, each mounted on…
-
A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor device that permits current to flow primarily in one direction, making it a fundamental component in electronics. Electrical characterization of diodes involves analyzing their current–voltage (I–V) relationship, which reveals distinct operating regions. In a diode, the anode and cathode are the two terminals that define its directionality and electrical…
-

Power Efficiency Theory states that the value of a thing is determined by how fast its performance improves and how quickly its energy cost per unit output declines. Starting from an initial value V₀, the value grows each year by the performance improvement factor (1 + rₚ) and is scaled upward by the inverse of…
-

In semiconductor technology, particularly within the foundational Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) structure, oxide charges represent a critical class of parasitic defects—localized electric charges trapped either within the gate oxide layer (typically silicon dioxide) or at its delicate interface with the semiconductor substrate. These charges are not intentional but are inevitable byproducts of fabrication imperfections, chemical contamination, or…
-
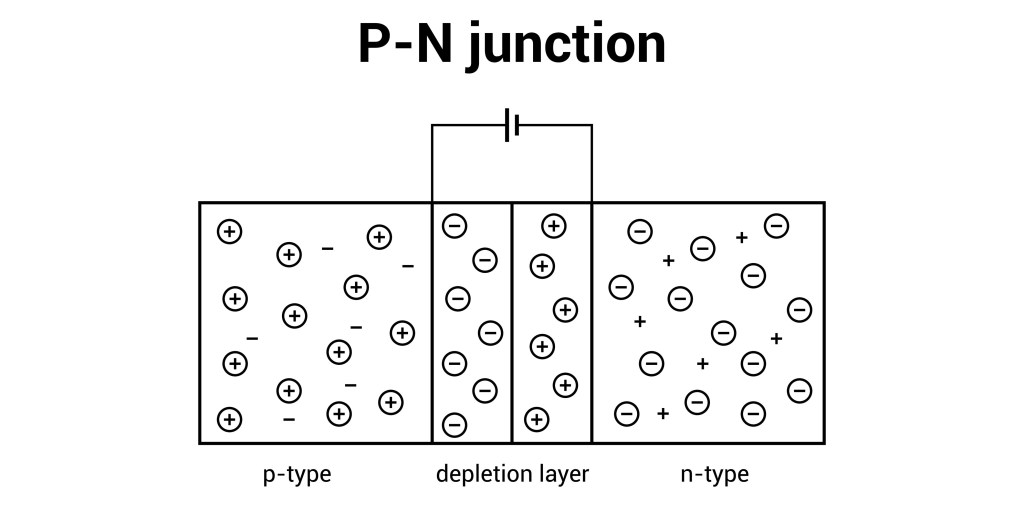
A p-n junction diode is the simplest form of a semiconductor electronic device, created by joining a p-type and an n-type semiconductor material within a single crystal. The p-type material is doped with acceptor impurities, resulting in an excess of holes (positive charge carriers), while the n-type material is doped with donor impurities, resulting in…
-

The I-V characteristics of a diode describe how the electric current flowing through the device responds to changes in the voltage applied across its terminals. In forward bias, when the positive terminal of a voltage source is connected to the diode’s anode and the negative to its cathode, the diode initially resists current flow until…
-
-
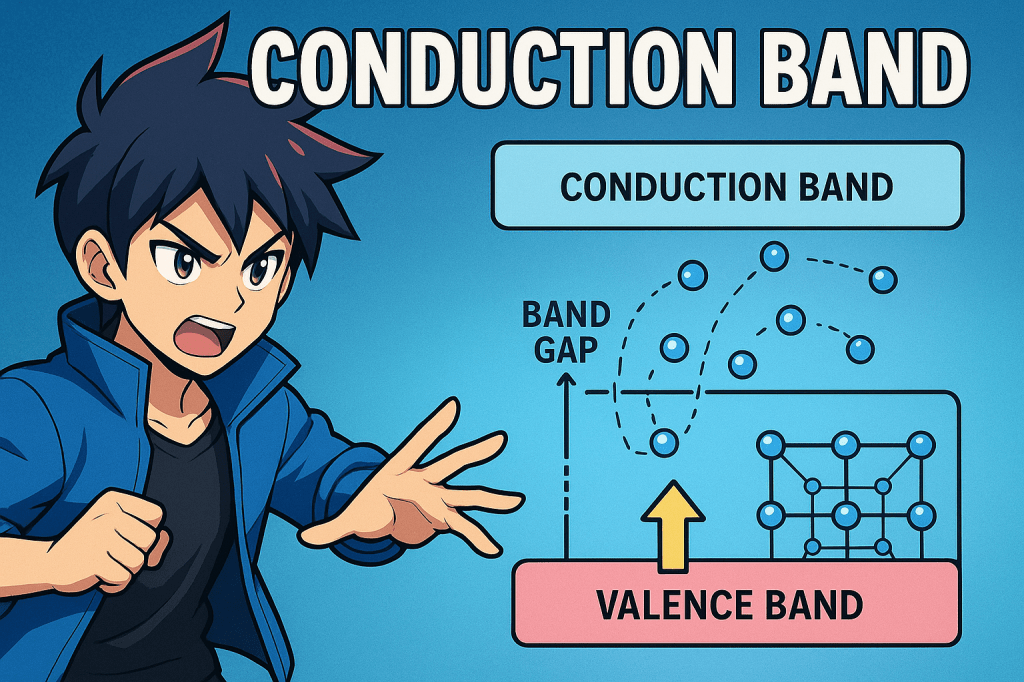
The conduction band is the range of electron energies in a solid where electrons are free to move and contribute to electrical conduction. It lies above the valence band and is typically empty at absolute zero temperature. When electrons gain sufficient energy to jump from the valence band to the conduction band, they become delocalized…
-
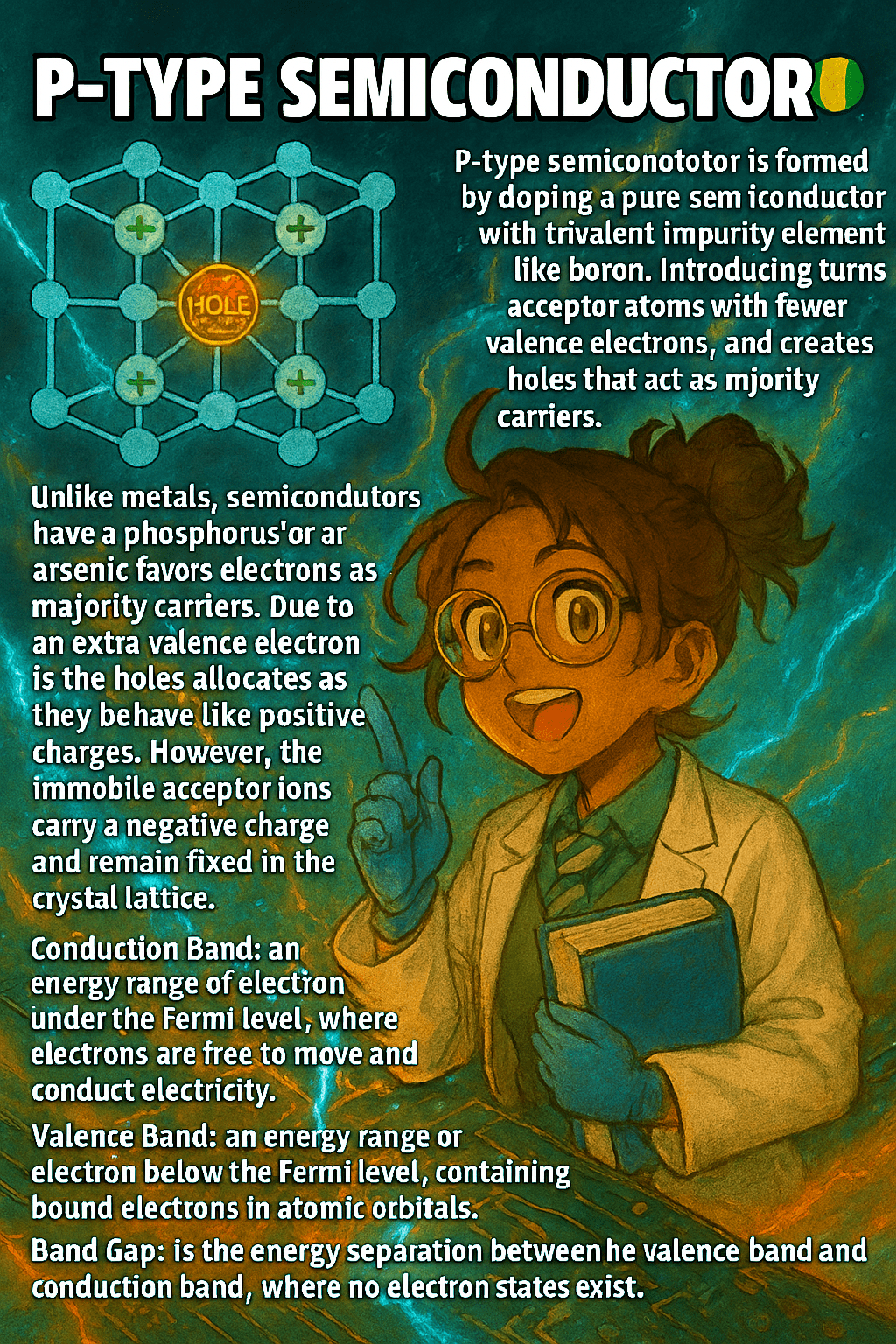
A p-type semiconductor is formed by doping a pure semiconductor, such as silicon, with trivalent elements like boron, gallium, or indium. These dopants have only three valence electrons, one fewer than silicon, which creates a vacancy or “hole” in the crystal lattice. Holes act as positive charge carriers because electrons from neighboring atoms can move…
-

The valence band is the highest range of electron energies in a solid where electrons are normally present at absolute zero temperature. These electrons are bound to atoms and participate in chemical bonding, such as covalent or metallic bonds. In crystalline solids, the valence band is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals, creating a…
-
An n-type semiconductor is created by doping a pure semiconductor, such as silicon, with pentavalent elements like phosphorus, arsenic, or antimony. These dopants have five valence electrons, one more than silicon, and the extra electron becomes loosely bound and available for conduction. As a result, electrons become the majority charge carriers in n-type materials, while…
-

Semiconductors are materials whose electrical conductivity lies between that of conductors and insulators, and they are unique because their properties can be controlled and modified. Semiconductors are chemically diverse materials whose electrical conductivity lies between that of conductors and insulators, and their behavior can be precisely engineered. The most common elemental semiconductors are silicon (Si),…
-

Conductors are materials that permit the easy flow of electric current due to the presence of free or loosely bound electrons in their atomic structure. In metals such as copper, silver, and aluminum, the outermost electrons are not tightly attached to their atoms, allowing them to move freely when a voltage is applied. This mobility…
-
Resistivity is a fundamental property of materials that describes how strongly they oppose the flow of electric current. Unlike resistance, which depends on the dimensions of a conductor, resistivity is an intrinsic characteristic that remains constant for a given material under specific conditions. It is mathematically expressed as, where is the resistance, is the cross-sectional…
-

Photon absorption and emission are fundamental processes in semiconductor physics that enable the operation of optoelectronic devices like solar cells, LEDs, and lasers. Absorption occurs when a photon strikes the semiconductor and excites an electron from the valence band to the conduction band, leaving behind a positively charged hole. This transition creates an electron–hole pair,…
-
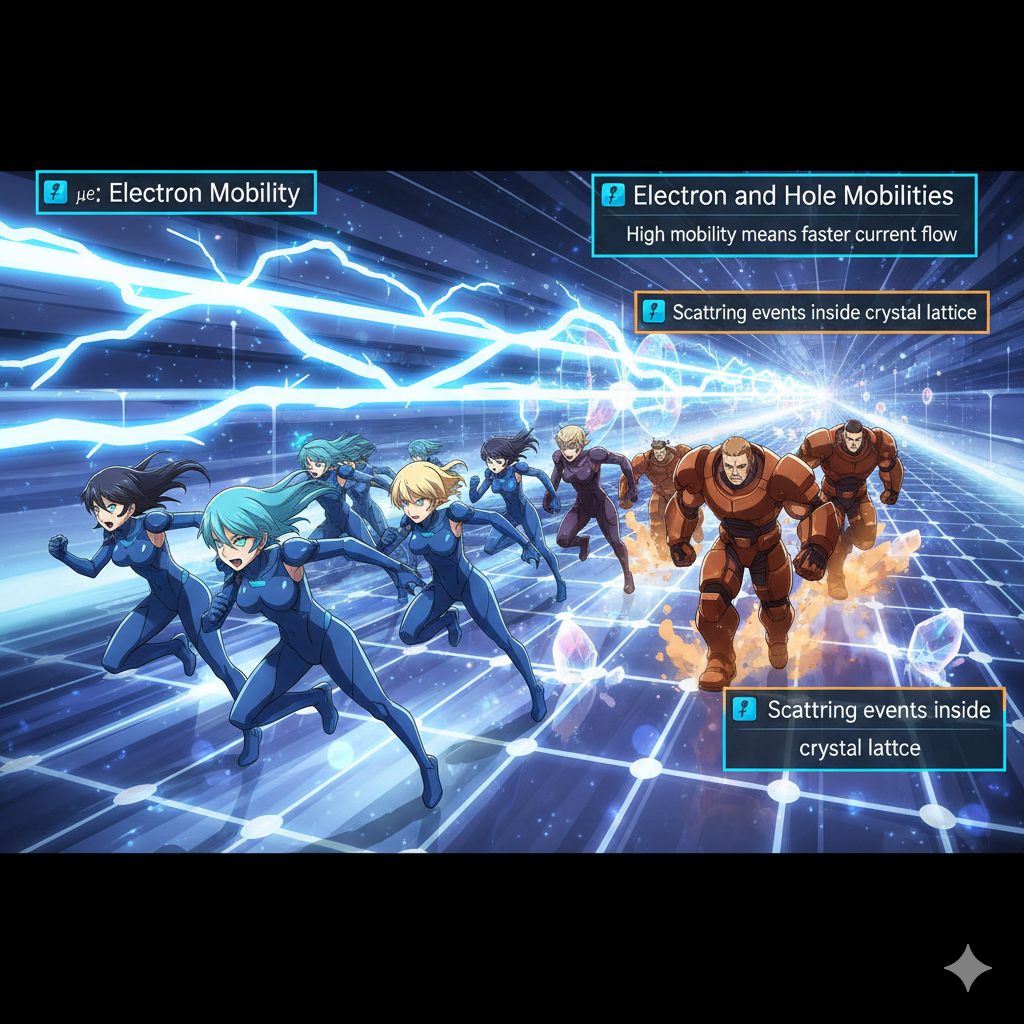
Mobility measures how quickly charge carriers move through a semiconductor when an electric field is applied. Electron mobility (μe): the speed of electrons per unit electric field. Hole mobility (μh): the speed of holes per unit electric field. High mobility means faster current flow and better device performance. Mobility depends on factors such as temperature,…
-
Photoelectric measurement in industrial robotics is a high-precision sensing technique that relies on the detection of light to determine the position, movement, or presence of objects within an automated system. It typically involves a light source, optics, a scanning grid, and a photoelectric sensor that responds to changes in illumination caused by transitions between light…
-

In robotics engineering, gearboxes play a crucial role by regulating torque, speed, and mechanical stability within a robot’s motion system. Engineers rely on gearboxes to ensure that robotic arms and actuators deliver precise, controlled movements under varying loads and operating conditions. Common gear types used in robotics include planetary gears, harmonic drives, and spur gears,…
-

Robot kinematics refers to the mathematical and geometric study of how robots move. It focuses on the relationships between joint angles, link lengths, and the position and orientation of the robot’s end effector (such as a gripper or tool). In industrial robots, kinematics helps engineers determine how to move a robotic arm from one point…
-

Drive systems are the mechanisms that power a robot’s joints and enable movement. They act like the robot’s muscles, converting energy into motion. The three main types are electric, hydraulic, and pneumatic drive systems. Electric drives, using motors like servos or steppers, are common due to their precision and control. Hydraulic systems offer high force…
-
Industrial robots are highly versatile automation systems designed for a wide range of tasks in manufacturing and production environments. They are freely programmable, meaning their operations can be customized and reconfigured for different applications. These robots are also freely positionable, allowing them to be installed in various locations within a facility. Their universal applicability makes…
-

In semiconductor crystals, the atomic arrangement is defined by a combination of a Bravais lattice and a basis. The Bravais lattice provides the geometric framework—an infinite array of points arranged with translational symmetry—where each point has an identical environment. There are 14 unique Bravais lattices in three dimensions, grouped into seven crystal systems such as…
-
Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) occurs when light traveling through a single-mode optical fiber splits into two orthogonal polarization components that propagate at slightly different velocities. This phenomenon is caused by random imperfections, asymmetries, and external stresses in the fiber, such as core ellipticity, bending, or temperature fluctuations. In an ideal fiber, both polarization modes would…
-

Polishing fiber is the final stage in preparing an optical fiber connector, ensuring a smooth, scratch-free end face that allows for minimal signal loss and optimal light transmission. The procedure begins after the fiber has been cleaved and secured in a connector ferrule using epoxy or a mechanical fit. Once the adhesive cures, the protruding…
-

WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a method of combining multiple optical signals onto one fiber strand by assigning each signal a unique wavelength. These wavelengths act like separate channels, allowing parallel transmission of data without interference. This dramatically increases the capacity of fiber networks without laying additional fiber. Each signal is generated by a laser…
-

A satellite dish system is designed to receive radio signals transmitted from communication satellites orbiting the Earth, converting them into usable data for televisions, modems, or network systems. The system is composed of several key components that work together to capture, focus, and transmit these signals efficiently. The dish, also called the parabolic reflector, is…
-
Fire safety in cable installations is a critical aspect of both data center and field operations, ensuring the protection of personnel, equipment, and infrastructure. The first step toward minimizing fire risk begins with selecting the correct cable type for the environment. Plenum-rated cables, labeled CMP, are designed for air-handling spaces such as ceiling voids or…
-

MoCA, or Multimedia over Coax Alliance, is a technology that allows for networking over existing coaxial cable systems in homes. It enables the use of coaxial cables to create a high-speed Ethernet connection, providing a reliable and efficient way to distribute internet access throughout a home without the need for new wiring. MoCA networks can…
-
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a networking standard that delivers DC electrical power along with data signals through standard twisted-pair Ethernet cabling (typically Cat5e, Cat6, or higher). This innovation eliminates the need for separate power cords or outlets near devices, simplifying installation and reducing infrastructure costs. PoE works by injecting power into the Ethernet cable…
-
Pickaxe is an open-source software agent developed for use with Foreman.mn, a Bitcoin mining management platform. It serves as the intermediary between ASIC mining hardware and the Foreman dashboard, enabling operators to collect, transmit, and visualize real-time performance data. Running locally on a computer or server within the mining environment, Pickaxe queries miners directly to…
-
-

Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) is the original analog telephone system that laid the foundation for modern voice communication. Operating over twisted-pair copper wires, POTS transmits voice signals as continuous electrical waveforms. It uses a circuit-switched network, meaning each call establishes a dedicated line between two endpoints, ensuring consistent voice quality. One of its defining…
-

Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT) is a type of signal interference that occurs when a transmitted signal on one wire pair induces unwanted noise onto an adjacent pair at the same end of the cable where the signal originated. NEXT is most commonly encountered in twisted-pair cabling systems, such as those used in Ethernet networks. It happens…
-

Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a powerful imaging technique that uses a beam of electrons transmitted through an ultrathin specimen to produce highly magnified images of its internal structure. TEM works by directing electrons through a sample that is typically less than 100 nanometers thick. As the electrons pass through, they interact with the atoms…
-
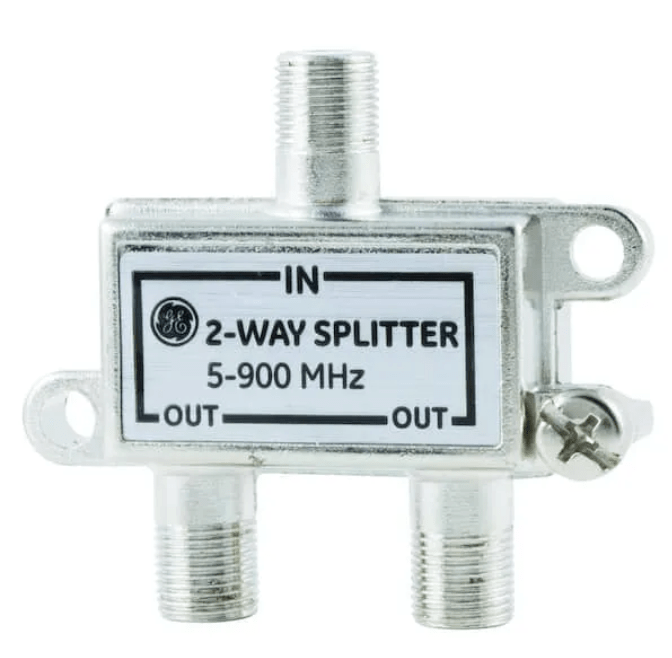
A splitter in terms of coaxial cable is a passive device that divides a single incoming radio frequency signal into multiple outputs, allowing several devices such as televisions, modems, or receivers to share the same signal source. It maintains a standard impedance of 75 ohms to prevent signal reflection and distortion, ensuring stable performance across…
-
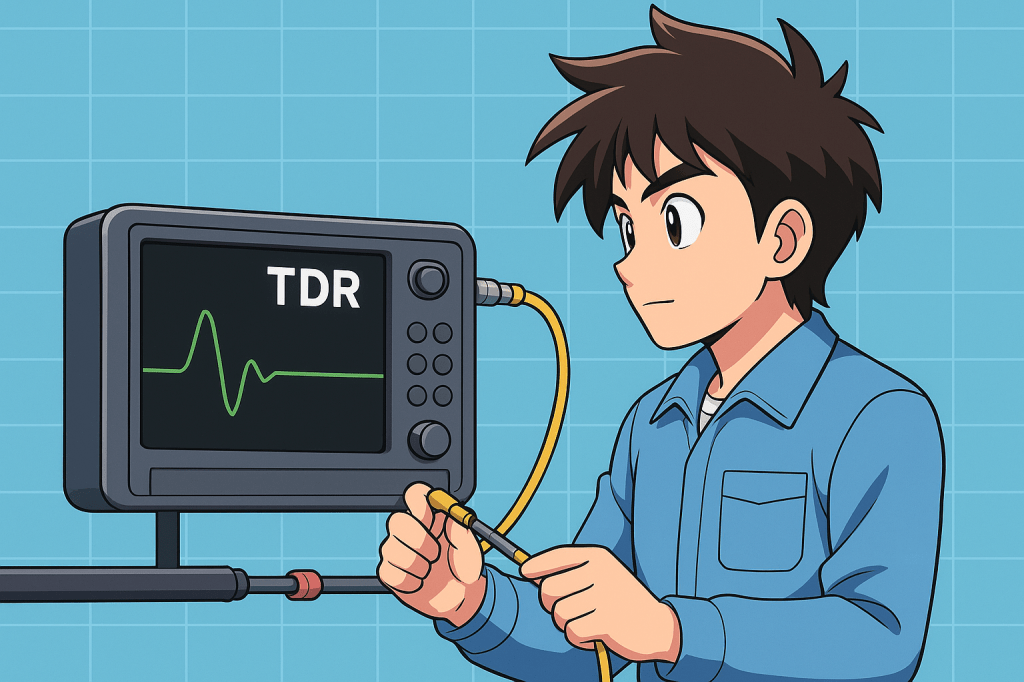
A Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR) is a diagnostic instrument used to detect faults, breaks, and impedance mismatches in coaxial cables by sending a signal pulse down the line and analyzing the reflections that return. When the pulse encounters a change in impedance—such as a splice, open, short, or damaged section—it reflects back to the TDR,…
-
A coaxial cable is a specialized electrical cable designed to carry high-frequency signals with minimal interference. Its name comes from its concentric structure—each layer shares the same axis, which helps preserve signal integrity. Coaxial cables are widely used in applications like cable television, internet service, radio transmission, and closed-circuit video systems. At the center of…
-

In telecom infrastructure, MXC is a synonym for MDF—both refer to the Main Cross-Connect, the central point where external carrier circuits interface with a building’s internal network. The Main Cross-Connect (MXC), also known as the Main Distribution Frame (MDF), is the primary physical interconnection point in a facility’s telecommunications system. It serves as the demarcation…
-

A patch cord is a short, pre-terminated cable with connectors on both ends, used to connect network devices for signal or data transmission. Patch cords are essential components in structured cabling systems, enabling flexible and efficient interconnections between equipment such as switches, routers, servers, and patch panels. They are typically used in environments like data…
-

The Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) was originally formed in 1924 as the Radio Manufacturers Association. It evolved into a major standards body for electronic components and systems in the United States. EIA was responsible for developing specifications that ensured interoperability and quality across manufacturers, particularly in consumer electronics and telecommunications. In 1988, EIA’s telecommunications division…
-

A premise cable technician specializes in installing and maintaining cabling systems within buildings or campuses. Their work typically involves running Ethernet, coaxial, and fiber optic cables through walls, ceilings, and conduits to support voice, data, and video services. These technicians are responsible for terminating cables at patch panels and jacks, testing and certifying cable runs…
-

At Tesla’s annual meeting in Austin, Texas, shareholders overwhelmingly approved CEO Elon Musk’s 2025 performance-based compensation plan, with more than 75% voting in favor. The plan, potentially worth up to $1 trillion, hinges on achieving ambitious milestones such as an $8.5 trillion market capitalization and deploying one million robotaxis by 2035. The approval effectively replaces…
-

A Visual Fault Locator (VFL) is a handheld optical testing device used in fiber optic networks to identify faults, breaks, or discontinuities in optical fibers. It emits a highly visible red laser light (usually around 650 nm) into the fiber, which allows technicians to visually trace the fiber path. Any break, bend, or poor connection…
-
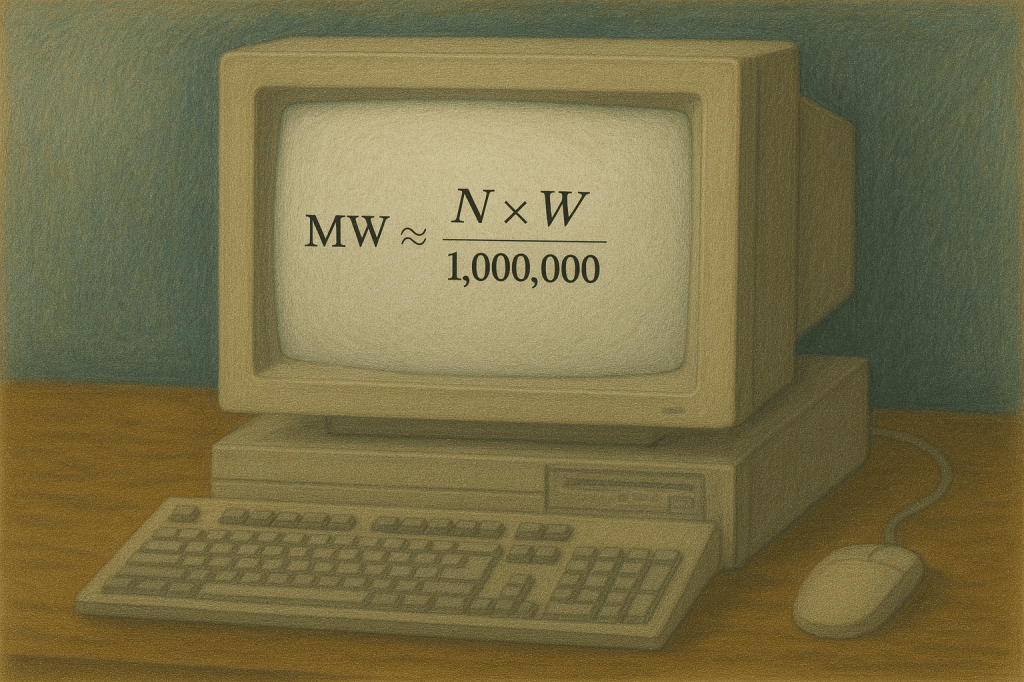
The Bitcoin Mining Air Coolant Energy Operation Equation offers a simple way for bitcoin mining engineers to translate machine count into megawatts in a language that utility operators and engineers understand. The core idea is that modern air cooled ASIC miners usually draw around 3,000 to 3,500 watts per machine, so a fleet’s IT load…
-

Direct burial in fiber optics refers to the installation of specially designed fiber optic cables directly into the ground without the need for protective conduits or ducts. These cables are engineered to withstand harsh underground conditions for long-term, maintenance-free operation. Direct burial fiber optic cables are constructed with multiple protective layers to endure soil pressure,…
-
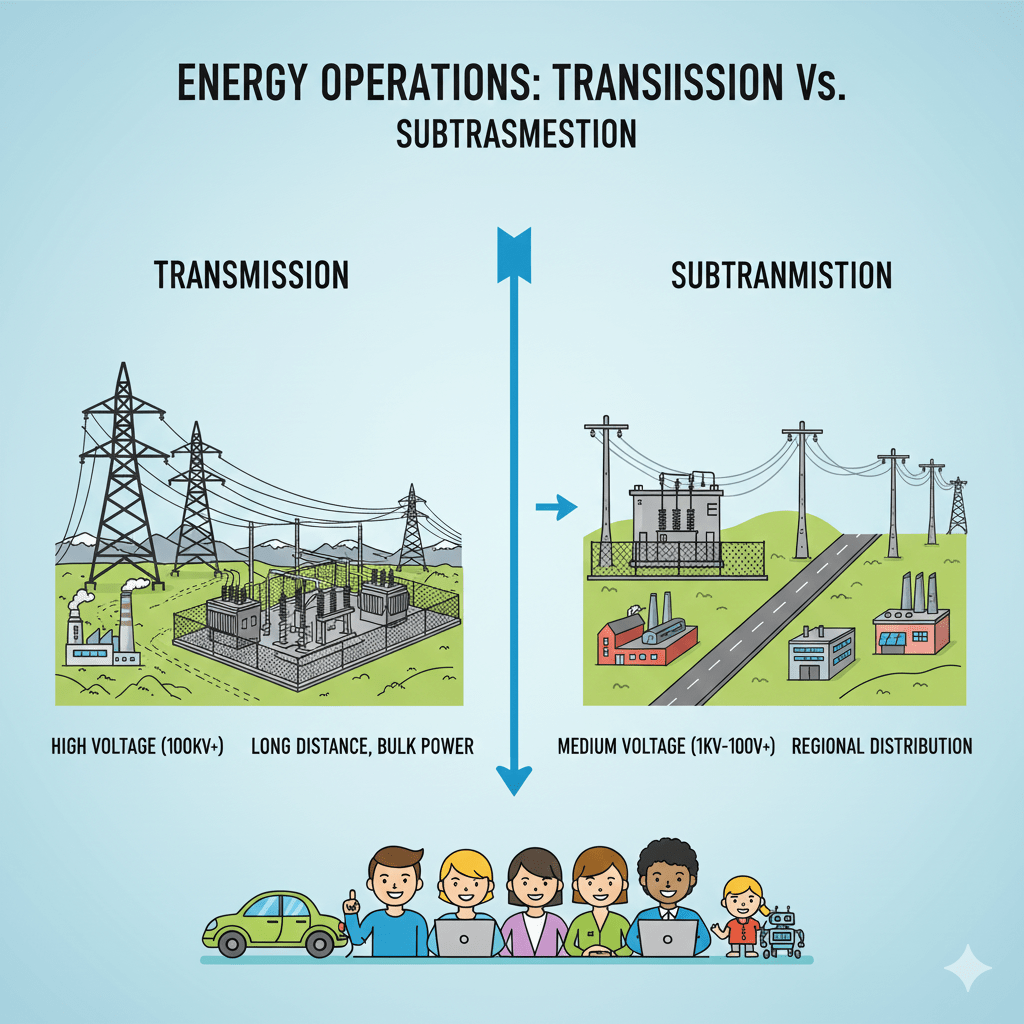
Transmission in electric power systems refers to the bulk transfer of electrical energy at very high voltages (typically 115 kV to 765 kV or higher) from generating stations to major substations, using interconnected networks of overhead or underground lines designed to move large amounts of power efficiently over long distances with minimal losses. Subtransmission, by…
-
-

A coupler functions by redistributing light from one or more input fibers into one or more output fibers. It does this without requiring external power, relying instead on physical principles like evanescent field coupling or fused biconical taper (FBT) technology. In FBT couplers, two or more fibers are precisely fused and tapered together, allowing light…
-

CoreThe core is the central strand of a fiber optic cable, composed of ultra-pure glass or plastic. It serves as the transmission medium for light signals. The diameter of the core depends on the fiber type—typically 9 microns for single-mode fibers and 50 or 62.5 microns for multimode. Its refractive index is slightly higher than…
-
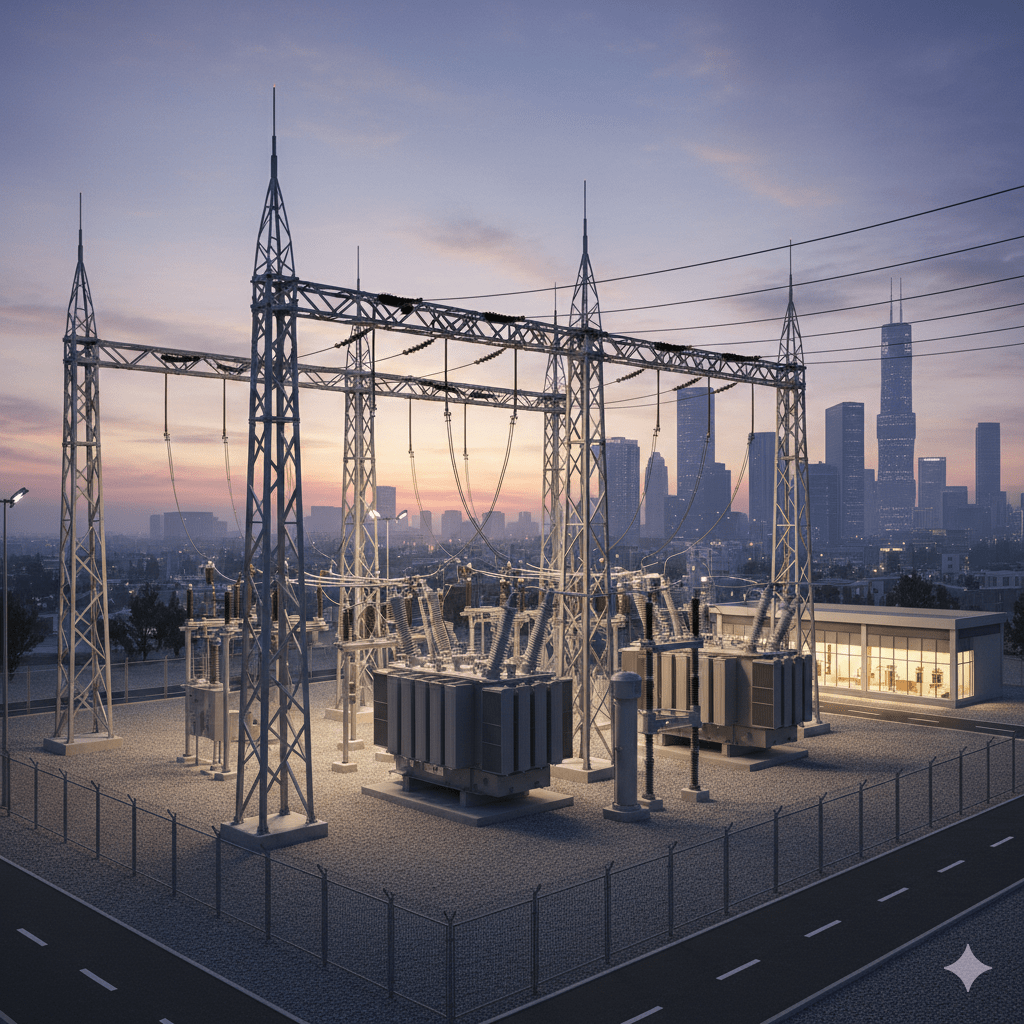
Substations are essential components of the electrical power system. They serve as the connection points between the high-voltage transmission lines and the lower-voltage distribution networks that deliver electricity to homes and businesses. At a substation, electricity is transformed from high voltage to a lower voltage, making it safe for use. This process is crucial because…
-
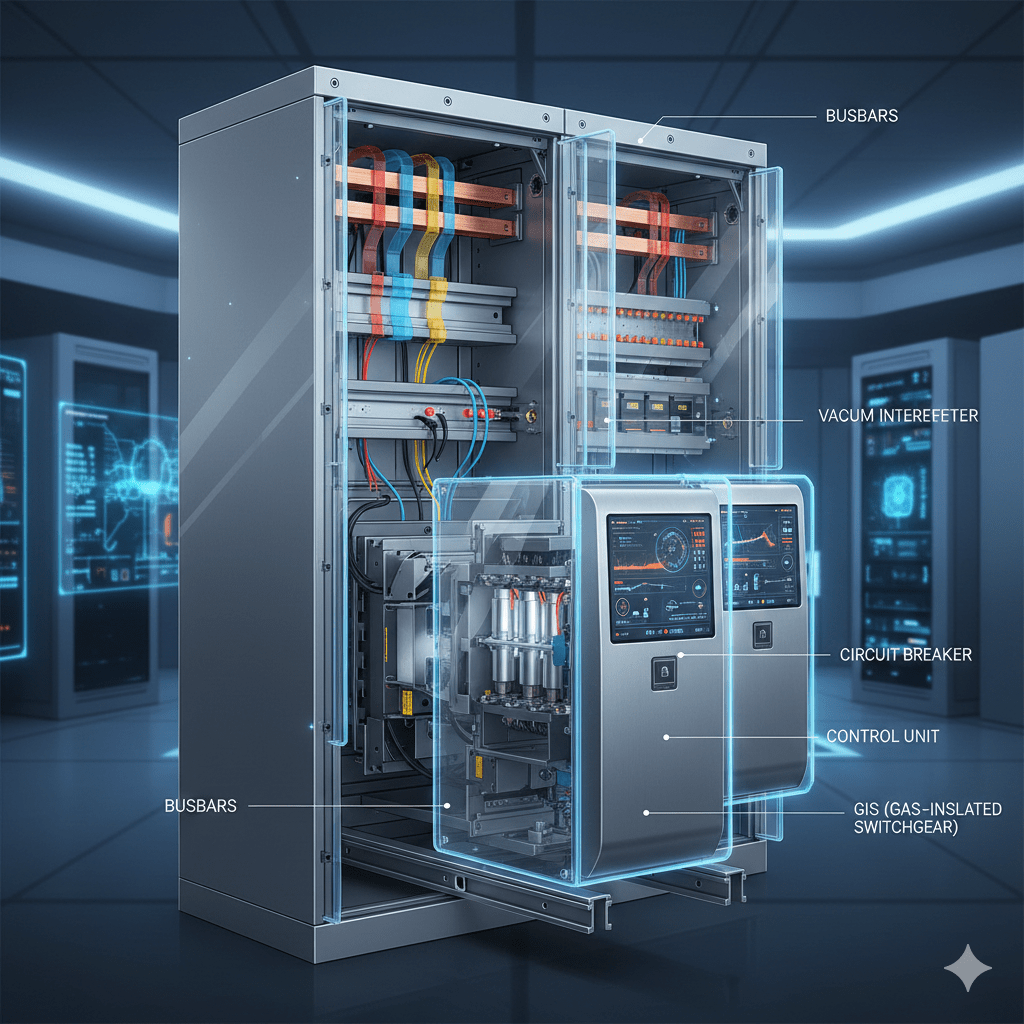
System design in electrical engineering involves planning and structuring power systems to ensure efficient, reliable, and safe distribution of electrical power. Switching devices, such as switches and circuit breakers, are integral components that control the flow of electricity within these systems. Circuit breakers are specialized safety devices designed to automatically disconnect electrical circuits during overloads…
-
Power distribution is the final stage of the power grid responsible for receiving bulk electric energy from the transmission system and delivering it safely, reliably, affordably, and at appropriate voltage and power quality to virtually every end-use customer—residential, commercial, and light industrial—across cities, suburbs, and rural areas. It begins at the distribution substation, where incoming…
-
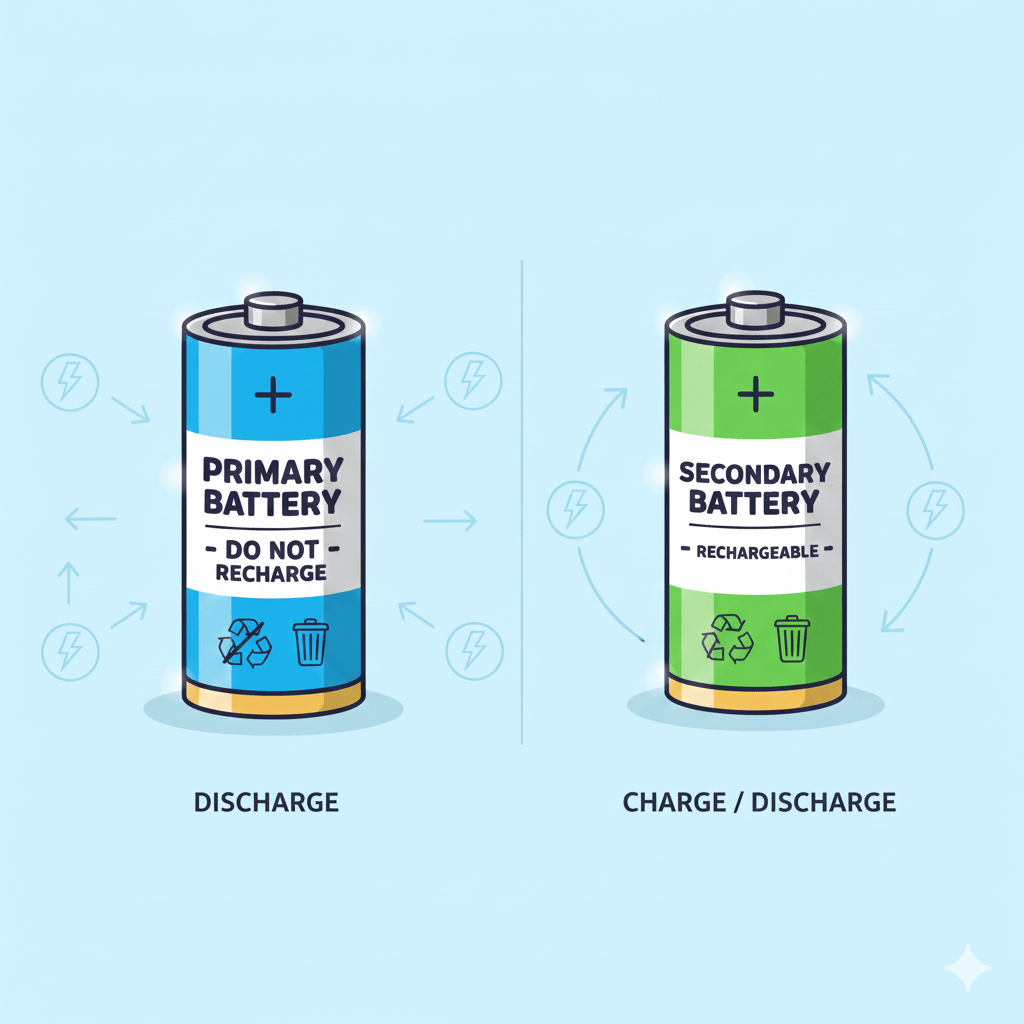
A battery is an electrochemical device that converts stored chemical energy directly into electrical energy (Direct Current or DC). It is composed of one or more electrochemical cells, each containing two electrodes—a positive cathode and a negative anode—which are separated by a conductive medium called an electrolyte. When an external circuit is connected, a chemical…
-
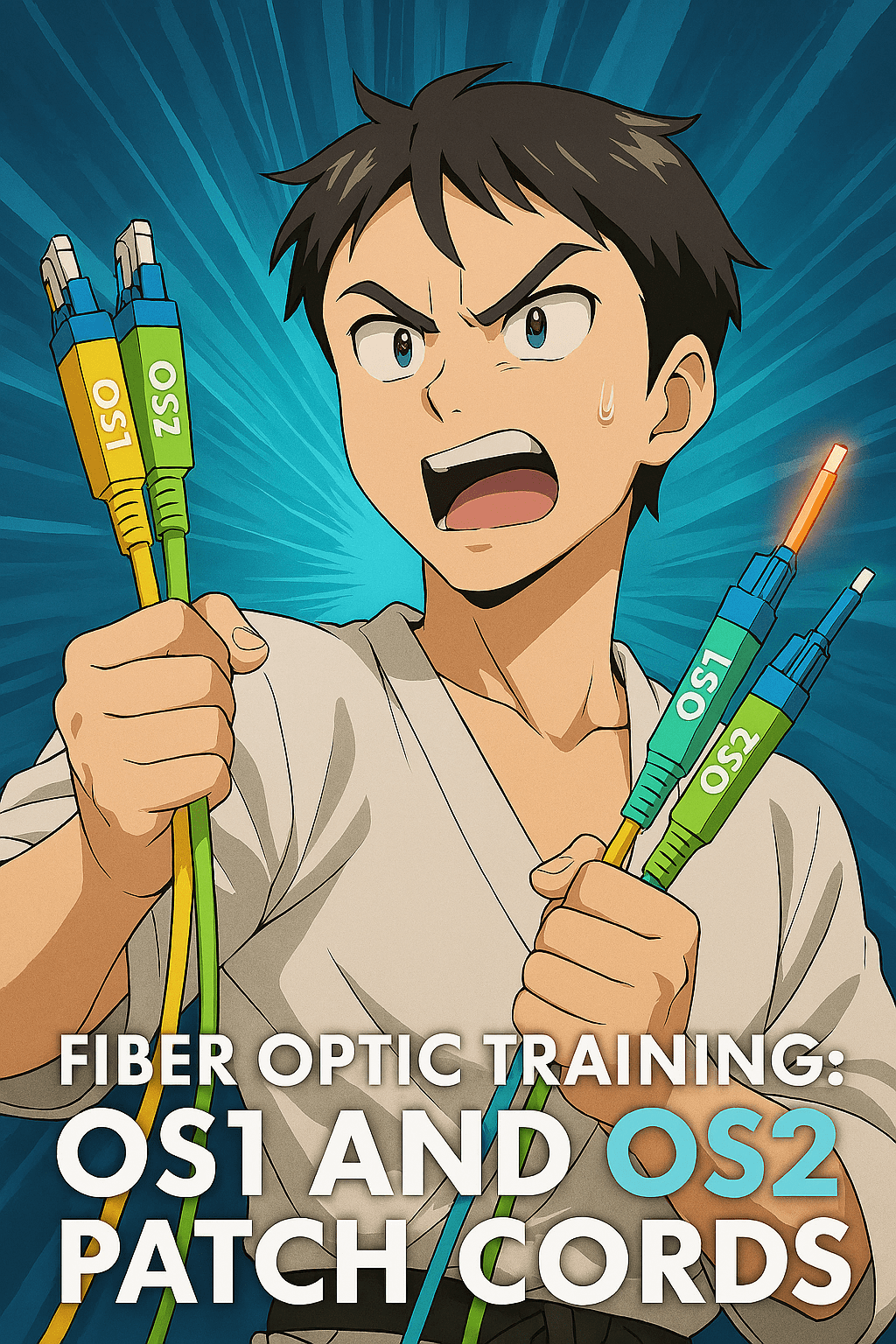
OS1 and OS2 are classifications of singlemode fiber optic cable defined by their construction and performance characteristics. OS stands for “Optical Singlemode.” OS1 is typically used for indoor applications and features tight-buffered construction, supporting up to 10 km at 1310 nm and 40 km at 1550 nm. OS2 is optimized for outdoor and long-haul deployments,…
-
Basic electrical properties describe how different materials respond to electric current and electric fields. The most fundamental of these is electrical conductivity, which measures how easily a material allows electric current to flow through it. Materials with high conductivity (like copper or silver) are called conductors; those with very low conductivity (like glass or rubber)…
-
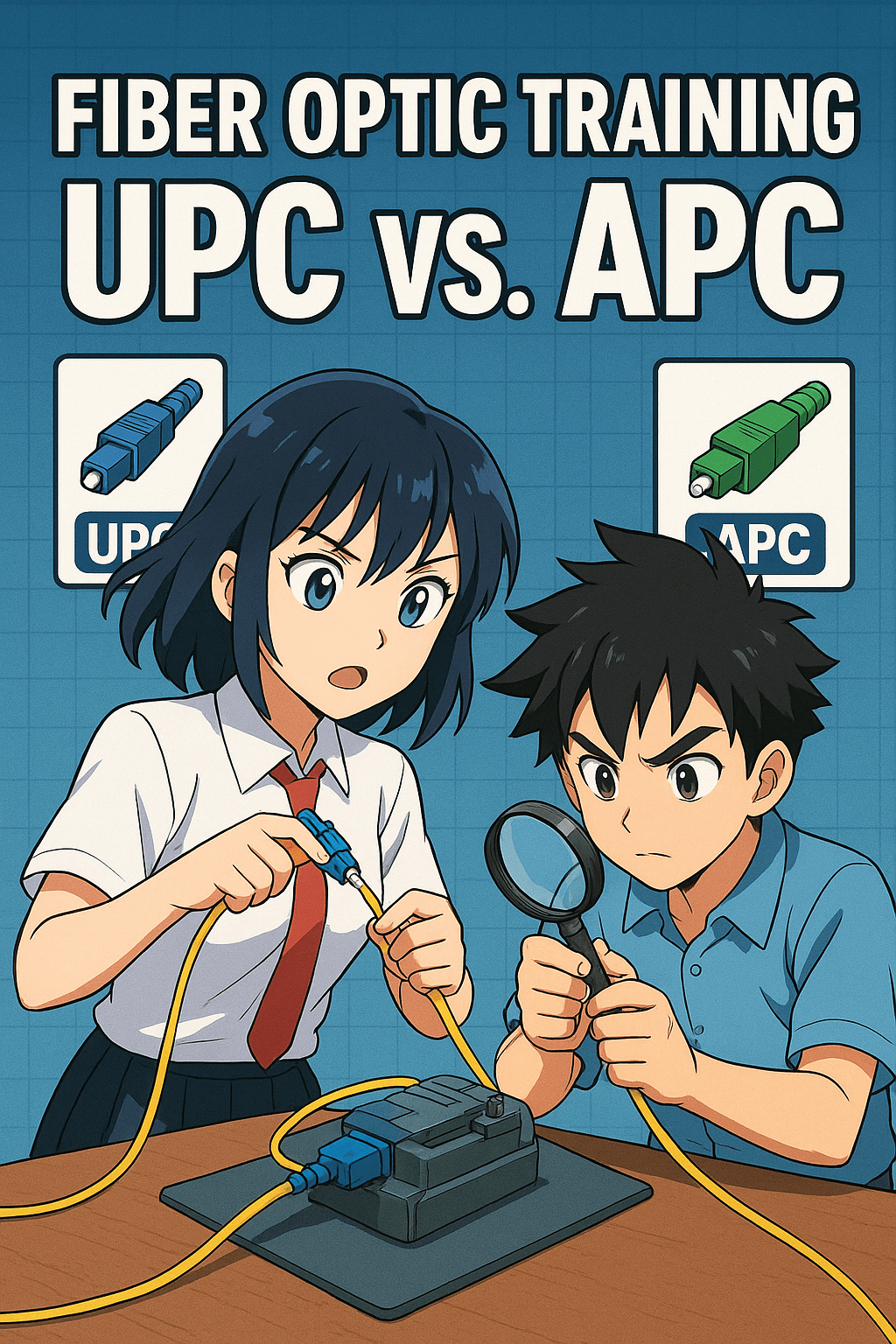
UPC and APC refer to two types of fiber optic connector polish styles: Ultra Physical Contact (UPC) and Angled Physical Contact (APC). UPC connectors have a flat, slightly domed end-face that provides low insertion loss and are commonly used in digital systems like Ethernet and CATV. APC connectors feature an 8-degree angled end-face that minimizes…
-
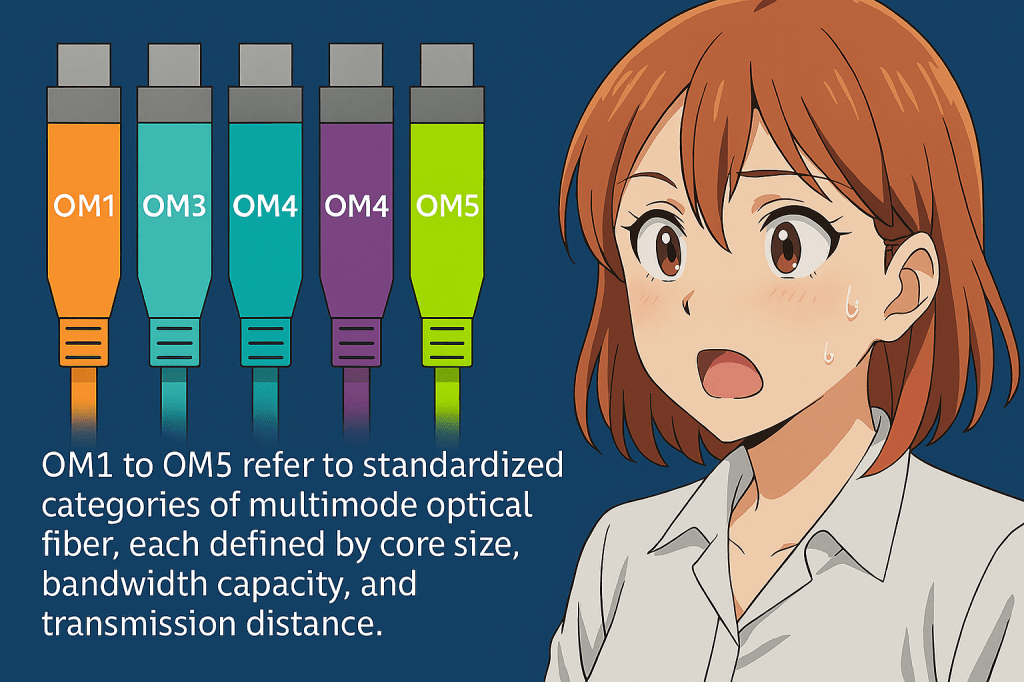
OM1 to OM5 refer to standardized categories of multimode optical fiber, each defined by core size, bandwidth capacity, and transmission distance. OM1 uses a 62.5 µm core and supports up to 1 Gbps over short distances, while OM2 through OM5 use a 50 µm core and are optimized for higher-speed VCSEL-based transmissions. OM3 and OM4…
-

Duplex patch cords are fiber optic cables that contain two strands—one for transmitting and one for receiving optical signals, allowing bidirectional communication between devices. These cords are typically used in full-duplex systems such as Ethernet or Fibre Channel, where simultaneous send and receive operations are required. Duplex patch cords often feature connectors like LC, SC,…
-
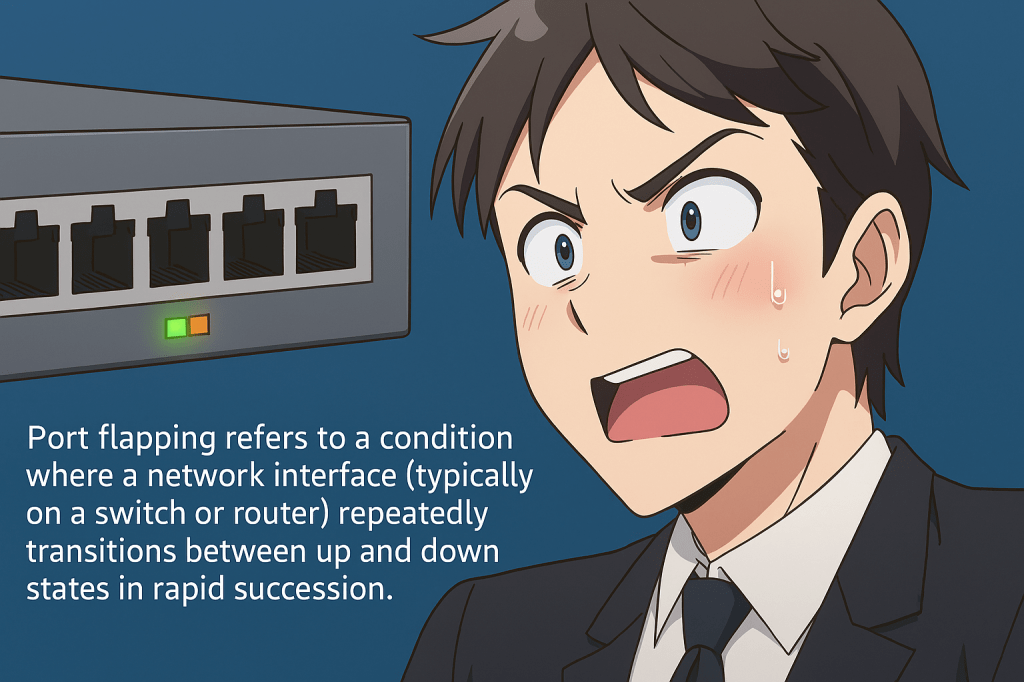
Port flapping is a network condition where a switch or router interface continuously transitions between an active (up) and inactive (down) state. This repetitive toggling disrupts link stability and can trigger frequent topology recalculations in protocols like STP (Spanning Tree Protocol), leading to packet loss, latency, and degraded performance across the network. Common causes include…
-

Insertion Loss in fiber optics refers to the amount of signal power lost when a component—such as a connector, splice, or device—is inserted into the optical path. It’s measured in decibels (dB), and lower values indicate better performance. When light travels through a fiber, any interruption or interface can cause some of the signal to…
-
Refraction in fiber optics refers to the change in direction of light as it passes between materials of different optical densities—specifically, from air into the fiber optic core, and between the core and cladding within the fiber. This bending of light is governed by Snell’s Law and is essential for initiating and maintaining the transmission…
-

Outside Plant (OSP) refers to all fiber optic infrastructure deployed outdoors—such as cables, splice enclosures, cabinets, and conduits—that connect central offices to service locations like homes, businesses, or data centers. OSP fiber networks form the backbone of modern telecommunications. They begin at a central office or headend, where optical signals originate, and extend through distribution…
-

Fiber optic characterization is the comprehensive process of testing and analyzing a fiber optic link or network to evaluate its performance, integrity, and ability to support high-speed data transmission. It involves a series of measurements and diagnostics designed to identify optical impairments, verify design specifications, and ensure that the fiber system meets required industry standards…
-

An optical power meter is a precision instrument used in fiber optic networks to quantify the optical signal power transmitted through a fiber. It operates by converting incoming light—usually in the infrared range—into an electrical signal using a calibrated photodetector, then displaying the power level in decibel-milliwatts (dBm) or milliwatts (mW). This measurement is critical…